反射机制学习笔记(尚硅谷康师傅2023)
资料&笔记
- 尚硅谷Java全套:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1GfkpJqPXGX9MszHDfyTM9g?pwd=yyds 提取码:yyds
- 老师笔记上传于:https://www.yuque.com/u27599042/un32ge/a7f681014ed3329710a9b092d4f7973d
- 本文章汇总整理于:https://www.yuque.com/u27599042/un32ge
- 反射机制学习笔记(尚硅谷康师傅2019)汇总整理于:https://www.yuque.com/u27599042/un32ge/tvdzfwdac1cm3e61
反射的概述
- Reflection(反射)是被视为动态语言的关键,反射机制允许程序在执行期借助于Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息,并能直接操作任意对象的内部属性及方法。
- 动态语言
- 是一类在运行时可以改变其结构的语言。
- 例如,新的函数、对象、甚至代码可以被引进,已有的函数可以被删除或是其他结构上的变化。
- 通俗点说就是在运行时代码可以根据某些条件改变自身结构。
- 主要动态语言:Object-C、C#、JavaScript、PHP、Python、Erlang。
- 静态语言
- 与动态语言相对应的,运行时结构不可变的语言就是静态语言。
- 如,Java、C、C++。
- Java不是动态语言,但Java可以称之为“准动态语言”。
- 即Java有一定的动态性,我们可以利用反射机制、字节码操作获得类似动态语言的特性。
- Java的动态性让编程的时候更加灵活。
- 动态语言
反射的体验
- 定义一个类 Person:
public class Person {
// 属性
private String name;
public int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person()");
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("你好,我是一个人");
}
private String showNation(String nation){
System.out.println("我的国籍是:" + nation);
return nation;
}
}
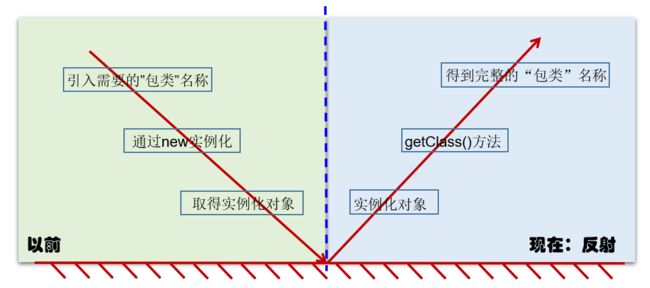
- 在学习反射之前,可以实现的操作:
- 通过Person类实例化一个person对象
- 可以通过实例化的person对象调用person对象的属性和方法,除了私有方法和私有属性及私有的构造器
- 反射可以实现的操作:
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReflectionTest {
@Test
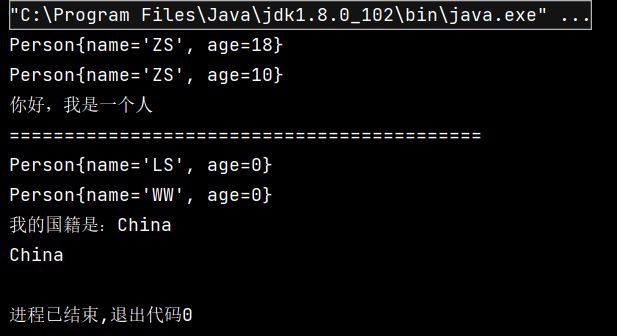
public void test() throws Exception {
// 1. 通过反射获取Person类对应的Class类型的实例对象
// 获取的Class类型对象可以认为就是Person类
Class personClass = Person.class;
// 2. 通过反射(通过Person类对应的Class类型的实例对象)获取Person类的构造器
// 获取参数为String类型和int类型的构造器
Constructor personPublicConstructor = personClass.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
// 3. 通过反射(通过获取的Person类的构造器)实例化person对象
// 实例化的对象 name = “ZS”; age = 18
Object personObj = personPublicConstructor.newInstance("ZS", 18);
System.out.println(personObj);
// 4. 通过反射获取类的属性和方法
// 获取Person类的属性
Field personAgeField = personClass.getField("age");
// 通过获取的Person类的属性修改person对象personObj的age属性
personAgeField.set(personObj, 10);
System.out.println(personObj);
// 获取Person类的方法
Method personShowMethod = personClass.getMethod("show");
// 通过反射调用person对象personObj的show方法
personShowMethod.invoke(personObj);
System.out.println("===========================================");
// 5. 通过反射获取Person类的私有结构,私有方法、私有属性等
// 通过反射获取Person类的私有构造器
Constructor personPrivateConstructor = personClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
personPrivateConstructor.setAccessible(true); // 允许调用私有构造器
// 使用Person类的私有构造器实例化对象
Person personObj2 = (Person) personPrivateConstructor.newInstance("LS");
System.out.println(personObj2);
// 6. 通过反射获取私有属性和方法
// 获取私有属性
Field name = personClass.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true); // 允许调用私有属性
name.set(personObj2, "WW");
System.out.println(personObj2);
// 获取私有方法
Method showNation = personClass.getDeclaredMethod("showNation", String.class);
showNation.setAccessible(true); // 允许调用私有方法
String nation = (String) showNation.invoke(personObj2, "China");
System.out.println(nation);
}
}
-
- 面向对象中创建对象,调用指定结构(属性、方法)等功能,可以不使用反射,也可以使用反射。请问有什么区别?
- 不使用反射,我们需要考虑封装性。比如:出了Person类之后,就不能调用Person类中私有的结构
- 使用反射,我们可以调用运行时类中任意的构造器、属性、方法。包括了私有的属性、方法、构造器。
-
- 以前创建对象并调用方法的方式,与现在通过反射创建对象并调用方法的方式对比的话,哪种用的多?场景是什么?
