k8s的 Headless Service和target port
在 Kubernetes 集群中,Service 是将运行在一组 Pods 上的应用程序公开为网络服务的抽象方法。Service 可以充当服务发现机制,使我们能轻松地和上游 Pod 通信,而无需知道各个 Pod 的确切 IP 地址。
在某些情况下,我们想检索并连接到特定 Service 所有 Pod 的 IP 地址。当 Pod 是有状态的(例如已部署的数据库)时,各个 Pod 需要与其同属实例进行通信。在这种情况下,Pod 如果想知道哪些其他成员是数据库集群的一部分时,Headless Service 可以派上用场。
什么是 Headless Service?
部署 Service时,可以设置三种不同的 ServiceTypes 以指定所需的 Service 类型:
ClusterIP:仅在集群内部 ip 地址上公开 Service,这也是默认的 ServiceType。
NodePort:允许通过节点上的静态端口公开 Service。
LoadBalancer:允许使用云提供商的外部负载均衡器公开 Service 。
为避免请求在单个 IP 地址后面进行负载均衡,当不需要单个 IP 地址时,我们可以通过指定 Cluster IP(spec.clusterIP)的值为 “None” 来创建 Headless Service。Kubernetes 不会为该 Service 分配任何 IP 地址。这种 Service 就称为 Headless Services。
DNS 解析和 Headless Service
部署 Service 时,Kubernetes 会为其分配一个 DNS 名称。集群中的其他组件可以使用此名称与 DNS 和上游 Pod 通信。DNS 名称遵循以下命名约定:

在 IP 地址上使用可读名称后,其他组件就不需要分配给 Service 实际 IP 地址。使用正确的 Pod 选择(selector)配置 Headless Service 时,Kubernetes 将为上游选定的 Pod 创建正确端点记录和 DNS 配置。
对于将连接到 Headless Service 的每个已连接 Pod,也会配置 A 或 AAAA 记录。这样就可以对 Headless Service 执行 DNS 查询,以解析所连接 Pod 的所有 IP 地址。
如何实践?
假设存在以下问题:Kubernetes 集群中运行着一组有状态的三个 MongoDB Pod。这三个 Pod 共同构成一个 MongoDB 副本集,这是一个高度可用的数据集。
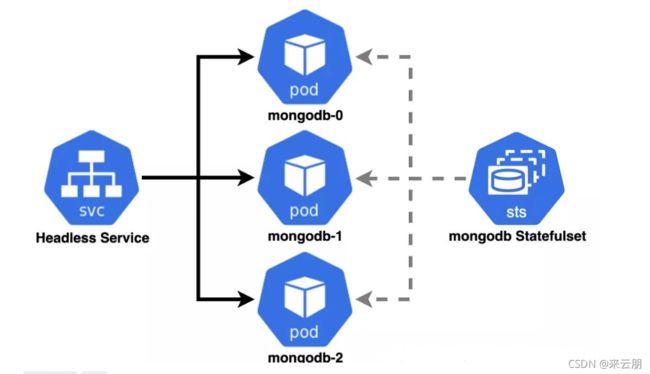
为了能够将控制台应用程序连接到 MongoDB 副本集,我们使用 MongoDB C# 驱动程序,同时需要显式定义三个 Pod 的地址。
我们用 Headless Service 解决这个问题。假定 MongoDb Pod 都带有 app=mongodb 标签,该标签可以在 Headless Service 中用于选择 Pod。我们定义的 Headless Service 资源如下所示:

通过将 clusterIp 设置为"none",我们告诉 Kubernetes 将此 Service 视为 Headless Service。由于我们定义了名称和命名空间,因此可以推断出 DNS 名称。我们在集群内部使用 mongodb-headless-service.infrastructure.svc.cluster.local 或 mongodb-headless-service.infrastructure 作为地址与 Service 进行通信。
接下来让我们来执行 DNS 查询,以检索连接 Pod 的 IP 地址。Dns.GetHostAddresses 方法位于 System.Net 命名空间中,可帮助我们执行该 DNS 查询并返回 IP 地址数组。它需要一个主机名或 IP 地址。最后,我们可以使用 MongoDB 创建连接字符串(connection string)。代码如下:

通过该解决方案,我们可以动态创建连接字符串,其主要优点是,在必须扩展数据库集群时,我们不必手动更改连接字符串。
注意:MongoDB 确实通过 DNS 实现了类似的服务发现过程,只需定义 Headless Service 的 DNS 名称即可,这样我们就不必自己生成连接字符串。
nodePort,targetPort,port
Kubernetes中的nodePort,targetPort,port的区别和意义(转)
原文https://blog.csdn.net/u013760355/article/details/70162242
https://blog.csdn.net/xinghun_4/article/details/50492041
1. nodePort
外部机器可访问的端口。
比如一个Web应用需要被其他用户访问,那么需要配置type=NodePort,而且配置nodePort=30001,那么其他机器就可以通过浏览器访问scheme://node:30001访问到该服务,例如http://node:30001。
例如MySQL数据库可能不需要被外界访问,只需被内部服务访问,那么不必设置NodePort
2. targetPort
容器的端口(最根本的端口入口),与制作容器时暴露的端口一致(DockerFile中EXPOSE),例如docker.io官方的nginx暴露的是80端口。
docker.io官方的nginx容器的DockerFile参考https://github.com/nginxinc/docker-nginx
3. port
kubernetes中的服务之间访问的端口,尽管mysql容器暴露了3306端口(参考https://github.com/docker-library/mysql/的DockerFile),但是集群内其他容器需要通过33306端口访问该服务,外部机器不能访问mysql服务,因为他没有配置NodePort类型
服务中的3个端口设置
这几个port的概念很容易混淆,比如创建如下service:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: app1
name: app1
namespace: default
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
nodePort: 30062
selector:
name: app1
port
The port that the service is exposed on the service’s cluster ip (virsual ip). Port is the service port which is accessed by others with cluster ip.
即,这里的port表示:service暴露在cluster ip上的端口,:port 是提供给集群内部客户访问service的入口。
nodePort
On top of having a cluster-internal IP, expose the service on a port on each node of the cluster (the same port on each node). You’ll be able to contact the service on any:nodePortaddress. So nodePort is alse the service port which can be accessed by the node ip by others with external ip.
首先,nodePort是kubernetes提供给集群外部客户访问service入口的一种方式(另一种方式是LoadBalancer),所以,:nodePort 是提供给集群外部客户访问service的入口。
targetPort
The port on the pod that the service should proxy traffic to.
targetPort很好理解,targetPort是pod上的端口,从port和nodePort上到来的数据最终经过kube-proxy流入到后端pod的targetPort上进入容器。
port、nodePort总结
总的来说,port和nodePort都是service的端口,前者暴露给集群内客户访问服务,后者暴露给集群外客户访问服务。从这两个端口到来的数据都需要经过反向代理kube-proxy流入后端pod的targetPod,从而到达pod上的容器内。
When a client connects to the VIP the iptables rule kicks in, and redirects the packets to the serviceproxy’s own port (random port). The service proxy chooses a backend, and starts proxying traffic from the client to the backend. This means that service owers can choose any port they want without risk of collision.The same basic flow executes when traffic comes in through a nodePort or through a LoadBalancer, though in those cases the client IP does get altered.