Java项目【仿牛客网1-2】
仿牛客网第一章
一、技术架构
- Spring Boot
- Spring、Spring MVC、MyBatis
- Redis、Kafka、Elasticsearch
- Spring Security、Spring Actuator
说明:
1.SpringBoot是Spring的简化,更方便管理对象,对其他技术整合
2.SpringMVC用于处理浏览器的请求
3.MyBatis用来访问数据库
4.Redis用作缓存,默认存在内存,性能好【对系统监控、运维人员掌握系统状态】
5.Kafka用作消息队列
6.Elasticsearch用作全文搜索
7.Spring Security可以管理系统权限
8.Spring Actuator用作系统上线后的状态监控
开发环境
构架工具Maven【最流行,创建、编译、测试、打包项目、生成文档】
集成开发工具:IDEA
数据库:MySQL【关系型】、Redis【NoSQL数据库】
版本控制工具Git【备份、团队协作】
二、环境搭建
1.Apache Maven:可以帮助我们构建项目、管理项目中的jar包
安装且配置环境变量后使用命令mvn -version检查如下图:
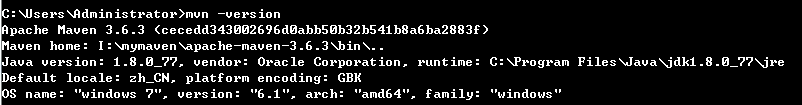 maven常用命令:
maven常用命令:
mvn compile : 编译maven项目,会出现target目录
mvn clean : 删除编译后的内容,target目录会被删除
mvn test :执行test中的方法,会首先编译test类
2.IDE:IntelliJ IDEA
3.快速构建springboot项目:Spring Initializer
4.Spring boot的核心作用:起步依赖,自动配置,端点监控
随时记:
server.port=80 //设置访问端口号
server.servlet.context-path=/community
//设置默认路径 项目的访问路径
三、Spring入门
1.Spring Framework
- Spring Core : IoC、AOP
- Spring Data Access : Transactions、Spring MyBatis
- Web Servlet : Spring MVC
- Integration : Email、Scheduling、AMQP、Security
2.Spring IoC
- Inversion of Control - 控制反转,是一种面向对象编程的设计思想。
- Dependency Injection - 依赖注入,是IoC思想的实现方式。
- IoC Container - IoC容器,是实现依赖注入的关键,本质上是一个工厂。
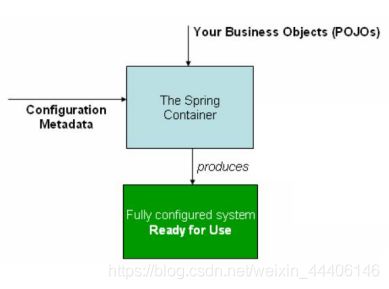
3.Ioc展示
此类其实是一个配置类
package com.hsw.community;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication //表示是一个配置文件
public class CommunityApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CommunityApplication.class, args);
//启动Tomcat,自动创建Spring容器、自动扫描对象,将对象装配到容器中
//扫描配置类以及子包下的对象,同时要有类似Controller的注解
}
}
如何使用spring容器?
@SpringBootTest //标识程序入口 配置类
@ContextConfiguration(classes = CommunityApplication.class) //使用配置类
//实现ApplicationContaxtAware接口并实现相应方法即可从参数中获取ApplicationContext
class CommunityApplicationTests implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Test
public void testApplication(){
System.out.println(applicationContext);
//常用方法
applicationContext.getBean(Dao.class);
applicationContext.getBean("mybatisDao",Dao.class);
}
}
随时记
/**使用场景比如我们有Dao接口下有两个实现类hibernateDao和mybatisDao
*我们用applicationContext获取bean时希望获取mybatisDao则加入此注解即可
*/
@Primary
@Repority("mybatisDao") //自定义bean的名字
@PostConstruct //在构造器之后调用
@PreDestroy //销毁之前调用
@Scope("prototype") //spring默认的bean都是单例的加此注解会在每次getBean方法调用时实例化对象
在配置类中配置要使用的bean(很笨拙的方法)
@Configuration //标识配置类
public class AlphaConfig {
@Bean
public SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat(){
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
}
}
随时记
@bean //bean的名称就是方法名如上simpleDateFormat
@Autowired //依赖注入,获取bean
@Qualifier("xxx") //把名字为xxx的bean注入,一般和Autowired一起使用
四、SpringMVC入门
Spring MVC 用于Web开发
HTTP:HyperText Transfer Protocol。
用于传输HTML等内容的应用层协议。
规定了浏览器和服务器之间如何通信,以及通信时的数据格式。
浏览器和服务器通信的步骤:
①建立TCP连接
②发送HTTP请求报文
③服务器返回响应报文信息
④关闭连接或者保持开启
-
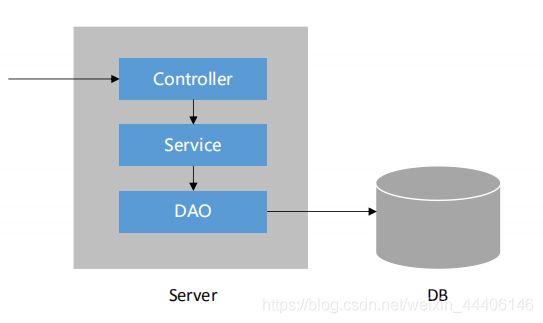
三层架构 - 表现层、业务层、数据访问层【分层目的:解耦、有利于代码维护】
-
MVC是一种设计模式,解决的是表现层的问题
- Model:模型层
- View:视图层
- Controller:控制层
-
核心组件【实际就是一个类】 - 前端控制器:DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet管理是基于Spring容器Servlet WebApplicationContext
管理Controller、视图以及映射相关注解
DispatcherServlet工作流程
请求、处理都由DispatcherServlet前端控制器处理
1.根据映射注解或方法,找到controller,并调用
2.controller把数据封装到model中返回给前端控制器
3.控制器调用视图模板,并把model传递给视图模板
4.视图模板动态替换、生成html,返回给前端控制器
5.前端控制器将html返回给浏览器
Thymeleaf 模板引擎:生成动态的HTML。
-
Thymeleaf【理念先进】
- 倡导自然模板,即以HTML文件为模板。
-
常用语法
随时记 实际为配置类
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false //开发中关闭thymeleaf的缓存,上线后开启[降低服务器压力]
//有缓存,开发时,页面可能有延迟
//Thymeleaf配置类,实际配置过程就是给某个bean设置属性【给一个配置类注入数据】
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThymeleafProperties.class)
public class ThymeleafAutoConfiguration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafProperties {
简单举几个例子
1.mvc 底层对象直观了解
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class AlphaController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public void demo(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){//声明请求对象、响应对象
//获取请求数据
System.out.println(request.getContextPath());
System.out.println(request.getMethod());
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();//请求行
while(headerNames.hasMoreElements()){
String name = headerNames.nextElement();
String value = request.getHeader(name);
System.out.println("header:"+name+" 的值是->"+value);
}
//返回响应数据
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");//声明类型
try(PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter()) {
writer.write("我会变强的");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.快速获取request中的参数【get 获取浏览器中一些参数】
/students?current=1&limit=20
@RequestMapping(path = "/testRequestParam",method = RequestMethod.GET)//声明请求路径、请求方式
@ResponseBody //响应
// /testRequestParam?i=10&j=100
public String testRequestParam(
//request中i这个参数赋值给i,也可以不传值,不传值默认为1【不传值的情况、第一次访问】
@RequestParam(name = "i",required = false,defaultValue = "1") int i,
@RequestParam(name = "j",required = false,defaultValue = "100")int j){
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(j);
return "hello world";
}
3.快速获取路径中的值【get 浏览器输入时,直接将参数放到路径上】
get请求,在地址栏上传递数据,且传递数据量有限
/students/123
@RequestMapping(path = "/testPathVariable/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
// /testPathVariable/123
public String testPathVariable(@PathVariable("id") int id){//路径变量,赋值给id
System.out.println(id); //123
return "hello world";
}
随时记:
@RequestParam //经过DispatcherServlet处理后会从request对象中获取参数
@PathVariable("xxx") //快速获取路径中的值如上所示
4.表单中数据的获取【post 浏览器向服务器提交数据】
<form method="post" action="/demo/testPost">
<p>
名字:<input name="name" type="text" >