- 从我们作为程序员开发者的角度来讲,我们开发中主要是完成业务代码,对于相关的对象、方法的调用都是确定的。所以,我们使用非反射的方式多一些。
- 因为反射体现了动态性,可以在运行时动态的获取对象所属的类,动态的调用相关的方法,所以我们在设计框架的时候,会大量的使用反射。
- 意味着,如果大家需要学习框架源码,那么就需要学习反射。
- 框架 = 注解 + 反射 + 设计模式
-
疑问:通过直接new的方式或反射的方式都可以调用公共的结构,开发中到底用那个?
- 一般情况下开发,直接使用new的方式。
- 什么时候会使用反射的方式。
- 反射的特征:动态性。
- 当我们在开发时候不知道具体要实例化哪个类,但是在项目运行的时候可以知道具体要实例化哪个类的时候,可以使用反射。
- 例如,web中,服务器不知道浏览器到底会发送什么请求,但是在项目运行时可以根据具体的请求可以确定需要进行的逻辑处理,此时能够确定要实例化哪个对象,这种情况下可以使用反射。
-
- 单例模式的饿汉式和懒汉式中,私有化类的构造器了! 此时通过反射,可以创建单例模式中类的多个对象吗?
- 是的!
-
- 通过反射,可以调用类中私有的结构,是否与面向对象的封装性有冲突?是不是Java语言设计存在Bug?
- 不存在bug!
- 封装性:体现的是是否建议我们调用内部api的问题。比如,private声明的结构,意味着不建议调用。
- 反射:体现的是我们能否调用的问题。因为类的完整结构都加载到了内存中,所有我们就有能力进行调用。
-
Java代码运行时,加载完类之后,在堆内存的方法区中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息。我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构。
-
反射,即有一个对象,但这个对象的类型为Class类型,一个Class类型的对象对应一个Java类,我们可以通过这个对象获取对应的Java类的结构信息,即可以获取这个Class类型对象对应Java类的方法和属性信息及其他信息。
反射的功能
- 在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
- 在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
- 在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
- 在运行时获取泛型信息
- 在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
- 在运行时处理注解
- 生成动态代理
反射相关的 API
- 与反射相关的API主要定义在lang包和lang包的子包下。
- java.lang.Class:代表一个类
- Class类是由所有的Java类抽象出来的一个类,所有的Java类都是Class类的实例对象,所有的Java类都是有Class类实例化出来的对象,所有的Java类的类型为Class。
- java.lang.reflect.Method:代表类的方法
- java.lang.reflect.Field:代表类的成员变量
- java.lang.reflect.Constructor:代表类的构造器
- ······
反射的优缺点
- 优点:
- 提高了Java程序的灵活性和扩展性,降低了耦合性,提高自适应能力
- 允许程序创建和控制任何类的对象,无需提前硬编码目标类
- 缺点:
- 反射的性能较低。
- 反射机制主要应用在对灵活性和扩展性要求很高的系统框架上
- 反射会模糊程序内部逻辑,可读性较差。
- 反射的性能较低。
Class类的理解
- 针对于编写好的.java源文件进行编译(使用javac.exe),会生成一个或多个.class字节码文件。接着,我们使用java.exe命令对指定的.class文件进行解释运行。这个解释运行的过程中,我们需要将.class字节码文件加载(使用类的加载器)到内存中(存放在方法区)。加载到内存中的.class文件对应的结构即为Class的一个实例。
- 例如:加载到内存中的Person类或String类或User类,都是Class的一个一个的实例
- Class clazz1 = Person.class;
- Class clazz2 = String.class;
- Class clazz3 = User.class;
- Class clazz4 = Comparable.class;
- 例如:加载到内存中的Person类或String类或User类,都是Class的一个一个的实例
- 加载到内存中的类为运行时类
- 反射的所有操作,如:获取类的构造器、方法、属性等操作,都需要先获取Java类对应的Class类型对象,在基于Class类型对象实现获取Java类的构造器等操作。所以说Class类型对象是反射的源头。
获取Class实例的方式
@Test
public void test01() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 方式一:
// 通过调用运行时类的class属性获取Class实例
// Class Class带泛型
// 获取的Class实例对象就是User类本身
Class userClass1 = User.class;
System.out.println(userClass1);
// 方式二:
// 通过运行时类的对象的getClass()方法获取Class实例
// 不管哪个对象都可以获取到该对象是由哪个类实例化的
User user = new User();
Class userClass2 = user.getClass();
System.out.println(userClass2);
// 方式三:
// 调用Class的静态方法,forName(String classPath)获取Class实例
// classPath为类的全类名,全类名包含包名在内的类的完整路径
String className = "study01.User";
Class userClass3 = Class.forName(className); // 在内存中加载User类
System.out.println(userClass3);
// 方式四:
// 使用当前类的加载器Classloader调用加载器中的loadClass(String classPath)方法获取Class实例
// classPath为类的全类名
// 获取系统类加载器调用加载器中的loadClass(String classPath)方法获取Class实例
Class userClass4 = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass(className); // 在内存中加载User类
System.out.println(userClass4);
// 不同的方法获取都是同一个Class实例对象,即都是同一个运行时类
System.out.println(userClass1 == userClass1);
System.out.println(userClass1 == userClass2);
System.out.println(userClass1 == userClass3);
System.out.println(userClass1 == userClass4);
}
可以作为Class对象的类型
- 简言之,所有Java类型!
