OC 对象的本质
在我们日常的开发中,会创建很多个自定义的对象,大部分是继承自 NSObject,但是具体到源码实现,就看不到了,怎么办呢?编译器 clang 就要登场了
Clang
Clang 是一个有 Apple 主导编写,基于 LLVM 的 C/C++/Objective-C 的编译器
主要用于底层编译,将一些文件输出为 C++ 文件,可以更好的查看底层的结构以及实现逻辑
探索对象本质
- 在
main中自定义一个类LGPerson,有一个属性name
@interface LGPerson : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@end
@implementation LGPerson
@end
- 通过终端,利用
clang将main.m编译成main.cpp,有以下几种编译命令,这里使用的是第一种
//1、将 main.m 编译成 main.cpp
clang -rewrite-objc main.m -o main.cpp
//2、将 ViewController.m 编译成 ViewController.cpp
clang -rewrite-objc -fobjc-arc -fobjc-runtime=ios-13.0.0 -isysroot / /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/iPhoneSimulator.platform/Developer/SDKs/iPhoneSimulator13.7.sdk ViewController.m
//以下两种方式是通过指定架构模式的命令行,使用xcode工具 xcrun
//3、模拟器文件编译
- xcrun -sdk iphonesimulator clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc main.m -o main-arm64.cpp
//4、真机文件编译
- xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc main.m -o main- arm64.cpp
-
打开编译好的main.cpp,找到
LGPerson的定义,发现LGPerson在底层会被编译成struct结构体LGPerson_IMPL中的第一个属性 其实就是isa,是继承自NSObject,属于伪继承,伪继承的方式是直接将NSObject结构体定义为LGPerson中的第一个属性,意味着LGPerson拥有NSObject中的所有成员变量。LGPerson中的第一个属性NSObject_IVARS等效于NSObject中的isa
//NSObject的定义
@interface NSObject {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
}
//NSObject 的底层编译
struct NSObject_IMPL {
Class isa;
};
//LGPerson的底层编译
struct LGPerson_IMPL {
struct NSObject_IMPL NSObject_IVARS; // 等效于 Class isa;
NSString *_name;
};
如下图所示
通过上述分析,理解了OC对象的本质,但是看到NSObject的定义,会产生一个疑问:为什么isa的类型是Class?
在iOS-底层原理 02:alloc & init & new 源码分析文章中,提及过
alloc方法的核心之一的initInstanceIsa方法,通过查看这个方法的源码实现,我们发现,在初始化isa指针时,是通过isa_t类型初始化的,-
而在
NSObject定义中isa的类型是Class,其根本原因是由于isa对外反馈的是类信息,为了让开发人员更加清晰明确,需要在isa返回时做了一个类型强制转换,类似于swift中的as的强转。源码中isa的强转如下图所示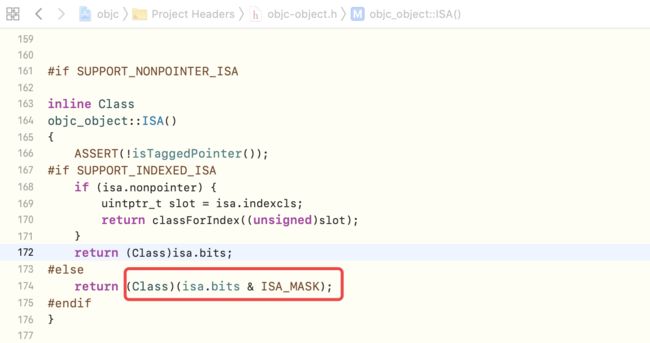 image
image
总结
所以从上述探索过程中可以得出:
OC对象的本质其实就是结构体LGPerson中的isa是继承自NSObject中的isa
cls 与 类的关联
在alloc 源码分析 & init & new中分析了 alloc 中核心三步的前两个,下面来探索initInstanceIsa是如何将cls与isa关联的
联合体
构造数据类型的方式有两种:结构体(struct)和 联合体(union)
- 结构体
所有变量是共存的,不管用不用,都会分配内存。优点是容量大,包容性强;缺点是 struct 内存空间的分配是粗放的,所有属性都会分配内存,容易造成内存浪费
- 联合体
各变量是“互斥”的,所有的成员共占一段内存。同一时刻只能保存一个成员的值,如果对新的成员赋值,就会将原来成员的值覆盖掉。优点是内存的使用更为精细灵活,节省内存空间,缺点是包容性弱
isa 的类型
源码中查看 isa_t 的定义,可以看出是通过联合体(union)定义的
union isa_t { //联合体
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
//提供了cls 和 bits ,两者是互斥关系
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
#if defined(ISA_BITFIELD)
struct {
ISA_BITFIELD; // defined in isa.h
};
#endif
};
从 isa_t 的定义源码可以看出
- 提供两个成员变量
cls和bits,这两个成员是互斥的 - 提供一个结构体定义的
位域,用于存储类信息及其他信息,结构体的成员ISA_BITFIELD,这是一个宏定义,有__arm64__和__x86_64__两个版本,分别对应 iOS 端 和 模拟器/Macos
# if __arm64__ //真机
# define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x000003f000000001ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x000001a000000001ULL
# define ISA_BITFIELD \
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1; \
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1; \
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1; \
uintptr_t shiftcls : 33; /*MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x1000000000*/ \
uintptr_t magic : 6; \
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1; \