p>
<p>
年龄:<input name="age" type="text">
p>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="submit">
p>
form>
@RequestMapping(path = "/testPost",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String testPost(String name,int age){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
return "hello world";
}
随时记:
直接让方法参数名和表单中定义的名字相等即可获取
5.填充模板数据【响应HTML数据】
@RequestMapping(path = "/teacher",method = RequestMethod.GET)//声明请求路径、请求方式
public ModelAndView testThymeleaf(){
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();//返回数据,返回model数据以及View数据
//动态传值
mv.addObject("name","狂徒张三");
mv.addObject("age","100");
mv.setViewName("teacher.html");//模板的路径和名字
return mv;
}
teacher.html位于templates下
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<p th:text="${name}">p>
<p th:text="${age}">p>
body>
html>
简化controller中的方式【更方便、简洁】
@RequestMapping(path = "/teacher",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String testThymeleaf(Model model){//返回数据,类型为model
model.addAttribute("name","电棍");
model.addAttribute("age","1000");
return "teacher.html";//返回view的路径
}
6.响应json数据(用于异步请求,java对象->json字符串->js对象)
异步请求:当前网页不刷新,但是访问服务器、数据库
@RequestMapping(path = "/testJson",method = RequestMethod.GET)//请求访问路径,请求方式
@ResponseBody //返回json字符串,不加默认返回html
public Map<String,Object> testJson(){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();//声明类型
map.put("name","猪猪侠");
map.put("age",19);
return map;//返回json字符串、【属性:属性值】
}
//返回一个集合
@RequestMapping(path = "/testJsons",method = RequestMethod.GET)//请求访问路径,请求方式
@ResponseBody //返回json字符串,不加默认返回html
public List<Map<String,Object>> testJsons(){
List<Map<String,Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();//声明类型
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","猪猪侠");
map.put("age",19);
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","迷糊老师");
map.put("age",55);
list.add(map);
return list;
}
五、MyBatis入门
提前安装MySQL Server以及MySQL WorkBench【比较好用的客户端】
初始化、安装服务、启动服务==》访问MySQL
第一次登录MySQL之后不能做任何操作,需要修改临时密码
MyBatis
使用MyBatis,底层能够自动的实现接口【前提:每个增删改查的方法依赖的SQL】
- 核心组件 【Spring Boot会自动创建前3个】
- SqlSessionFactory:用于创建SqlSession的工厂类。
- SqlSession:MyBatis的核心组件,用于向数据库执行SQL。
- 主配置文件:XML配置文件,可以对MyBatis的底层行为做出详细的配置。【连接数据库参数、连接池等配置】
- Mapper接口:就是DAO接口,在MyBatis中习惯性的称之为Mapper。
- Mapper映射器:用于编写SQL,并将SQL和实体类映射的组件,采用XML、注解均可实现。
- 示例
- 使用MyBatis对用户表进行CRUD操作。
参考手册1
参考手册2
引入依赖【导入jar包】
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.47version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.0.1version>
dependency>
添加配置【application.properties文件里配置】
# DataSourceProperties 配置MySQL连接池【又叫数据源:统一管理连接、管理连接上限(避免数据库瘫痪)】
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/community?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Hongkong
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
spring.datasource.hikari.maximum-pool-size=15
spring.datasource.hikari.minimum-idle=5
spring.datasource.hikari.idle-timeout=30000
# MybatisProperties
#resources目录下新建一个mapper目录存放xml文件
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.hsw.community.entity
#启动自动设置主键
mybatis.configuration.useGeneratedKeys=true
#下划线命名方式和驼峰命名方式匹配 如:header_url==headerUrl
mybatis.configuration.mapUnderscoreToCamelCase=true
创建entity包并创建User类
import java.util.Date;
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String salt;
private String email;
private int type;
private int status;
private String activationCode;
private String headerUrl;
private Date createTime;
写完属性之后,按【Alt】+【Insert】添加属性的get和set方法
生成toString的方法,方便观察打印数据
访问数据库,只用写接口,不需要写具体的类
在dao包下创建UserMapper接口【①注解②方法】
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
User selectById(int id);
User selectByName(String username);
User selectByEmail(String email);
int insertUser(User user);
int updateStatus(int id, int status);
int updateHeader(int id, String headerUrl);
int updatePassword(int id, String password);
}
在mapper文件夹下建立user-mapper.xml文件【mapper映射结构】
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.hsw.community.dao.UserMapper">
<sql id="insertFields">
username, password, salt, email, type, status, activation_code, header_url, create_time
sql>
<sql id="selectFields">
id, username, password, salt, email, type, status, activation_code, header_url, create_time
sql>
<select id="selectById" resultType="User">
select <include refid="selectFields">include>
from user
where id = #{id}
select>
<select id="selectByName" resultType="User">
select <include refid="selectFields">include>
from user
where username = #{username}
select>
<select id="selectByEmail" resultType="User">
select <include refid="selectFields">include>
from user
where email = #{email}
select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="User" keyProperty="id">
insert into user (<include refid="insertFields">include>)
values(#{username}, #{password}, #{salt}, #{email}, #{type}, #{status}, #{activationCode}, #{headerUrl}, #{createTime})
insert>
<update id="updateStatus">
update user set status = #{status} where id = #{id}
update>
<update id="updateHeader">
update user set header_url = #{headerUrl} where id = #{id}
update>
<update id="updatePassword">
update user set password = #{password} where id = #{id}
update>
mapper>
测试一波
@SpringBootTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = CommunityApplication.class)
public class MapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;//注入userMapper,进行测试
@Test
public void testSelectUser(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(101);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