- (1)class:外部类,成员(成员内部类,静态内部类),局部内部类,匿名内部类
- (2)interface:接口
- (3)[]:数组
- 对于数组,只要数组中元素的类型和数组的维度相同,则获取到的数组对应的Class就是同一个Class的实例对象
- 注意:与数组的长度无关,即与每个维度中数据元素的个数无关
- (4)enum:枚举
- (5)annotation:注解@interface
- (6)primitive type:基本数据类型
- (7)void
- (8)Class
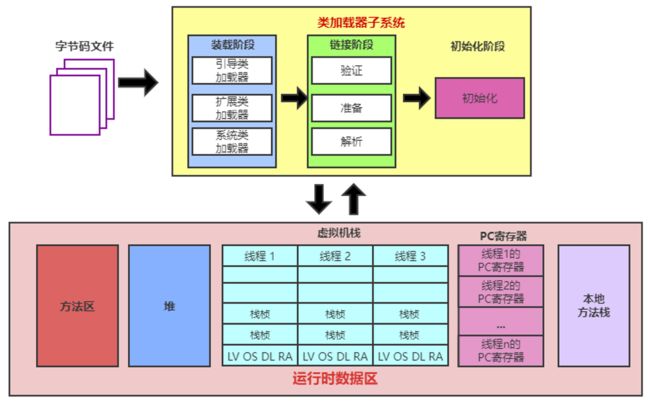
类的加载过程
- 类的加载过程,就是类对应的字节码文件加载到Java虚拟机的方法区中的过程
- 加载到内存中的类,我们就称为运行时类,此运行时类,是Class的一个实例。
- 以Person类为例,对Person.java文件进行编译,会生成一个对应的Person.class文件,然后运行Person.class字节码文件,即将Person类加载到内存中,此时内存中的Person类就是一个运行时类,为Class的实例对象。
- 换句话说,Class的实例就对应着一个运行时类。
- 加载到内存中的运行时类,会缓存一定的时间。在此时间之内,我们可以通过不同的方式来获取此运行时类。
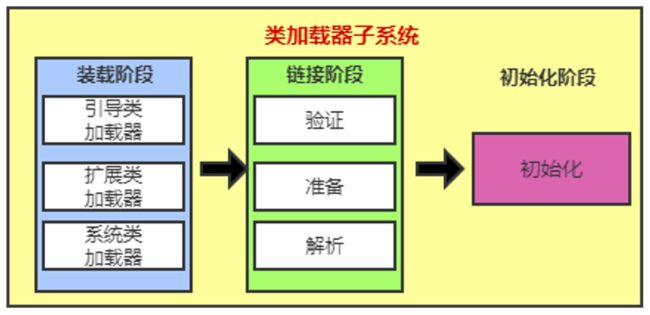
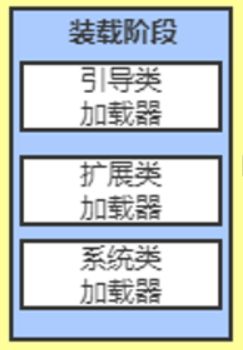
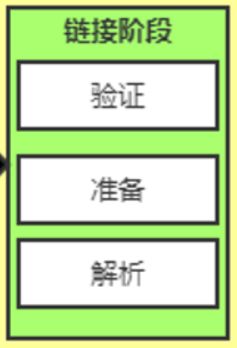
- 类加载到方法区中需要经历:类的装载(loading)=> 类的链接(linking)=> 类的初始化(initialization)
类的装载(loading)
- 类的装载:通过类加载器,将类的class文件读入内存,并为之创建一个java.lang.Class对象
- 所以在类的装载这个过程完成之后,内存中就有了类对应的Class实例对象
- 创建的java.lang.Class对象作为方法区中类数据的访问入口,所有需要访问和使用类数据只能通过这个Class对象
- 类的装载这个过程需要类加载器的参与。
类的链接(linking)
- 验证(Verify):确保加载的类信息符合JVM规范,如,Java能够识别的字节码文件都是以“cafebabe”开头,没有安全方面的问题
- 准备(Prepare):正式为类变量(static)分配内存并设置类变量默认初始值的阶段,这些内存都将在方法区中进行分配
- 准备阶段就是为类的静态变量分配方法区的内存空间并为其赋默认的初始值
- 解析(Resolve):虚拟机常量池内的符号引用(常量名)替换为直接引用(地址)的过程。
- 在字节码文件还未被加载到内存中时,程序中使用的地址为符号引用地址,并不是内存中的真实地址,当字节码文件记载到内存之后,不能再使用符号引用地址,因为在内存中使用符号引用地址不能找到真正需要的变量在内存中的位置,所以需要替换为直接引用地址,即在内存中的真正可以使用的地址
- 在字节码文件还未被加载到内存中时,程序中使用的地址为符号引用地址,并不是内存中的真实地址,当字节码文件记载到内存之后,不能再使用符号引用地址,因为在内存中使用符号引用地址不能找到真正需要的变量在内存中的位置,所以需要替换为直接引用地址,即在内存中的真正可以使用的地址
类的初始化(initialization)
- 类的初始化过程,是执行类构造器
() - 类构造器
() - 类构造器是构造类信息的,不是构造该类对象的构造器。
- 类的初始化过程,就是为类中的静态变量赋程序员指定的初始值的过程,以及执行静态代码块的过程
- 类构造器
- 当初始化一个类的时候,如果发现其父类还没有进行初始化,则需要先触发其父类的初始化。
- 虚拟机会保证一个类的
()
类的加载器
类加载器的作用
- 负责类的加载,并生成一个对应的Class的实例对象
- 类加载器会将class文件字节码内容加载到内存中,并将静态数据转换成方法区的运行时数据结构,然后在堆中生成一个代表这个类的java.lang.Class对象,该对象作为方法区中类数据的访问入口。
- 类缓存: 标准的JavaSE类加载器可以按要求查找类,但一旦某个类被类加载器加载到内存中,它将维持加载(缓存)一段时间。
类加载器的分类(以 JDK8 为例)
- 引导类加载器(Bootstrap ClassLoader),或者称为启动类加载器
- 这个类加载使用C/C++语言实现的,嵌套在JVM内部,获取它的对象时往往返回null,不能通过Java代码获取其实例对象
- 它用来加载Java的核心库(JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/rt.jar或sun.boot.class.path路径下的内容)。用于提供JVM自身需要的类。
- 继承于 ClassLoader 的类加载器
- 扩展类加载器(ExtensionClassLoader)
- Java语言编写,由sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader实现。
- 继承于ClassLoader类
- 父类加载器为启动类加载器
- 启动类加载器与扩展类加载器并没有继承关系,启动类加载器为父类加载器,是由于扩展类加载器中有一个属性parent指向启动类加载器
- 从java.ext.dirs系统属性所指定的目录中加载类库,或从JDK的安装目录的jre/lib/ext子目录下加载类库。如果用户创建的JAR放在此目录下,也会自动由扩展类加载器加载。
- 系统类加载器或应用程序类加载器(SystemClassLoader/ApplicationClassLoader)
- java语言编写,由sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader实现
- 继承于ClassLoader类
- 父类加载器为扩展类加载器
- 扩展类加载器与系统类加载器并没有继承关系,扩展类加载器为父类加载器,是由于系统类加载器中有一个属性parent指向扩展类加载器
- 实际上,扩展类加载器与系统类加载器为并列关系,都继承于ClassLoader类
- 它负责加载环境变量classpath或系统属性 java.class.path 指定路径下的类库
- 用户自定义的类,默认使用该类加载器加载
- 应用程序中的类加载器默认是系统类加载器。
- 它是用户自定义类加载器的默认父加载器
- 通过ClassLoader的getSystemClassLoader()方法可以获取到该类加载器
- 用户自定义类加载器
- 扩展类加载器(ExtensionClassLoader)
类加载器的使用
ClassLoader 获取类加载器
@Test
public void test01() {
// 获取系统类加载器
// 该方法默认获取的类加载器为系统类加载器
// SystemClassLoader就是ApplicationClassLoader
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader);
// 获取系统类加载器的父加载器 ExtensionClassLoader
ClassLoader extensionClassLoader = systemClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(extensionClassLoader);
// 获取引导类记载器
ClassLoader bootstrapClassLoader = extensionClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(bootstrapClassLoader);
}
获取加载某个类的加载器
@Test
public void test02() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 获取User类的运行时类对象,对应的Class实例对象
Class<User> userClass = User.class;
// 获取加载User类的加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = userClass.getClassLoader();
// jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@63947c6b
// 用户自定义的类是系统类加载器加载的
System.out.println(classLoader);
// 将 String 这个类主动进行加载