uintptr_t deallocating : 1; \
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1; \
uintptr_t extra_rc : 19
# define RC_ONE (1ULL<<45)
# define RC_HALF (1ULL<<18)
# elif __x86_64__ //模拟器/Mac os
# define ISA_MASK 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x001f800000000001ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x001d800000000001ULL
# define ISA_BITFIELD \
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1; \
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1; \
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1; \
uintptr_t shiftcls : 44; /*MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x7fffffe00000*/ \
uintptr_t magic : 6; \
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1; \
uintptr_t deallocating : 1; \
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1; \
uintptr_t extra_rc : 8
# define RC_ONE (1ULL<<56)
# define RC_HALF (1ULL<<7)
nonpointer:表示是否对 isa 指针开启指针优化;0:纯 isa 指针,1:不止是类对象地址,isa 中包含了类信息、对象引用计数等
has_assoc:关联对象标志位,0 没有,1 存在
has_cxx_dtor:该对象是否有 C++ 或者 ObjC 的析构器,如果有析构函数,则需要做析构逻辑处理;如果没有,则可以更快的释放对象
shiftcls:存储类指针的值。开启指针优化的情况下,在 arm64 架构下有 33 位用来存储类指针
magic:用于调试器判断当前对象是真的对象还是没有初始化的空间
weakly_referenced:标志对象是否被指向或者曾经指向一个 ARC 的弱变量,没有弱引用的对象释放的更快
deallocating:标志对象是否正在释放内存
has_sidetable_rc:当对象弱引用计数大于 10 时,则需要借用该变量存储进位
extra_rc:表示该对象的引用计数值,实际上是引用计数值减1,(例如,如果对象的引用计数为 10,那么 extra_rc 为 9。如果引用计数大于10,则需要使用到下面的 has_sidetable_rc)
isa_t 使用联合体的原因也是基于 内存优化 的考虑,这里的内存优化是指在isa 指针中通过 char + 位域的原理实现。isa 占用 8 字节,即 64 位,已经足够存储很多的信息了,这样可以极大的节省内存,提高性能
原理探索
下面进入 initInstanceIsa 的探索,首先查看它的源码实现
inline void
objc_object::initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor)
{
ASSERT(!cls->instancesRequireRawIsa());
ASSERT(hasCxxDtor == cls->hasCxxDtor());
initIsa(cls, true, hasCxxDtor);
}
initInstanceIsa 的源码实现中,主要是调用了 initIsa,继续跳到 initIsa 的源码
inline void
objc_object::initIsa(Class cls, bool nonpointer, bool hasCxxDtor)
{
ASSERT(!isTaggedPointer());
if (!nonpointer) {
isa = isa_t((uintptr_t)cls);
} else {
ASSERT(!DisableNonpointerIsa);
ASSERT(!cls->instancesRequireRawIsa());
isa_t newisa(0);
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
ASSERT(cls->classArrayIndex() > 0);
newisa.bits = ISA_INDEX_MAGIC_VALUE;
// isa.magic is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
// isa.nonpointer is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
newisa.has_cxx_dtor = hasCxxDtor;
newisa.indexcls = (uintptr_t)cls->classArrayIndex();
#else
newisa.bits = ISA_MAGIC_VALUE;
// isa.magic is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
// isa.nonpointer is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
newisa.has_cxx_dtor = hasCxxDtor;
newisa.shiftcls = (uintptr_t)cls >> 3;
#endif
// This write must be performed in a single store in some cases
// (for example when realizing a class because other threads
// may simultaneously try to use the class).
// fixme use atomics here to guarantee single-store and to
// guarantee memory order w.r.t. the class index table
// ...but not too atomic because we don't want to hurt instantiation
isa = newisa;
}
}
源码主要是初始化 isa,两种方式
- 通过 cls 初始化
非nonpointer,存储着 Class、Meta-Class 对象的内存地址信息 - 通过 bits 初始化
nonpointer,进行一系列的初始化操作