遇到的问题:
最初在UserMapper 接口上只是用了@Mapper注解也能跑但是idea总是提示找不到bean
单独加@Repository其实也能跑
这里把两个都写上去了其实没必要
随时记:
因为mapper.xml文件中的sql语句写错很难被发现,为了排错可以设置日志级别为debug便于调错
#logger
logging.level.com.hsw.community=debug
六、开发社区首页
Web项目,主要解决浏览器和服务器信息交互的问题
请求提交给服务器的视图层【主要由Controller和模板构成】,controller处理请求时访问业务层,业务组件处理具体的业务,过程会访问数据库,调用DAO访问组件
开发流程:功能拆解【实现功能==》不断完善】
- 1次请求的执行过程
- 分步实现
- 开发社区首页,显示前10个帖子
- 开发分页组件,分页显示所有的帖子
社区首页
-
开发社区首页,显示前10个帖子
数据访问层
-
创建实体类
-
写对应dao【即Mapper】
-
写对应xml【配置文件】
业务层
-
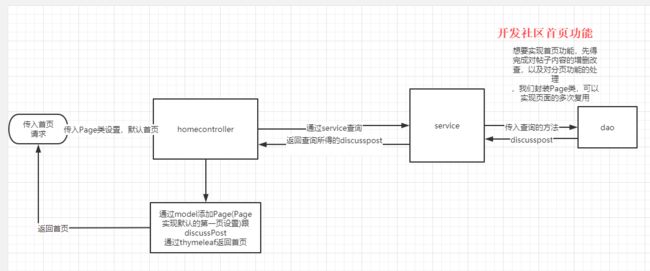
创建service,因为在首页得到的DiscussPost并不携带userid,所以需要创建DiscusspostService和UserService来实现首页展示10个帖子的功能
视图层:静态资源和模板(html、图片…)
-
写controller,将查询到的数据注入到model中
-
修改index.html
-
-
开发分页组件,分页显示所有的帖子
- 创建page类,在Page中设置当前页码,显示上限,数据总数,查询路径
- 在开发社区首页的controller方法中,第一次访问自动注入page,page会自动注入到model中,然后我们让前端在跳转页面的时候在参数上添加页数,我们的SpringMVC会自动注入Page页面
- index.html首页中修改分页组件
【1-3数据访问层】
1.创建实体类
public class DiscussPost {
private int id;
private int userId;
private String title;
private String content;
//0-普通; 1-置顶;
private int type;
//0-正常; 1-精华; 2-拉黑;
private int status;
private Date createTime;
private int commentCount;
private double score;
}
生成get、set方法;方便打印==》生成ToString方法
2.写对应dao【通常一张表,创建一个Mapper】
首页的查询功能
@Repository
public interface DiscussPostMapper {
/**
* @param userId 考虑查看我的帖子的情况下设置动态sql,看mapper就知道了【动态sql,若首页帖子则无userId;个人主页,则有userId】
* @param offset
* @param limit
* @return
*/
List<DiscussPost> selectDiscussPosts(int userId,int offset,int limit);//offset每页起始行号,limit每页最多的数据
//如果需要动态拼接条件(里使用)并且这个方法有且只有一个参数需要用@Param起别名
//@Param用于给参数取别名
int selectDiscussPostRows(@Param("userId") int userId);//查询总共多少帖子
}
3.mapper目录下写个discusspost-mapper.xml
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.hsw.community.dao.DiscussPostMapper">
<sql id="selectFields">
id, user_id, title, content, type, status, create_time, comment_count, score
sql>
<select id="selectDiscussPosts" resultType="DiscussPost">
select <include refid="selectFields">include>
from discuss_post
where status != 2
<if test="userId!=0">
and user_id = #{userId}
if>
order by type desc, create_time desc
limit #{offset}, #{limit}
select>
<select id="selectDiscussPostRows" resultType="int">
select count(id)
from discuss_post
where status != 2
<if test="userId!=0">
and user_id = #{userId}
if>
select>
mapper>
xml容易出错,测试
注入==》方法
4.【业务层】创建DiscussPostService类和UserService类
@Service //让其能被容器访问到
public class DiscussPostService {
//调用Mapper,注入Mapper
@Autowired
private DiscussPostMapper discussPostMapper;
//业务处理方法
public List<DiscussPost> findDiscussPosts(int userId,int offset,int limit){
return discussPostMapper.selectDiscussPosts(userId,offset,limit);
}
public int findDiscussPostRows(int userId){
return discussPostMapper.selectDiscussPostRows(userId);
}
}
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//因为上边只有userId根据此方法可得到userName
public User findUserById(int id){
return userMapper.selectById(id);
}
}
5.【视图层】复制静态资源和模板
6.【视图层】写HomeController
package com.hongna.community.entity;
/**
* 封装分页相关的信息.
*/
public class Page {
// 当前页码
private int current = 1;
// 显示上限
private int limit = 10;
// 数据总数(用于计算总页数)
private int rows;
// 查询路径(用于复用分页链接)
private String path;
public int getCurrent() {
return current;
}
public void setCurrent(int current) {
if (current >= 1) {
this.current = current;
}
}
public int getLimit() {
return limit;
}
public void setLimit(int limit) {
if (limit >= 1 && limit <= 100) {
this.limit = limit;
}
}
public int getRows() {
return rows;
}
public void setRows(int rows) {
if (rows >= 0) {
this.rows = rows;
}
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
/**
* 获取当前页的起始行
*
* @return
*/
public int getOffset() {
// current * limit - limit
return (current - 1) * limit;
}
/**
* 获取总页数
*
* @return
*/
public int getTotal() {
// rows / limit [+1]
if (rows % limit == 0) {
return rows / limit;
} else {
return rows / limit + 1;
}
}
/**
* 获取起始页码
*
* @return
*/
public int getFrom() {
int from = current - 2;
return from < 1 ? 1 : from;
}
/**
* 获取结束页码
*
* @return
*/
public int getTo() {
int to = current + 2;
int total = getTotal();
return to > total ? total : to;
}
}
package com.hsw.community.controller;
import com.hsw.community.entity.DiscussPost;
import com.hsw.community.entity.Page;
import com.hsw.community.entity.User;
import com.hsw.community.service.DiscussPostService;
import com.hsw.community.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller //Controller注解,Controller 可以不加访问路径
public class HomeController {
//调用service,注入service
@Autowired
private DiscussPostService discussPostService;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
//增加处理请求的方法
@RequestMapping(path="/index",method = RequestMethod.GET)
//方法调用之前SpringMVC会自动实例化Model和Page,并将Page注入到Model中,所以可以直接访问page对象
//若是路径中带有参数如index?current=2 current的值会自动封装进page中
public String getIndexPage(Model model,Page page){
page.setRows(discussPostService.findDiscussPostRows(0));
page.setPath("/index");
//list不包含userName
List<DiscussPost> list = discussPostService.findDiscussPosts(0, page.getOffset(), page.getLimit());
//定义一个集合discussPosts,包含post以及userName
List<Map<String,Object>> discussPosts = new ArrayList<>();
if(list!=null){
for (DiscussPost post:list) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("post",post);
User user = userService.findUserById(post.getUserId());
map.put("user",user);
discussPosts.add(map);
}
}
model.addAttribute("discussPosts",discussPosts);
//model.addAttribute("page",page);
return "/index";
}
}
7.完成index.html
渲染页面中的帖子
<ul class="list-unstyled">