Class<?> stringClass = Class.forName("java.lang.String");
// 获取加载String的类加载器
ClassLoader stringClassClassLoader = stringClass.getClassLoader();
// null
// java核心库中的类有引导类加载器加载
System.out.println(stringClassClassLoader);
}
双亲委派机制
- 当有个类要进行加载时,先交给系统类加载器进行加载,但是系统类加载器并不会真正进行加载,而是会将该类交给扩展类加载器进行加载,当然扩展类加载器也不会直接进行加载,而是会将其交给引导类加载器进行加载,引导类加载器会进行判断自己是否合适加载该类(该类是否在规定的自己加载类的目录下),是则加载该类,下面的扩展类加载器和系统类加载器则不会加载该类,否则不加载该类,将该类交给扩展类加载器进行加载,扩展类加载器会进行判断自己是否合适加载该类(该类是否在规定的自己加载类的目录下),是则加载该类,下面的系统类加载器则不会加载该类,否则不加载该类,将该类交给系统类加载器进行加载,最后系统类加载器会进行加载
- 该机制可以放置核心库中的类被用户自定义的同包同名的类覆盖,例如,对于java.lang.String该名字的类,启动类加载器会判断出该类应该由自己进行加载,然后会去java核心类库中加载相应的类,从而放置核心类被覆盖,可以保护程序
package java.lang;
/**
* ClassName: String
* Package: java.lang
* Description:
*
* @Author tcw
* @Create 2023-05-22 18:32
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello world...");
}
}
用户自定义类加载器
- 对于一个类(class字节码文件),每个类加载器只能加载一次该类字节码文件
- 对于一个类,如果需要在内存中加载多次,则需要自定义类加载器
- 使用场景:如果对于某个类,具有多个不同的版本,都想加载到内存中,此时就需要自定义类加载器
使用类加载器获取流加载配置文件
- 通过ClassLoader加载指定的配置文件
原先加载配置文件
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
// 实例化Properties对象
Properties pros = new Properties();
// 获取文件输入流对象
// 文件默认位于当前模块下(测试方法默认从当前模块下开始读取文件)
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");
// Properties对象加载配置文件中的内容
pros.load(fis);
// 读取配置文件中的user password
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("user = " + user + ",password = " + password);
}
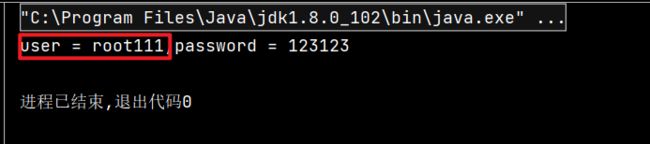
使用类加载器加载配置文件
- 使用该方式读取配置文件,默认的读取位置为:当前模块的src下
@Test
public void test6() throws Exception {
Properties pros = new Properties();
// 使用ClassLoader获取系统类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoader.getClassLoader();
// 通过系统类加载器以流的方式获取资源
// 使用该方式读取配置文件,默认的读取位置为:当前模块的src下
InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("jdbc1.properties");
// Properties对象加载配置文件中的内容
pros.load(is);
// 读取数据
String user = pros.getProperty("user");
String password = pros.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("user = " + user + ",password = " + password);
}
反射的应用
- 自定义注解
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();
}
- 自定义接口
public interface MyInterface {
void method();
}
- 自定义带泛型的类
public class Creature<T> {
boolean gender;
public int id;
public void breath(){
System.out.println("呼吸");
}
private void info(){
System.out.println("我是一个生物");
}
}
- Person 类
@MyAnnotation("t_persons")
public class Person extends Creature<String> implements Comparable<Person>,MyInterface{
private String name;
public int age = 1;
@MyAnnotation("info")
private static String info;
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person()...");
}
protected Person(int age){
this.age = age;
}
private Person(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void show() throws RuntimeException,ClassNotFoundException{
System.out.println("你好,我是一个Person");
}
@MyAnnotation(value="show_nation")
private String showNation(String nation,int age){
System.out.println("showNation...");
return "我的国籍是:" + nation + ",生活了" + age + "年";
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void method() {
}
public static void showInfo(){
System.out.println("我是一个人");
}
}
创建运行时类的对象
- 利用反射创建 Person 类的对象
- 通过 Class 实例对象调用 newInstance() 方法即可
- 运行时类中必须提供一个空参构造器
- 并且空参构造器的权限必须足够
- newInstance() 方法,由于使用该方法的要求较高,所以在JDK9开始不被推荐使用,推荐使用
Class实例对象.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance()- getDeclaredConstructor() 得到公开的构造器,使用得到的构造器进行对象的创建
// InstantiationException 没有空参构造器会抛出该异常
// IllegalAccessException 空参的构造器权限不足会抛出该异常
@org.junit.Test
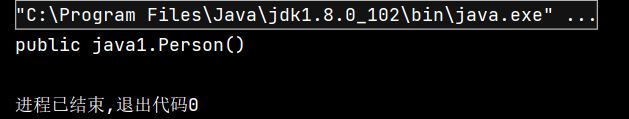
public void test01() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// 加载类到内存,获取 Person 类对应的运行时类对象
Class<?> personClass = Class.forName("study02.data.Person");
// 创建 Person 类的实例对象
Person person = (Person) personClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(person);
