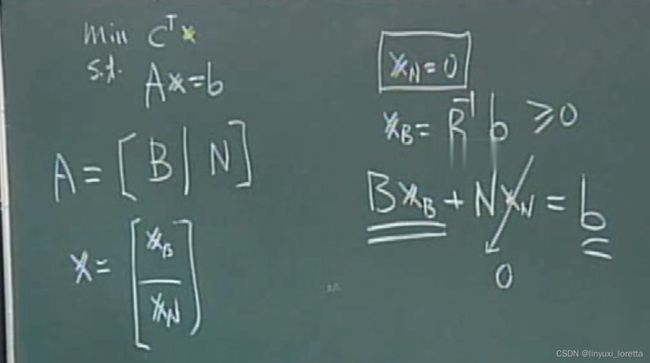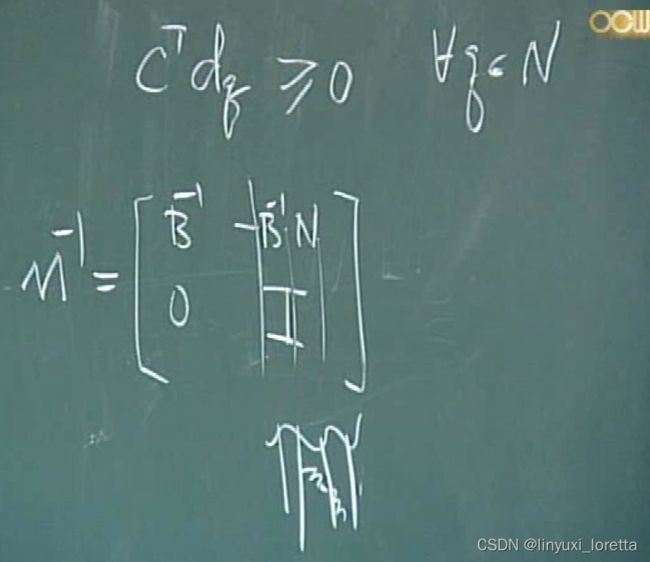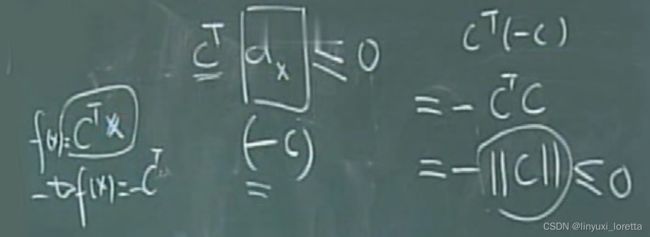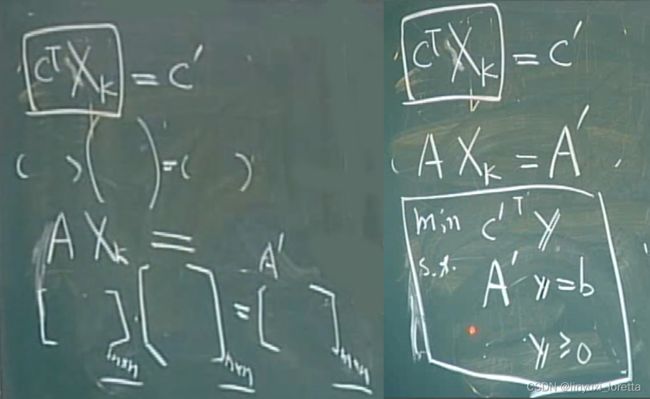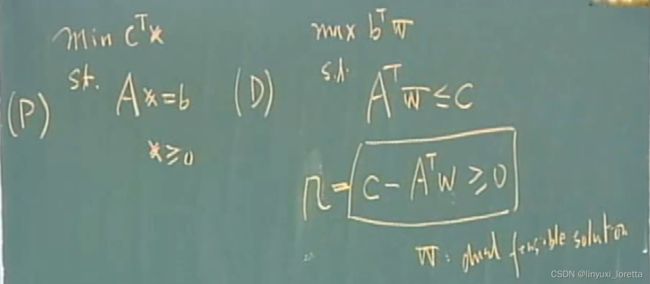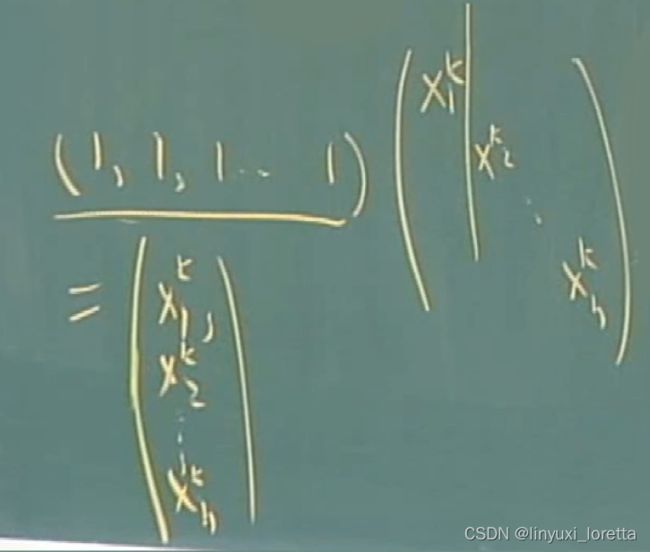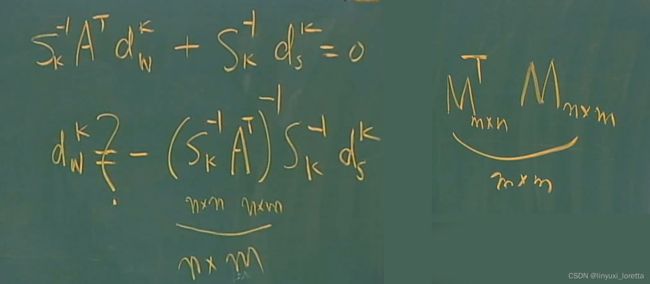内点法(方述诚 笔记5
interior point method
motivation:大型计算时
不是第一个多项式时间算法,
如果看到很好的方向,可以直接过去,(沿边走、方向被限制),但是看多个方向,计算量增加
Key knowledge • 1.Who is in the interior? - Initial solution • 2. How do we know a current solution is optimal? - Optimality condition • 3. How to move to a new solution? - Which direction to move? (good feasible direction) - How far to go? (step-length)
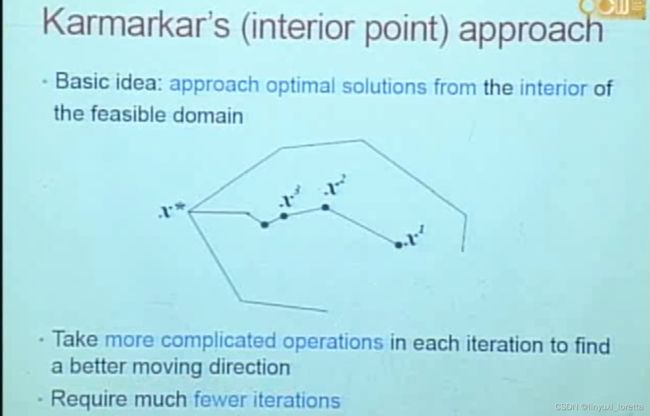
good enough 时,到边附近足够多,就跳上边界点,进化purification(identify谁是nbv 设为0)
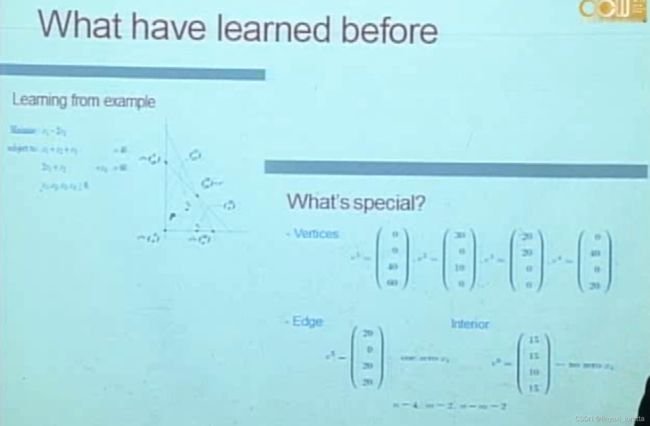
1. Who is in the interior?
2. How do we know a current solution is optimal?
in simplex method:
Q2 - How do we know a current solution is optimal?
• Basic concept of optimality:
A current feasible solution optimal if and only if
no feasible direction at this point is a good direction.
• In other words, “every feasible direction is not a good direction to move!”
在该点,能走的都不是好方向
Feasible direction • In an interior-point method, a feasible direction at a current solution is a direction allows it to take a small movement while staying to be interior feasible. 本身是一个interior feasible solution - There is no problem to stay interior if the step-length is small enough. - To maintain feasibility, we need
移动一点点,linear constraint不feasible 才能约束
A矩阵作用在向量上 =0,数学上叫做 向量落在矩阵A的零空间里,
Good direction • In an interior-point method, a good direction at a current solution is a direction towards it to a new solution with a lower objective value. • Observations:
Optimality check
principle:
3. How to move to a new solution?
- Which direction to move? (good feasible direction)
沿着负梯度方向,会降低objective(steepest descent Algorithm for negative gradient method最速下降法)
梯度=0时,linear objective func. =0,每点都是optimal(feasible solution就是optimal solution)
二次凸优化问题
project mapping 是 把一个好的方向(-c),投到一个可行的方向(N(A))里
- How far to go? (step-length)
we may use the “minimum ratio test" to determine the step-length. Observation: - when is close to the boundary, the step-length may be very small. Question: then what?