<li class="media pb-3 pt-3 mb-3 border-bottom" th:each="map:${discussPosts}">
<a href="site/profile.html">
<img th:src="${map.user.headerUrl}" class="mr-4 rounded-circle" alt="用户头像" style="width:50px;height:50px;">
a>
<div class="media-body">
<h6 class="mt-0 mb-3">
<a href="#" th:utext="${map.post.title}">备战春招,面试刷题跟他复习,一个月全搞定!a>
<span class="badge badge-secondary bg-primary" th:if="${map.post.type==1}">置顶span>
<span class="badge badge-secondary bg-danger" th:if="${map.post.status==1}">精华span>
h6>
<div class="text-muted font-size-12">
<u class="mr-3" th:utext="${map.user.username}">寒江雪u> 发布于 <b th:text="${#dates.format(map.post.createTime,'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}">2019-04-15 15:32:18b>
<ul class="d-inline float-right">
<li class="d-inline ml-2">赞 11li>
<li class="d-inline ml-2">|li>
<li class="d-inline ml-2">回帖 7li>
ul>
div>
div>
li>
ul>
<nav class="mt-5" th:if="${page.rows>0}">
<ul class="pagination justify-content-center">
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=1)}">首页a>
li>
<li th:class="|page-item ${page.current==1?'disabled':''}|">
<a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${page.current-1})}">上一页a>li>
<li th:class="|page-item ${i==page.current?'active':''}|" th:each="i:${#numbers.sequence(page.from,page.to)}">
<a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${i})}" th:text="${i}">1a>
li>
<li th:class="|page-item ${page.current==page.total?'disabled':''}|">
<a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${page.current+1})}">下一页a>
li>
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" th:href="@{${page.path}(current=${page.total})}">末页a>
li>
ul>
nav>
div>
div>
七、项目调试技巧
- 响应状态码的含义
- 服务端断点调试技巧
- 客户端断点调试技巧
- 设置日志级别,并将日志输出到不同的终端
1.响应状态码的含义
1XX:指临时性的响应,需要执行者继续操作即可解决的状态码
2XX:指已经成功地处理了请求,用户可以正常的打开了这个页面。
3XX:进行重定向相关操作
4XX:客户端的错误
5XX:服务器端的错误
详细介绍:点此
一些常用状态码的总结
- 301:被请求的资源已永久移动到新位置,并且将来任何对此资源的引用都应该使用本响应返回的若干个 URI 之一。如果可能,拥有链接编辑功能的客户端应当自动把请求的地址修改为从服务器反馈回来的地址。除非额外指定,否则这个响应也是可缓存的。
- 302:请求的资源现在临时从不同的 URI 响应请求。由于这样的重定向是临时的,客户端应当继续向原有地址发送以后的请求。只有在Cache-Control或Expires中进行了指定的情况下,这个响应才是可缓存的。【浏览器自主的再发一次请求】
- 404:请求失败,请求所希望得到的资源未被在服务器上发现。
- 500:服务器遇到了不知道如何处理的情况。
2.服务端断点调试技巧
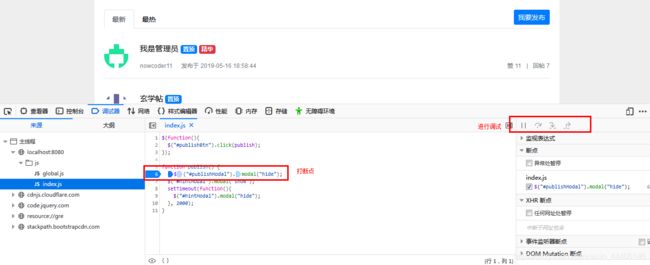
3.客户端断点调试技巧
- 打断点
- 调试
主要用于调试js,如下图

4.设置日志级别,并将日志输出到不同的终端
springboot默认日志logback:官网
package org.slf4j;
public interface Logger {
//我们可以在配置文件中启动不同的级别,则其以上级别日志可以显示低级别日志不会显示。
// Printing methods:
public void trace(String message);
public void debug(String message);
public void info(String message);
public void warn(String message);
public void error(String message);
}
写个测试类
package com.hsw.community;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
@SpringBootTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = CommunityApplication.class)
public class LoggerTest {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggerTest.class);
@Test
public void testLogger1(){
System.out.println(logger.getName());
logger.trace("hello trace");
//程序调试日志
logger.debug("hello debug");
//普通级别日志
logger.info("hello info");
logger.warn("hello warn");
//错误日志
logger.error("hello log");
}
}
添加配置文件
# logger
logging.level.com.hsw.community=debug
输出结果
com.hsw.community.LoggerTest
2020-05-04 15:25:59.505 DEBUG 2644 --- [ main] com.hsw.community.LoggerTest : hello debug
2020-05-04 15:25:59.505 INFO 2644 --- [ main] com.hsw.community.LoggerTest : hello info
2020-05-04 15:25:59.505 WARN 2644 --- [ main] com.hsw.community.LoggerTest : hello warn
2020-05-04 15:25:59.505 ERROR 2644 --- [ main] com.hsw.community.LoggerTest : hello log
更改配置文件
logging.level.com.hsw.community=warn
在此运行测试类查看输出结果
com.hsw.community.LoggerTest
2020-05-04 15:28:54.515 WARN 9020 --- [ main] com.hsw.community.LoggerTest : hello warn
2020-05-04 15:28:54.515 ERROR 9020 --- [ main] com.hsw.community.LoggerTest : hello log
日志输出到文件中的配置
#文件都是以log结尾
logging.file.name=d:work.log
注意:这么搞有个问题,不同级别日志混杂不易查看且文件庞大。
解决方法:使用配置文件配置(放到resource目录下)
<configuration>
<contextName>communitycontextName>
<property name="LOG_PATH" value="D:/work/data"/>
<property name="APPDIR" value="community"/>
<appender name="FILE_ERROR" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${LOG_PATH}/${APPDIR}/log_error.logfile>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${LOG_PATH}/${APPDIR}/error/log-error-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.logfileNamePattern>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>5MBmaxFileSize>
timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
<maxHistory>30maxHistory>
rollingPolicy>
<append>trueappend>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<pattern>%d %level [%thread] %logger{10} [%file:%line] %msg%npattern>
<charset>utf-8charset>
encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>errorlevel>
<onMatch>ACCEPTonMatch>
<onMismatch>DENYonMismatch>
filter>
appender>
<appender name="FILE_WARN" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${LOG_PATH}/${APPDIR}/log_warn.logfile>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${LOG_PATH}/${APPDIR}/warn/log-warn-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.logfileNamePattern>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>5MBmaxFileSize>
timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
<maxHistory>30maxHistory>
rollingPolicy>
<append>trueappend>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<pattern>%d %level [%thread] %logger{10} [%file:%line] %msg%npattern>
<charset>utf-8charset>
encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>warnlevel>