}
JavaBean 应当提供一个公共的空参构造器
- 子类对象在实例化时,子类的构造器的首行默认调用父类空参的构造器。
- 在反射中,经常用来创建运行时类的对象。那么我们要求各个运行时类都提供一个空参的构造器,便于我们编写通用的创建运行时类对象的代码。
获取运行时类的属性
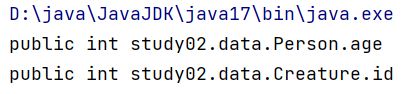
getFields()
- 获取运行时类及其父类中声明为public访问权限的属性。
@org.junit.Test
public void test1() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// 使用getFields()获取运行时类及其父类中声明为public访问权限的属性。
// 返回值为一个Field类型的数组
Field[] fields = personClass.getFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
getDeclaredField()
- 获取运行时类中声明的所有属性,不包含父类中声明的属性。
@Test
public void test2() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// getDeclaredField()获取运行时类中声明的所有属性,不包含父类中声明的属性。
// 返回值为一个Field类型的数组
Field[] fields = personClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field: fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
获取属性的结构
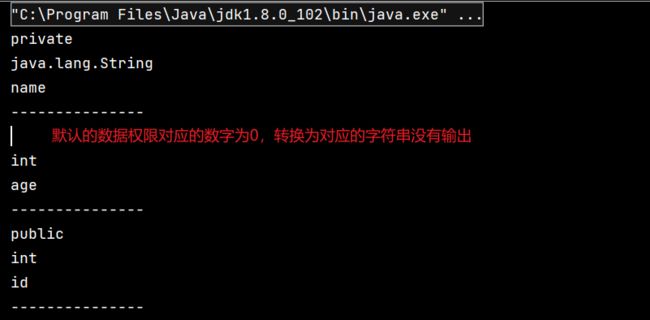
- 属性的权限修饰符、数据类型、变量名等也可以通过反射进行获取。
field.getModifiers()
- 获取属性的权限修饰符
- 得到的为权限修饰符对应的数字,默认权限为0
- 可以使用
Modifier.toString(modifiers)将权限修饰符对应数字转换为对应的权限修饰符字符串
field.getType()
- 获取属性的数据类型
- 返回值类型为Class
- type.getName()会返回数据类型的全类名
field.getName()
- 获取属性的变量名
@Test
public void test3() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
Field[] fields = personClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field: fields) {
// 1. 获取属性的权限修饰符
// field.getModifiers()得到的为权限修饰符对应的数字
// 默认权限为0
// 可以使用Modifier.toString(modifiers)将权限修饰符对应数字转换为对应的权限修饰符字符串
int modifiers = field.getModifiers();
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifiers));
// 2. 获取属性的数据类型
// 返回值类型为Class
Class type = field.getType();
// type.getName()会返回数据类型的全类名
System.out.println(type.getName());
// 3. 获取属性的变量名
String fieldName = field.getName();
System.out.println(fieldName);
System.out.println("---------------");
}
}
权限修饰符对应的数字转换为字符串的对应关系
// 对于权限修饰符,将其数字转换为对应的字符串的对应关系
// 0x是十六进制
// * PUBLIC = 0x00000001; 1 1
// * PRIVATE = 0x00000002; 2 10
// * PROTECTED = 0x00000004; 4 100
// * STATIC = 0x00000008; 8 1000
// * FINAL = 0x00000010; 16 10000
public static String toString(int mod) {
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner(" ");
if ((mod & PUBLIC) != 0) sj.add("public");
if ((mod & PROTECTED) != 0) sj.add("protected");
if ((mod & PRIVATE) != 0) sj.add("private");
/* Canonical order */
if ((mod & ABSTRACT) != 0) sj.add("abstract");
if ((mod & STATIC) != 0) sj.add("static");
if ((mod & FINAL) != 0) sj.add("final");
if ((mod & TRANSIENT) != 0) sj.add("transient");
if ((mod & VOLATILE) != 0) sj.add("volatile");
if ((mod & SYNCHRONIZED) != 0) sj.add("synchronized");
if ((mod & NATIVE) != 0) sj.add("native");
if ((mod & STRICT) != 0) sj.add("strictfp");
if ((mod & INTERFACE) != 0) sj.add("interface");
return sj.toString();
}
获取运行时类的方法
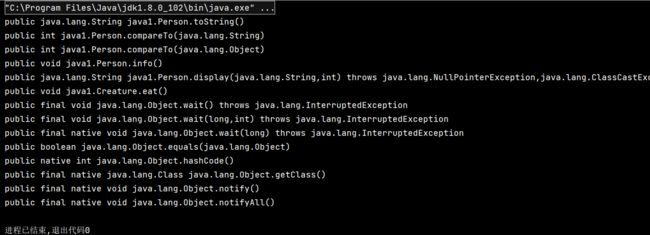
getMethods()
- 获取运行时类及其所有父类中声明为public访问权限的方法。
@Test
public void test1() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// getMethods()获取运行时类及其所有父类中声明为public访问权限的方法。
// 返回值为Method类型的数组
Method[] methods = personClass.getMethods();
for (Method method: methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
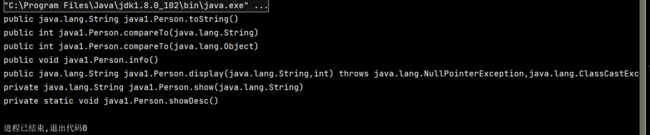
getDeclaredMethods()
- 获取运行时类中声明的所有方法,不包含父类中声明的方法
@Test
public void test2() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// getDeclaredMethods()获取运行时类中声明的所有方法,不包含父类中声明的方法
// 返回值为Method类型的数组
Method[] methods = personClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method: methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
获取方法的结构
- 方法的结构:
@Xxxx
权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型1 参数名1, ...) throws Exception {}
method.getAnnotations()
- 获取方法声明的注解
- 返回值为Annotation类型的数组,因为一个方法上可以加多个注解
method.getModifiers()
- 得到的为权限修饰符对应的数字
- Modifier.toString()将权限修饰符数字转换为对应的字符串
method.getReturnType()
- 获取方法的返回值类型
- type.getName() 获取返回值类型对应的字符串
method.getName()
