通俗易懂的epoll
目录
- 理解epoll工作原理
-
- epoll的两种工作模式
- 如何使用epoll
- epoll的优点
- 使用epoll实现一个服务器
理解epoll工作原理
- 每一个epoll对象都有eventepoll结构体
- epoll底层是一颗红黑数来管理文件描述符中的事件。
- 而所有添加到epoll中的事件都会与设备(网卡)驱动程序建立回调关系,也就是说,当响应的事件发生时会调用这个回调方法
- 当事件发生时,回调方法会拷贝一份该节点到一个队列中,该队列的用双链表实现的。
- 在epoll中没一个事件都会建立节点(epitem结构体)
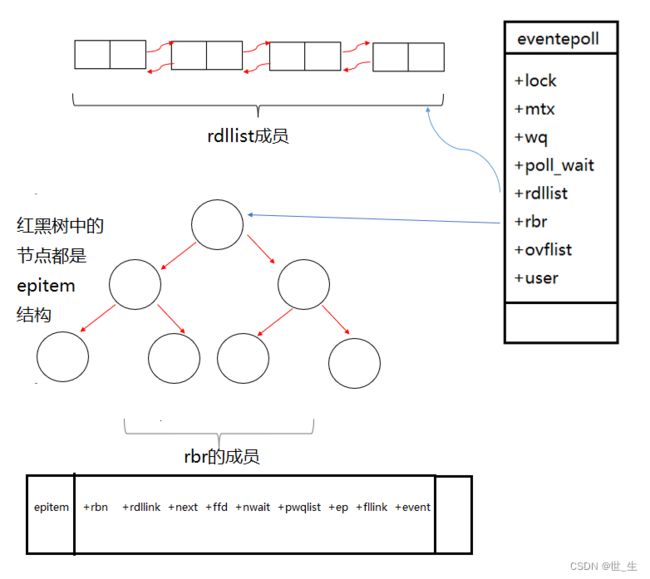
例子:我们在编写套接字编程的代码时,要把监听套接字放在epoll中来,让epoll帮我们来进行等待连接到来,连接到来事件叫做读事件。
这时候我们通过调用函数把监听套接字放入到红黑树中,Linux内核会对每一个事件对象创建一个epintm结构体。
判断也没有事件只需要通过rdllist是否为空。
struct epitem{
struct rb_node rbn;//红黑树节点
struct list_head rdllink;//双向链表节点
struct epoll_filefd ffd; //事件句柄信息
struct eventpoll *ep; //指向其所属的eventpoll对象
struct epoll_event event; //期待发生的事件类型
}
epoll的两种工作模式
LT:水平触发,不断的提醒你有事件到来,直到你把事件全部执行完
ET:边缘触发:只提醒你一次有事件到来,如果不执行,就要等下一次事件到来。
ET模式下:要采用非阻塞的方式进行读操作。且要不断的读,直到读完。
如果不采用非阻塞方式读取,则可能会阻塞住。
如何使用epoll
创建句柄
int epoll_create(int size);
返回一个整数,是一个文件描述符。
使用:int epfd=epoll_create(256);
添加事件到红黑树中
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
op:是一个宏
EPOLL_CTL_ADD:添加
EPOLL_CTL_MOD:修改
EPOLL_CTL_DEL:删除
struct epoll_event{
uint32_t events; //事件
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
}
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd; //文件描述符
uint32_t u32;
uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t;
一般events填EPOLLIN(读事件)、EPOLLOUT(写事件)。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1
//拿出事件
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
timeout:轮询检查的事件
返回值:成功返回事件到达的数量。
使用:
int epfd=epoll_create(256);
struct epoll_event item;
item.data.fd=sock; //添加套接字
item.events=EPOLLIN //只关心读时间
epoll_ctl(epfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,sock,&item);//添加事件到红黑树
struct events eve[64];
int num=epoll_wait(epfd,eve,64,1000);
//有事件到来,会把事件的节点拷贝到eve数组中,
//我们只需要遍历数组就可以进行读或者写。
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
if(eve[i].events & EPOLLIN){
int sock=eve[i].data.fd;
开始进行读操作(进行读操作时要区分是连接到来,还只是进行读取)
}
else if(eve[i].event& EPOLLOUT){
int sock=eve[i].data.fd;
开始进行写操作
}
}
epoll的优点
- 接口使用方便: 虽然拆分成了三个函数, 但是反而使用起来更方便高效. 不需要每次循环都设置关注的文件描述符, 也做到了输入输出参数分离开
- 数据拷贝轻量: 只在合适的时候调用 EPOLL_CTL_ADD 将文件描述符结构拷贝到内核中, 这个操作并不频繁(而select/poll都是每次循环都要进行拷贝)
- 事件回调机制: 避免使用遍历, 而是使用回调函数的方式, 将就绪的文件描述符结构加入到就绪队列中,
- epoll_wait 返回直接访问就绪队列就知道哪些文件描述符就绪. 这个操作时间复杂度O(1). 即使文件描述符数目很多, 效率也不会受到影响.
- 没有数量限制: 文件描述符数目无上限
使用epoll实现一个服务器
sock.hpp//创建套接字
#pragma once
#include reactor.hpp
#pragma once
#include insertface.hpp
#pragma once
#include log.hpp//日志,方便知道走到哪里了
#pragma once
#include util.hpp
#pragma once
#include server.cc
#include