<onMatch>ACCEPTonMatch>
<onMismatch>DENYonMismatch>
filter>
appender>
<appender name="FILE_INFO" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${LOG_PATH}/${APPDIR}/log_info.logfile>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${LOG_PATH}/${APPDIR}/info/log-info-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.logfileNamePattern>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>5MBmaxFileSize>
timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
<maxHistory>30maxHistory>
rollingPolicy>
<append>trueappend>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<pattern>%d %level [%thread] %logger{10} [%file:%line] %msg%npattern>
<charset>utf-8charset>
encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.LevelFilter">
<level>infolevel>
<onMatch>ACCEPTonMatch>
<onMismatch>DENYonMismatch>
filter>
appender>
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d %level [%thread] %logger{10} [%file:%line] %msg%npattern>
<charset>utf-8charset>
encoder>
<filter class="ch.qos.logback.classic.filter.ThresholdFilter">
<level>debuglevel>
filter>
appender>
<logger name="com.hsw.community" level="debug"/>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="FILE_ERROR"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE_WARN"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE_INFO"/>
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
root>
configuration>
八、版本控制
作用:代码备份、历史记录、团队协作
-
认识Git
-
Git的简介
分布式的版本控制
本地仓库,无问题,推送到远程仓库
-
Git的安装和配置
-
-
Git常用命令
- 将代码提交到本地仓库
- 将代码上传至远程仓库
-
IDEA集成Git
- commit 提交到本地仓库
- push 推送到远程仓库
- pull 从远程仓库拉下来代码
Git官网:点此
推荐阅读:书籍
1.配置用户名和邮箱
$ git config --global user.name "hsw"
$ git config --global user.email [email protected]
2.把代码放进本地代码库
- 找到目标代码文件夹,右键gitbash Here
- $ git init
Initialized empty Git repository in I:/ideaworkspace/test/.git/
本地文件出现隐藏文件夹

- git status 查看状态

- 添加所有文件 git add *

- git status 查看状态(绿了只是加到了本地仓库中,但未提交)

- git status 查看状态
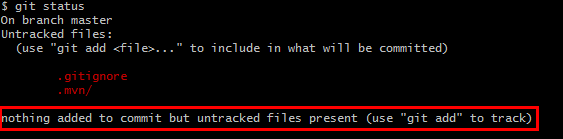
- 修改代码(加了一个注释)后查看状态 git status

- 然后可以git add,git commit提交修改的代码
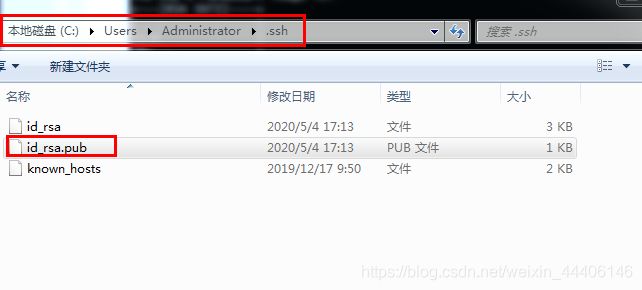
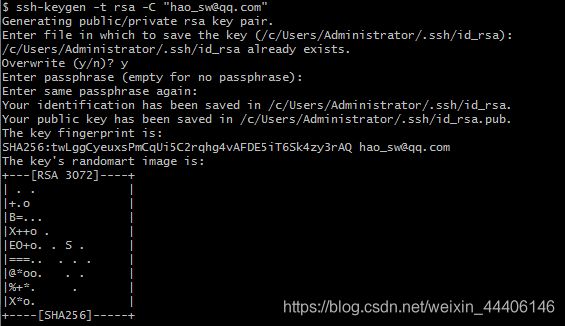
3.上传至远程仓库之生成密钥 $ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C “邮箱地址”
- 创建项目
$ git remote add 仓库名 仓库地址
- 上传至远程仓库
$ git push -u 仓库名 分支名
$ git clone https://git.nowcoder.com/xxx/xxxx.git
牛客网第二章
产品的角度考虑功能怎么去思考、实现,注意产品细节
运用Spring Boot,以及SSM框架【Spring Boot、Spring MVC、MyBatis】
一、发送邮件
- 邮箱设置
- 启用客户端SMTP服务
- Spring Email技术
- 导入 jar 包
- 邮箱参数配置
- 使用 JavaMailSender 发送邮件
- 模板引擎
- 使用 Thymeleaf 发送 HTML 邮件
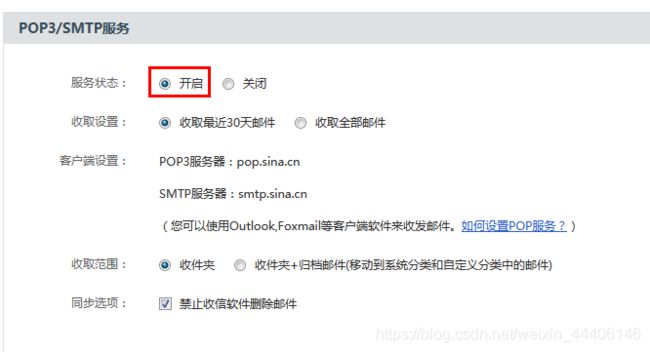
邮箱设置
跟教程一致选用新浪邮箱,开启SMTP服务
Spring Email
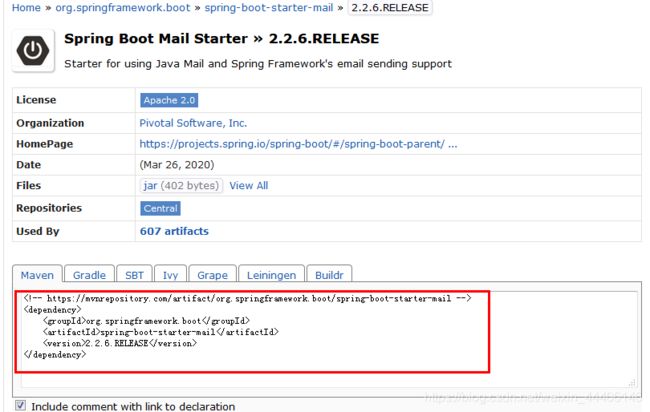
1.导入jar包
在mavenrepository中搜索Spring mail的相关jar包
![]()
把上述红框内容复制到pom文件中
2.邮箱参数设置
此项目配置如下 application.properties里面配置
spring.mail.host: smtp.163.com
spring.mail.port: 466
spring.mail.username: [email protected]
spring.mail.password: xxx(此处写你的授权码)
spring.mail.protocol: smtps
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enable=true
注意
password设置的值是授权码,可以参考此链接说明
3.使用JavaMailSender发送邮件
建立一个工具包util,写一个工具类MailClien,方便复用,
@Component
public class MailClient {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MailClient.class);
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender mailSender;
//直接使用配置文件中的用户名
@Value("${spring.mail.username}")
private String from;
public void sendMail(String to,String subject,String content){
try {
MimeMessage message = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(message);
helper.setFrom(from);
helper.setTo(to);
helper.setSubject(subject);
//不加true说明支持字符文本,加true说明支持html文本
helper.setText(content,true);
mailSender.send(helper.getMimeMessage());
} catch (MessagingException e) {
logger.error("发送邮件失败"+e.getMessage());
}
}
}
测试一波
@SpringBootTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = CommunityApplication.class)
public class MailTest {
@Autowired
private MailClient client;
@Autowired
private TemplateEngine templateEngine;
//测试发送普通邮件
@Test
public void testMail(){
client.sendMail("[email protected]","Test","hello world");
}
//测试发送html文件,这里想要根据用户名设置对应的html所以用了Thymeleaf
@Test
public void testHtmlMail(){
Context context = new Context();
context.setVariable("username","hsw");
String html = templateEngine.process("mail/demo", context);
//System.out.println(html);
client.sendMail("[email protected]","TestHtml",html);
}
}
html
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>邮件示例title>
head>
<body>
<p>欢迎你,<span style="color: red" th:text="${username}"/>p>
body>
html>
二、开发注册功能
- 访问注册页面
- 点击顶部区域内的链接,打开注册页面。
- 提交注册数据
- 通过表单提交数据。
- 服务端验证账号是否已存在、邮箱是否已注册。
- 服务端发送激活邮件。
- 激活注册账号
- 点击邮件中的链接,访问服务端的激活服务
个人思想
-
点击注册页面,然后打开注册页面
-
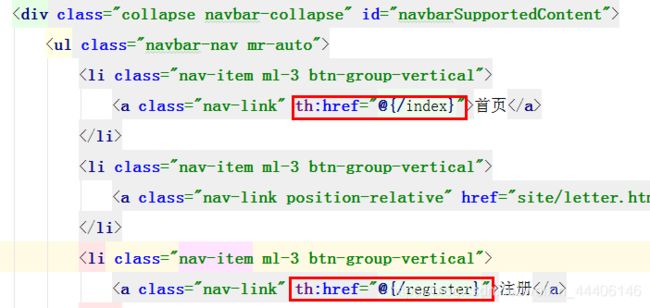
在首页模板中设置跳转,因为通过th:fragment共用了模板,所以只需要修改首页模板
通过lang3工具包,检测前台传过来的数据是否为空
如果为空或者邮箱等已被占用返回前台消息错误提醒
-
在service中完成注册功能,并通过service进行加盐
通过templateEngine和Email发送激活邮件
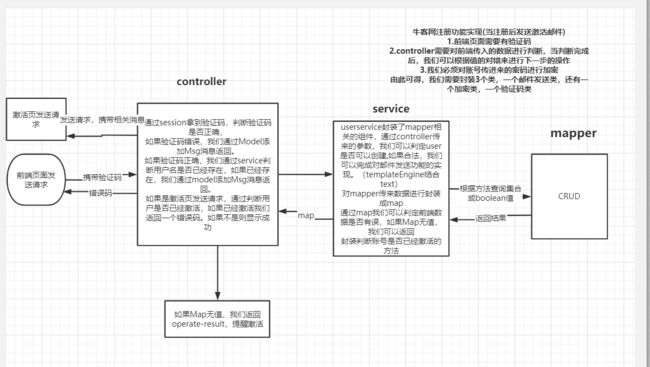
/activation/{userId}/{code} 通过后面两个属性,我们可以得到userId和激活码,我们通过方法找到userId,并校验数据库中的code是否正确(激活状态),如果是则会校验status值是否已被修改为1,不是则修改成功。通过templateEngine我们可以实现动态的注入返回页面
访问注册页面
开发顺序一般为:数据访问层、业务层、视图层。
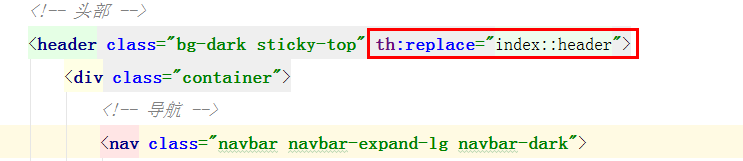
1.共用头部
一般头部的代码都是一样的
![]() 可以用Thymeleaf提供的th:fragment标签来共用这部分代码,如下index.html中部分内容
可以用Thymeleaf提供的th:fragment标签来共用这部分代码,如下index.html中部分内容
register.html中部分头部内容
2.把纯html的注册页面修改成Thymeleaf的格式
先修改index.html中内容
因为共用头部了,index.html修改了这部分内容之后register.html就不用修改了
提交注册数据
首先导入一个常用的包 commons lang
主要是字符串判空等功能
pom中添加如下
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3artifactId>
<version>3.9version>