- 获取方法的方法名
method.getParameterTypes()
- 获取方法的形参列表
- 返回 Class 类型的数组
method.getExceptionTypes()
- 获取方法抛出的异常
- 返回 Class 类型的数组,因为抛出的异常可能有多个也可能没有异常的抛出
@Test
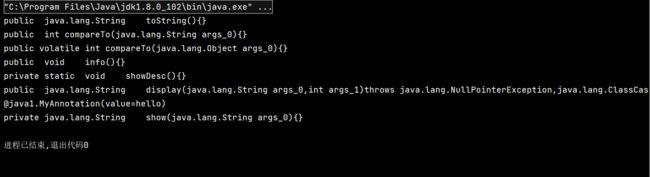
public void test4() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
//1.获取方法声明的注解
//返回值为Annotation类型的数组,因为一个方法上可以加多个注解
Annotation[] annos = m.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation a : annos) {
System.out.println(a);
}
//2.权限修饰符
//m.getModifiers()得到的为权限修饰符对应的数字
//Modifier.toString()将权限修饰符数字转换为对应的字符串
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(m.getModifiers()) + "\t");
//3.返回值类型
System.out.print(m.getReturnType().getName() + "\t");
//4.方法名
System.out.print(m.getName());
System.out.print("(");
//5.形参列表
Class[] parameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes();
//判断方法是否有形参列表
if (!(parameterTypes == null || parameterTypes.length == 0)) {
// 循环输出参数类型
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
// 最后一个形参的输出进行特殊处理
if (i == parameterTypes.length - 1) {
System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName() + " args_" + i);
break;
}
System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName() + " args_" + i + ",");
}
}
System.out.print(")");
//6.抛出的异常
//抛出的异常可能有多个也可能没有异常的抛出
Class[] exceptionTypes = m.getExceptionTypes();
//判断是否有异常的抛出
if (exceptionTypes.length > 0) {
System.out.print("throws ");
for (int i = 0; i < exceptionTypes.length; i++) {
if (i == exceptionTypes.length - 1) {
System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName());
break;
}
System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName() + ",");
}
}
System.out.println("{}");
}
}
获取运行时类的构造器
getConstructors()
- 获取运行时类中声明为public访问权限的构造器。
@Test
public void test1() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// getConstructors()获取运行时类中声明为public访问权限的构造器。
// 返回值为Constructor类型的数组,构造器可能有多个
Constructor[] constructors = personClass.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
}
getDeclaredConstructors()
- 获取运行时类中声明的所有构造器
@Test
public void test2() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// getDeclaredConstructors()获取运行时类中声明的所有构造器
// 返回值为Constructor类型的数组,构造器可能有多个
Constructor[] constructors = personClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
}
- 通过反射也可以获取构造器的结构,获取方法与获取方法的结构类似。
获取运行时类的父类
@Test
public void test() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// 获取运行时类的父类
// 运行时类的父类的类型也为Class
Class superClass = personClass.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superClass);
}
获取运行时类的带泛型的父类
@Test
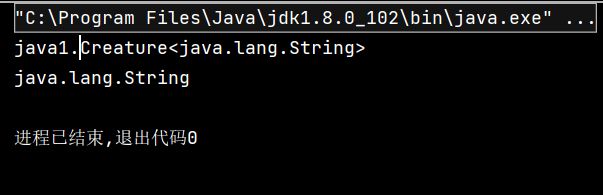
public void test() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// 获取运行时类的带泛型的父类
Type genericSuperclass = personClass.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(genericSuperclass);
}
获取运行时类的带泛型的父类的泛型
@Test
public void test() {
Class personClass = Person.class;
// 先获取带泛型的父类
// Type 是一个接口,Class 实现了该接口
Type genericSuperclass = personClass.getGenericSuperclass();
System.out.println(genericSuperclass);
// 已经确定genericSuperclass带有泛型,将其强转为带有参数类型ParameterizedType类型
ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass;
//调用getActualTypeArguments()获取泛型
//返回的为数组,是由于有时候泛型有多个,如Map就有两个泛型
Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments();
System.out.println(actualTypeArguments[0].getTypeName());
}
获取运行时类实现的接口
获取运行时类实现的接口
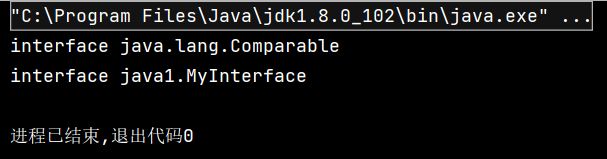
@Test
public void test() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
// 获取运行时类实现的接口
// 由于实现的接口可能有多个,所以返回的为数组
Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
for(Class c : interfaces){
System.out.println(c);
}
}
获取运行时类的父类实现的接口
@Test
public void test() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//获取运行时类的父类实现的接口
//先获取运行时类的父类
//然后获取运行时类的父类实现的接口
Class[] interfaces1 = clazz.getSuperclass().getInterfaces();
for(Class c : interfaces1){