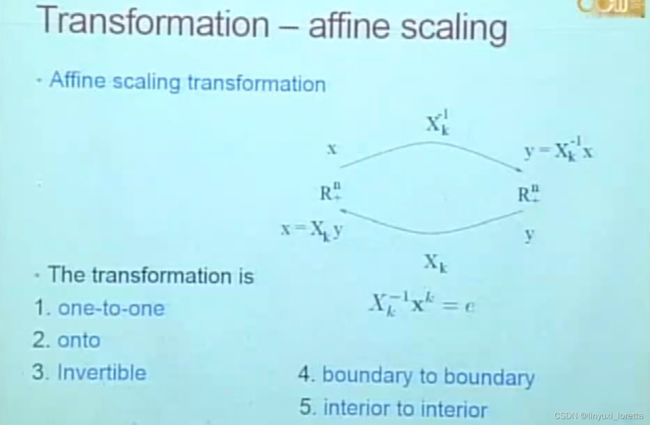
primal affine scaling algorithm
仿射几何
re-scale,to 中心, how?
matrix 作用在原来的空间上,就到了(y1,y2,y3,y4)空间
线性尺度变换 affine scaling。 原来的点,变成矩阵,take inverse
transformation ---- 用的mapping ,从第一象限送到第一象限
几何是重新copy,只不过是用不同的坐标来写
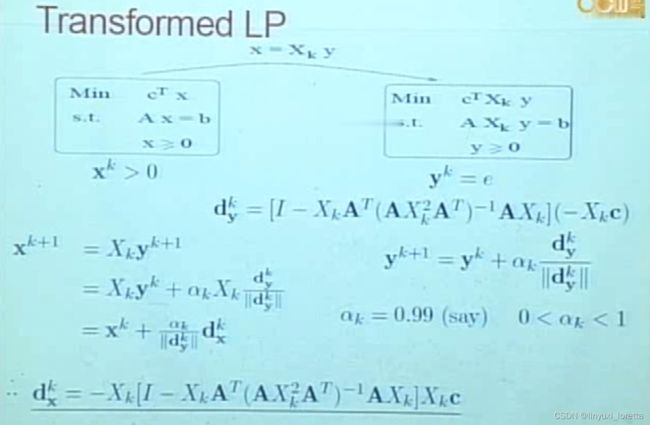
在y空间里不仅仅可以走1步:
----- dual information
dual slack, 经过尺度变换回来,得到方向
性质2、3: good feasible direction
在N()里
内积
性质4: =0 ,没有方向可以移动了。。 则 保证已经optimal
reduced cost
内点法 基本精神:从可行域内部,在每一步寻找方向上花多一些时间,不过可以快速达到optimal
How to find an initial interior solution?
• Like the simplex method, we have - Big M method - Two-phase method (to be discussed later!)
convergence 收敛到
super-linear rate , 连Newton method都赶不上(至少是quadratic convergence,收敛速度比较快)
may be sensitive to primal degeneracy. 太靠近边时,会被trap住,
在一个等高线(value 相等)上找点,只是多一个constraint,
到边,至少有一个component =0, 越靠边,-logx 越大,barrier
objective func. non-linear,解决:project negative gradient to the null space of constraint
μ---> ∞, --->
这个问题可以用primal affine scaring方法做,
Dual affine scaling algorithm
w^k---> w^k+1 在w space里找方向
s^k---> s^k+1 在s space里找方向
一起移,方向不一样,步长一样
Key knowledge Dual scalling (centering) Dual feasible direction Dual good direction — increase the dual objective value Dual step-length Primal estimate for stopping rule
Performance of dual affine scaling
• No polynomial-time proof! 只有convergence proof • Computational bottleneck 越degenerate越多0,invert就无穷大,越不精准 primal degenerate时,performance不好 • Less sensitive to primal degeneracy and numerical errors, but sensitive to dual degeneracy. - Improves dual objective value very fast, but attains primal feasibility slowly.不解完没有primal feasible
ordinary differential equation O.D.E.常微分方程
instead of 一步一步走,可以光滑的过去, iteration可以减少一半
比较stable,鲁棒 large-scale时,
primal-dual affine:
需要画出primal-dual的 trajectory弹道、轨迹,然后用Newton method follow 这个trajectory,这个方法又叫path following