dependency>
添加配置信息
因为开发、上线域名不一样所以用户打开邮箱激活的链接也不一样所以给他弄成可变的
#community
community.path.domain=http://localhost:8080
写个工具类【很简答,直接调用就行,不需要容器托管】
package com.hsw.community.util;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.util.DigestUtils;
import java.util.UUID;
public class CommunityUtil {
// 生成随机字符串
public static String generateUUID(){
return UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-","");
}
//MD5加密
//MD5只能加密不能解密
//原串加salt拼接新串加密防破解
public static String md5(String key){
//null,空串,空格都会判空
if(StringUtils.isBlank(key)){ //commons lang包里的功能
return null;
}
return DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(key.getBytes());
}
}
正式开发功能
1.Dao已经写完
2.编写Service
在userService中添加如下代码
@Autowired
private MailClient mailClient;
@Autowired
TemplateEngine templateEngine;
@Value("${community.path.domain}")
private String domain;
@Value("${server.servlet.context-path}")
private String contextPath;
public Map<String,Object> register(User user){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//空值处理
if(user==null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空");
}
if(StringUtils.isBlank(user.getUsername())){
//因为这不是异常需要返回给客户端
map.put("usernameMsg","账号不能为空");
return map;
}
if(StringUtils.isBlank(user.getPassword())){
map.put("passwordMsg","密码不能为空");
return map;
}
if(StringUtils.isBlank(user.getEmail())){
map.put("emailMsg","邮箱不能为空");
return map;
}
//验证账号
User u = userMapper.selectByName(user.getUsername());
if(u!=null){
map.put("usernameMsg","该账号已经存在");
return map;
}
//验证邮箱
u = userMapper.selectByEmail(user.getEmail());
if(u!=null){
map.put("emailMsg","邮箱已经注册");
return map;
}
//注册用户
//1.随机生成盐
user.setSalt(CommunityUtil.generateUUID().substring(0,5));
//2.加盐并加密
user.setPassword(CommunityUtil.md5(user.getPassword()+user.getSalt()));
//'0-普通用户; 1-超级管理员; 2-版主;'
user.setType(0);
//'0-未激活; 1-已激活;'
user.setStatus(0);
user.setActivationCode(CommunityUtil.generateUUID());
//牛客头像地址0-1000
user.setHeaderUrl(String.format("http://images.nowcoder.com/head/%dt.png", new Random().nextInt(1000)));
user.setCreateTime(new Date());
//插入后user内会回填id 具体看user-mapper.xml
userMapper.insertUser(user);
//激活邮件
Context context = new Context();
context.setVariable("email",user.getEmail());
//url规定这么搞:http://localhost:8080/community/activation/101/code #101-用户id,#code-激活码
//域名+项目名+功能的访问名+用户id+激活码
String url = domain+contextPath+"/activation/"+user.getId()+"/"+user.getActivationCode();
context.setVariable("url",url);
String html = templateEngine.process("/mail/activation", context);
mailClient.sendMail(user.getEmail(),"牛客网激活账号",html);
return map;
}
3.邮件模板内容
mail目录下activation.html
doctype html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="icon" href="https://static.nowcoder.com/images/logo_87_87.png"/>
<title>牛客网-激活账号title>
head>
<body>
<div>
<p>
<b th:text="${email}">[email protected]b>, 您好!
p>
<p>
您正在注册牛客网, 这是一封激活邮件, 请点击
<a th:href="${url}">此链接a>,
激活您的牛客账号!
p>
div>
body>
html>
4.写controller
在LoginController类中增加如下内容
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/register",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String register(Model model, User user){
Map<String, Object> map = userService.register(user);
if(map==null||map.isEmpty()){
model.addAttribute("msg","注册成功,我们已经向您的邮箱发送一封邮件,请查收并激活账号");
model.addAttribute("target","/index");
return "site/operate-result";
}else{
//注册失败返回注册页面
model.addAttribute("usernameMsg",map.get("usernameMsg"));
model.addAttribute("passwordMsg",map.get("passwordMsg"));
model.addAttribute("emailMsg",map.get("emailMsg"));
return "/site/register";
}
}
注册失败处理重新回到register.html页面
处理register.html页面
-
为每个字段增加name属性便于springmvc封装进user
-
注册过程中的错误处理
注册成功的中间页面
site/operate-result.html
激活注册账号
1.util包中定义几个激活状态常量
让UserService实现此接口
package com.hsw.community.util;
public interface CommunityContant {
//激活成功
int ACTIVATION_SUCCESS = 0;
//重复激活
int ACTIVATION_REPEAT = 1;
//激活失败
int ACTIVATION_FAILURE = 2;
}
2.业务层中UserService类增加新方法
public int activion(int userId,String code){
User user = userMapper.selectById(userId);
if(user==null){
return ACTIVATION_FAILURE;
}else if(user.getStatus()==1){//重复激活
return ACTIVATION_REPEAT;
}else if(!code.equals(user.getActivationCode())){//激活失败
return ACTIVATION_FAILURE;
}else{
//设置激活状态、激活成功
userMapper.updateStatus(userId,1);
return ACTIVATION_SUCCESS;
}
}
3.controller层增加方法
LoginController类
//url规定这么搞:http://localhost:8080/community/activation/101/code #101-用户id,#code-激活码
@RequestMapping(path="/activation/{userId}/{code}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String activation(Model model,
@PathVariable("userId")int userId,
@PathVariable("code") String code){
int result = userService.activion(userId, code);
if(result==ACTIVATION_SUCCESS){
model.addAttribute("msg","激活成功,您的账号可以使用");
model.addAttribute("target","/login");
}else if(result==ACTIVATION_REPEAT){
model.addAttribute("msg","无效操作,该账号已经激活");
model.addAttribute("target","/login");
}else{
model.addAttribute("msg","激活失败,激活码不正确请重新注册");
model.addAttribute("target","/register");
}
return "site/operate-result";
}
//访问登录页面的请求+login.html添加上声明
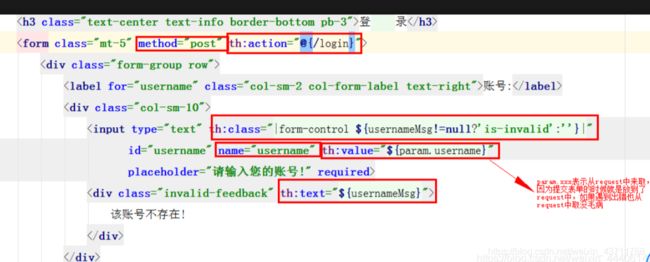
@RequestMapping(value = "/login",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getLoginPage(Model model){
return "site/login";
}
处理下site下的login页面 login.html
就是加入Thymeleaf中的东西。
三、 会话管理
HTTP的基本性质
- HTTP是简单的
- HTTP是可扩展的
- HTTP是无状态的,有会话的
Cookie
- 是服务器发送到浏览器,并保存在浏览器端的一小块数据。
- 浏览器下次访问该服务器时,会自动携带块该数据,将其发送给服务器。
Session
- 是JavaEE的标准,用于在服务端记录客户端信息。
- 数据存放在服务端更加安全,但是也会增加服务端的内存压力。