System.out.println(c);
}
}
获取运行时类所在的包
@Test
public void test() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Package pack = clazz.getPackage();
System.out.println(pack);
}
获取运行时类的注解
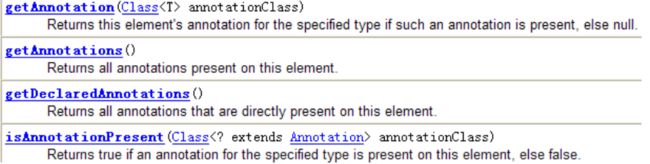
- JDK 5.0 在 java.lang.reflect 包下新增了 AnnotatedElement 接口, 该接口代表程序中可以接受注解的程序元素。当一个 Annotation 类型被定义为运行时 Annotation 后, 该注解才是运行时可见,当 class 文件被载入时保存在 class 文件中的 Annotation 才会被虚拟机读取,程序可以调用 AnnotatedElement对象的如下方法来访问 Annotation 信息:
@Test
public void test() {
Class clazz = Person.class;
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation annos : annotations){
System.out.println(annos);
}
}
调用指定的属性
- 调用指定属性的步骤:
- 步骤1:通过Class实例调用getDeclaredField(String fieldName),获取运行时类指定名的属性
- 步骤2:setAccessible(true):确保此属性是可以访问的
- 步骤3:通过Filed类的实例调用get(Object obj) (获取的操作)或 set(Object obj,Object value) (设置的操作)进行操作。
@org.junit.Test
public void test03() throws Exception {
// 加载类,获取该类对应的Class实例
Class<?> personClass = Class.forName("study02.data.Person");
// 创建对象
Person person = (Person) personClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
/*
* 公共的非静态的属性
*/
// 获取运行时类的指定名的属性
Field age = personClass.getField("age"); // 该属性公共的非静态的
// 获取属性值
// 由于是非静态的,所以要指明获取哪个对象的属性
Object personAge = age.get(person); // 返回的为该对象的属性值
System.out.println("person age 属性的初始值为:" + personAge);
// 设置属性值
age.set(person, 22); // 设置person的age属性的属性值为22
System.out.println("person age 属性的当前值为:" + age.get(person));
/*
* 私有的属性(获取当前运行时类的公共属性或私有属性都可以采用下面的方法)
*/
// getField() 获取运行时类及其父类中声明为 public 访问权限的属性
// 获取私有属性需要使用 getDeclaredField() 获取运行时类中声明的所有属性,不包含父类中声明的属性
Field name = personClass.getDeclaredField("name");
// 私有权限默认不能进行访问
// 要访问私有权限,需要修改其是否可以访问 确保属性可以访问
name.setAccessible(true); // 修改为可以进行访问
name.set(person, "张三"); // 设置person的name为 “张三”
String personName = (String) name.get(person); // 获取person的name
System.out.println("person 的 name 为:" + personName);
/*
* 运行时类的静态属性
*/
Field info = personClass.getDeclaredField("info"); // 获取属性
info.setAccessible(true); // 设置为可以访问
// 对应静态变量,info.set(null, "Person 类的信息..."); 也是可以的
// 因为获取 静态属性 时已经知道该属性是哪个类的了,无向再次指明
info.set(personClass, "Person 类的信息..."); // 由于是静态属性所以调用该方法的对象为类对应的Class实例
// info.get(null)
Object PersonInfo = info.get(personClass); // 获取属性值
System.out.println(PersonInfo);
}
调用指定的方法
- 调用指定方法的步骤:
- 步骤1.通过Class的实例调用getDeclaredMethod(String methodName,Class … args),获取指定的方法
- 步骤2. setAccessible(true):确保此方法是可访问的
- 步骤3.通过Method实例调用invoke(Object obj,Object … objs),即为对Method对应的方法的调用。
- invoke()的返回值即为Method对应的方法的返回值
- 特别的:如果Method对应的方法的返回值类型为void,则invoke()返回值为null
@org.junit.Test
public void test04() throws Exception {
// 获取运行时类Class对象
Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;
// 创建Person对象
Person person = personClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 获取方法 private String showNation(String nation,int age) {}
// 参数一:方法名
// 参数二:可变形参,方法的形参列表中的各参数的类型(参数类型要对应)
// 类型不能自动装箱,类型的值才可以自动装箱
Method showNation = personClass.getDeclaredMethod("showNation", String.class, int.class);
// 设置方法是否可以访问
showNation.setAccessible(true);
// 参数一:调用哪个对象的该方法
// 参数二:可变形参,方法的形参
// 返回值为方法的返回值
Object invokeBack = showNation.invoke(person, "中国", 23);
System.out.println(invokeBack);
}
调用指定的构造器
- 调用指定构造器的步骤:
- 步骤1.通过Class的实例调用getDeclaredConstructor(Class … args),获取指定参数类型的构造器
- 步骤2.setAccessible(true):确保此构造器是可以访问的
- 步骤3.通过Constructor实例调用newInstance(Object … objs),返回一个运行时类的实例。
@org.junit.Test
public void test05() throws Exception {
// 获取运行时类
Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;
// 获取构造器 private Person(String name, int age) {}
// 参数:可变形参,构造器形参的类型
Constructor<Person> personConstructor = personClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
// 设置构造器可以进行访问
personConstructor.setAccessible(true);
// 利用获取的构造器创建对象
Person person = personConstructor.newInstance("张三", 34);
System.out.println(person);