- 服务器分布式部署的时候存放session并没有十分完美的解决方案,所以一般我们都把数据存放进数据库中(redis)解决此问题。
四、生成验证码
Kaptcha
- 导入 jar 包
- 编写 Kaptcha 配置类
- 生成随机字符、生成图片
个人想法:
参考手册
Kaptcha核心接口
![]()
默认实现类
1.导包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pengglegroupId>
<artifactId>kaptchaartifactId>
<version>2.3.2version>
dependency>
2.配置
因为并没有整合进spring所以我们需要自己做整合,写一个配置类
@Configuration
public class KaptchaConfig {
@Bean
public Producer kaptchaProducer(){
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("kaptcha.image.width","100");
properties.setProperty("kaptcha.image.height","40");
properties.setProperty("kaptcha.textproducer.font.size","32");
properties.setProperty("kaptcha,textproducer.font.color","0,0,0");
properties.setProperty("kaptcha.textproducer.char.string","0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ");
properties.setProperty("kaptcha.textproducer.char.length","4");
properties.setProperty("kaptcha.noise.impl","com.google.code.kaptcha.impl.NoNoise");
DefaultKaptcha kaptcha = new DefaultKaptcha();
Config config = new Config(properties);
kaptcha.setConfig(config);
return kaptcha;
}
3.LoginController增加新方法
@Autowired
private Producer kaptchaProducer;
@RequestMapping(path="/kaptcha",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void getKaptcha(HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session){
//生成验证码
String text = kaptchaProducer.createText();
BufferedImage image = kaptchaProducer.createImage(text);
//将验证码存入session
session.setAttribute("kaptcha",text);
//将图片输出给浏览器
response.setContentType("image/png");
try {
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
ImageIO.write(image,"png",outputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("响应验证码获取失败:"+e.getMessage());
}
}
4.修改login.html
五、开发登陆、退出功能
- 访问登录页面
-
- 点击顶部区域内的链接,打开登录页面。
- 登录
-
- 验证账号、密码、验证码。
- 成功时,生成登录凭证,发放给客户端。
- 失败时,跳转回登录页。
- 退出
-
- 将登录凭证修改为失效状态。
- 跳转至网站首页。
登陆凭证相关
现在先存到数据库中
访问登录页面
上边已经完成
登陆
1.写dao层LoginTicketMapper类
@Repository
public interface LoginTicketMapper {
@Insert({
"insert into login_ticket(user_id,ticket,status,expired)" ,
" values(#{userId},#{ticket},#{status},#{expired})"
})
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyProperty = "id")
int insertLoginTicket(LoginTicket loginTicket);
@Select({
"select id,user_id,ticket,status,expired from login_ticket where ticket=#{ticket}"
})
LoginTicket selectByTicket(String ticket);
@Update({
"update login_ticket set status=#{status} where ticket=#{ticket}"
})
int updateStatus(String ticket,int status);
}
2.写service层
@Service
public class LoginService {
@Autowired
LoginTicketMapper loginTicketMapper;
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
public Map<String,Object> login(String username, String password,int expiredSeconds){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//空值的处理
if(StringUtils.isBlank(username)){
map.put("usernameMsg","用户名不能为空");
return map;
}else if(StringUtils.isBlank(password)){
map.put("passwordMsg","密码不能为空");
return map;
}
//验证账号
User user = userMapper.selectByName(username);
if(user==null){
map.put("usernameMsg","用户不存在");
return map;
}
//验证状态
if(user.getStatus()==0){
map.put("usernameMsg","该账号未激活");
return map;
}
//验证密码
password = CommunityUtil.md5(password+user.getSalt());
if(!password.equals(user.getPassword())){
map.put("passwordMsg","密码不正确");
return map;
}
//生成登陆凭证
LoginTicket loginTicket = new LoginTicket();
loginTicket.setUserId(user.getId());
loginTicket.setTicket(CommunityUtil.generateUUID());
loginTicket.setStatus(user.getStatus());
loginTicket.setExpired(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()+expiredSeconds*1000));
loginTicketMapper.insertLoginTicket(loginTicket);
map.put("loginTicket",loginTicket.getTicket());
return map;
}
}
3.写controller层
LoginService loginService;
("${server.servlet.context-path}")
String context_path;
//用于处理表单数据
(value = "/login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String Login(String username,String password,String code,boolean rememberMe,
Model model,
HttpSession session,
HttpServletResponse response){
String kaptcha = (String)session.getAttribute("kaptcha");
//检查验证码 , 业务层只处理业务逻辑 这种验证码校验可在这里直接做
if(StringUtils.isBlank(kaptcha)||StringUtils.isBlank(code)||!StringUtils.equalsIgnoreCase(code,kaptcha)){
model.addAttribute("codeMsg","验证码不正确");
return "site/login";
}
//检查账号,密码
int expiredSeconds = rememberMe?REMEMBERME_SECONDS:DEFAULT_SECONDS;
Map<String, Object> msg = loginService.login(username, password, expiredSeconds);
if(msg.containsKey("loginTicket")){
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("ticket",(String)msg.get("loginTicket"));
cookie.setPath(context_path);
cookie.setMaxAge(expiredSeconds);
response.addCookie(cookie);
//重定向到首页
return "redirect:/index";
}else{
model.addAttribute("usernameMsg",msg.get("usernameMsg"));
model.addAttribute("passwordMsg",msg.get("passwordMsg"));
return "site/login";
}
}
4.login.html页面的更改
退出
在LoginService类中加一个方法
public void logout(String ticket){
if(StringUtils.isBlank(ticket)){
return;
}
//1表示无效
loginTicketMapper.updateStatus(ticket,1);
}
2.controller层增加一个跳转方法
@RequestMapping(path="/logout",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String logout(@CookieValue("ticket") String ticket){
loginService.logout(ticket);
return "redirect:/login";
}
3.修改index页面
自我思考:这样搞每次登陆都会在login_ticket表中增加一条登陆记录啊,不知道后续功能咋实现先把问题搁这。
六、显示登陆信息
- 拦截器示例
-
- 定义拦截器,实现HandlerInterceptor
- 配置拦截器,为它指定拦截、排除的路径
- 拦截器应用
-
- 在请求开始时查询登录用户
- 在本次请求中持有用户数据
- 在模板视图上显示用户数据
- 在请求结束时清理用户数据
拦截器示例
1.定义一个拦截器类在interceptor包下
问题:参数中的handler是啥?
@Component
public class AlphaInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AlphaInterceptor.class);
//在controller之前执行
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
logger.debug("preHander:"+handler.toString());
return true;
}
//在controller之后执行
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
logger.debug("postHander:"+handler.toString());
}
//在模板引擎之后执行
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
logger.debug("afterCompletion:"+handler.toString());
}
}
2.写一个配置类
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
private AlphaInterceptor alphaInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(alphaInterceptor) //不写下几行会拦截一切请求
.excludePathPatterns("/**/*.css","/**/*.js","/**/*.jpg","/**/*.jpeg") //这么写会排除拦截一些静态资源
.addPathPatterns("/register","/login") //这么写会增加拦截的路径
;
}
3.访问/login页面查看日志
真相大白:handler是指拦截的目标
拦截器应用
业务逻辑
1.新建一个拦截器LoginTicketInterceptor
@Component
public class LoginTicketInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@Autowired
HostHolder hostHolder;
//可以简单理解为controller之前通过ticket取用户登录信息
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//从cookie中取凭证
String ticket = CookieUtil.getValue(request, "ticket");
if(ticket!=null){
//查询凭证
LoginTicket loginTicket = userService.findLoginTicket(ticket);
//检查凭证是够有效
if(loginTicket!=null&&loginTicket.getStatus()==0&&loginTicket.getExpired().after(new Date())){
//根据凭证查询用户
User user = userService.findUserById(loginTicket.getUserId());
//在本次请求中持有用户
hostHolder.setUser(user);
}
}
return true;
}
//在controller之后把用户信息传递给模板
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
if(user!=null && modelAndView!=null){
modelAndView.addObject("loginUser",user);
}
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
hostHolder.clear();
}
}
util包下HostHolder类可以模拟服务端的Session功能,存放是否有登陆的User
防止多线程出事用ThreadLocal
@Component
public class HostHolder {
private ThreadLocal<User> users = new ThreadLocal<User>();
public void setUser(User user){
users.set(user);
}
public User getUser(){
return users.get();
}
public void clear(){
users.remove();
}
}
CookieUtil根据key取cookie因为常用所以封装成一个工具类
public class CookieUtil {
public static String getValue(HttpServletRequest request,String key){
if(request==null||key==null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数为空");
}
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for(Cookie cookie:cookies){
if(cookie.getName().equals(key)){
return cookie.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
}
2.在配置中加入拦截器
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
private AlphaInterceptor alphaInterceptor;
@Autowired
private LoginTicketInterceptor loginTicketInterceptor;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(alphaInterceptor) //不写下几行会拦截一切请求
.excludePathPatterns("/**/*.css","/**/*.js","/**/*.jpg","/**/*.jpeg") //这么写会排除拦截一些静态资源
.addPathPatterns("/register","/login") //这么写会增加拦截的路径
;
registry.addInterceptor(loginTicketInterceptor)
.excludePathPatterns("/**/*.css","/**/*.js","/**/*.jpg","/**/*.jpeg");
}
}
3.模板中头部的处理
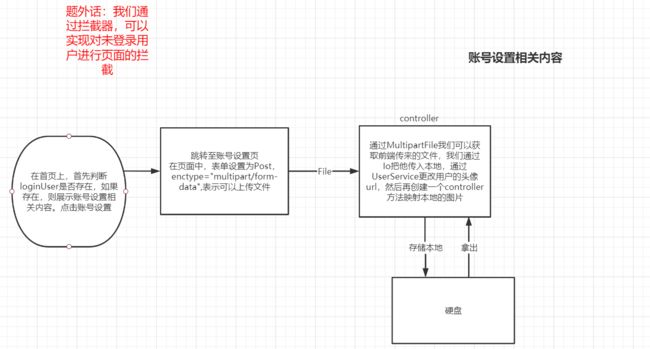
七、账号设置
- 上传文件
-
- 请求:必须是POST请求
- 表单:enctype=“multipart/form-data”
- Spring MVC:通过 MultipartFile 处理上传文件
- 开发步骤
-
- 访问账号设置页面
- 上传头像
- 获取头像
上传文件之访问账号设置页面
1.新建一个UserController类,增加一个方法,请求方式为get
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(path="/setting",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getSettingPage(){
return "/site/setting";
}
}
2.修改site/setting.html文件改成Thymeleaf的形式
3.修改index.html
上传头像和获取头像
1.在UserController类中完成
multipartFile 类可以控制从前台传入的文件。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@Value("${server.servlet.context-path}")
private String contextPath;
@Value("${community.path.domain}")
private String domain;
@Value("${community.path.upload}")
private String uploadPath;
@Autowired
private HostHolder hostHolder;
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class);
@RequestMapping(path="/setting",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getSettingPage(){
return "/site/setting";
}
/**
* 把文件存到服务器中
* @param multipartFile
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path="/upload",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String uploadHeader(MultipartFile multipartFile, Model model){
if(multipartFile==null){
model.addAttribute("error","您没有上传任何图片");
return "/site/setting";
}
String fileName = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
String suffix = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//System.out.println(suffix.equals(".jpg"));
if(StringUtils.isBlank(suffix)||!(suffix.equals(".png")||suffix.equals(".jpg"))){
model.addAttribute("error","文件格式错误,请重新上传");
return "/site/setting";
}
fileName = CommunityUtil.generateUUID()+suffix;
File dst = new File(uploadPath+"/"+fileName);
try {
multipartFile.transferTo(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("上传失败:"+e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException("服务器发生失败,上传出现异常"+e);
}
//更新headerUrl这里规定格式张这样
//http://localhost:8080/community/user/header/filename
String headerUrl = domain+contextPath+"/user/header/"+fileName;
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
userService.uploadHeader(user.getId(),headerUrl);
return "redirect:/user/setting";
}
/**
* 当用户读取headerUrl时从本地读取后返回
* @param filename
* @param response
*/
@RequestMapping(path = "header/{filename}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void getImg(@PathVariable("filename")String filename, HttpServletResponse response){
//服务器存放地址
filename = uploadPath+"/"+filename;
try (ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(filename);)
{
int len = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("读取文件失败:"+e.getMessage());
}
}
}
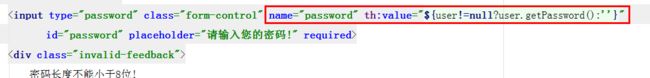
2.修改setting.html文件
密码修改
1.增加UserService中的方法
public int updatePassword(int userId,String password){
return userMapper.updatePassword(userId,password);
}
2.增加UserController中的方法
@RequestMapping(path="password",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String changePassword(Model model,
String oldPassword,
String newPassword,
String confirmPassword){
if(StringUtils.isBlank(oldPassword)){
model.addAttribute("olderror","请输入原密码");
return "/site/setting";
}
if(StringUtils.isBlank(newPassword)){
model.addAttribute("newerror","请输入新密码");
return "/site/setting";
}
if(StringUtils.isBlank(confirmPassword)){
model.addAttribute("confirmerror","请输入确认密码");
return "/site/setting";
}
if(!newPassword.equals(confirmPassword)){
model.addAttribute("confirmerror","两次密码不一致请重新输入");
return "/site/setting";
}
User user = hostHolder.getUser();
String password = user.getPassword();
if(!CommunityUtil.md5(oldPassword+user.getSalt()).equals(password)){
model.addAttribute("olderror","原密码输入错误,请重新输入");
return "/site/setting";
}
newPassword = CommunityUtil.md5(newPassword+user.getSalt());
userService.updatePassword(user.getId(),newPassword);
return "redirect:/logout";
}
3.修改setting.html
八、检查登陆状态
- 使用拦截器
-
- 在方法前标注自定义注解
- 拦截所有请求,只处理带有该注解的方法
- 自定义注解
-
- 常用的元注解:
@Target、@Retention、@Document、@Inherited - 如何读取注解:
Method.getDeclaredAnnotations()
Method.getAnnotation(Class annotationClass)
- 常用的元注解:
一个问题
但是如果用户知道url也可直接到相关界面
自定义注解
常用的元注解
- @Target:声明自定义注解可以作用在什么类型上,类上方法上等
- @Retention:声明自定义注解保留的时间
- @Document:声明自定义注解生成文档的时候要不要把注解也带上去
- @Inherited:用于继承的,一个子类继承父类,父类有注解,子类要不要继承这个注解
读取注解的方法
- Method.getDeclaredAnnotations()
- Method.getAnnotation(Class< T > annotationClass)
使用拦截器解决问题
1.定义自定义注解,主要作用就是标识
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LoginRequired {
}
2.对需要拦截的方法上加此注解
3.新建拦截器进行处理
@Component
public class LoginRequiredInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private HostHolder hostHolder;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if(handler instanceof HandlerMethod){
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
LoginRequired annotation = method.getAnnotation(LoginRequired.class);
if(annotation!=null&&hostHolder.getUser()==null){
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/login");
//false表示不让继续执行
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
4.WebMvcConfig类上加上这个拦截器