}
获取指定的注解
自定义注解
/**
* ClassName: Table
* Package: PACKAGE_NAME
* Description:
* 普通Java对象和数据库中哪个表对应
*
* @Author tcw
* @Create 2023-05-25 9:25
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) // 该注解只能使用在类、接口、枚举、记录上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 在运行时需要可以通过反射获取该注解,所以RUNTIME
public @interface Table {
String value();
}
/**
* ClassName: Column
* Package: PACKAGE_NAME
* Description:
*
* @Author tcw
* @Create 2023-05-25 9:32
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) // 该注解只能在属性上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 在运行时需要可以通过反射获取该注解,所以RUNTIME
public @interface Column {
String columnName(); // 对应数据库表中字段的字段名
String columnType(); // 对应数据库表中字段的字段类型
}
Java 类
/**
* ClassName: Customer
* Package: PACKAGE_NAME
* Description:
*
* @Author tcw
* @Create 2023-05-25 9:29
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Table("t_customer") // 该Java类与数据库中的t_customer表对应
public class Customer {
@Column(columnName = "name", columnType = "varchar(10)")
private String name;
@Column(columnName = "age", columnType = "int")
private Integer age;
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
}
}
获取注解
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
// 加载类获取类对应的Class实例
Class<?> customer = Class.forName("Customer");
// 获取类上的注解(Table)
Table customerDeclaredAnnotation = customer.getDeclaredAnnotation(Table.class);
// 获取注解的属性
System.out.println("该Java类对应的数据库表为:" + customerDeclaredAnnotation.value());
// 获取属性
Field[] customerDeclaredFields = customer.getDeclaredFields();
// 获取属性上的注解
for (Field customerDeclaredField : customerDeclaredFields) {
Column fieldAnnotation = customerDeclaredField.getAnnotation(Column.class);
System.out.print("对应数据库中的字段:" + fieldAnnotation.columnName());
System.out.println(" 类型为:" + fieldAnnotation.columnType());
}
}
反射练习
案例:榨汁机榨水果汁,水果分别有苹果(Apple)、香蕉(Banana)、桔子(Orange)等。
提示:
1、声明(Fruit)水果接口,包含榨汁抽象方法:void squeeze(); /skwiːz/
2、声明榨汁机(Juicer),包含运行方法:public void run(Fruit f),方法体中,调用f的榨汁方法squeeze()
3、声明各种水果类,实现水果接口,并重写squeeze();
4、在src下,建立配置文件:config.properties,并在配置文件中配上fruitName=xxx(其中xx为某种水果的全类名)
5、在FruitTest测试类中,
(1)读取配置文件,获取水果类名,并用反射创建水果对象,
(2)创建榨汁机对象,并调用run()方法
接口声明
/**
* ClassName: Fruit
* Package: PACKAGE_NAME
* Description:
*
* @Author tcw
* @Create 2023-05-25 10:07
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface Fruit {
/**
* 水果榨汁的方法
*/
void squeeze();
}
水果类
/**
* ClassName: Apple
* Package: PACKAGE_NAME
* Description:
*
* @Author tcw
* @Create 2023-05-25 10:09
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Apple implements Fruit{
@Override
public void squeeze() {
System.out.println("苹果汁...");
}
}
public class Banana implements Fruit{
@Override
public void squeeze() {
System.out.println("香蕉汁....");
}
}
public class Orange implements Fruit{
@Override
public void squeeze() {
System.out.println("橘子汁...");
}
}
榨汁机类
public class Juicer {
/**
* 使用需要进行榨汁的水果榨汁
*
* @param fruit 水果
*/
public static void run(Fruit fruit) {
fruit.squeeze(); // 榨汁
}
}
配置文件
fruitName=Apple
测试
/**
* ClassName: FruitTest
* Package: PACKAGE_NAME
* Description:
*
* @Author tcw
* @Create 2023-05-25 10:14
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class FruitTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 利用类加载器加载配置文件
ClassLoader classLoader = FruitTest.class.getClassLoader();
InputStream resource = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("config.properties"); // 默认从src下开始查找文件
// 使用Properties对象加载文件中的内容
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(resource);
// 获取需要进行榨汁的水果(获取全类名)
String fruitName = (String) properties.get("fruitName");
// 利用反射创建相应水果的实例对象
Class<?> fruitClass = Class.forName(fruitName); // 加载类
Fruit fruit = (Fruit) fruitClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); // 虽然不知道是什么水果但是一定是水果
// 调用榨汁机榨汁方法进行榨汁
Juicer.run(fruit);
}
}