【Vue2】Vuex 的使用
Vuex 简介
- Vuex 是官方提供的一个插件,用于集中式管理组件共用的数据
- 使用 Vuex 后,任何组件之间都可以进行通信
- Vuex 会将数据存储到 store (仓库) 中,供所有组件使用
- Vuex 的数据存储是响应式的,当组件从 store 中获取并改变数据时,模版会被重新渲染
-
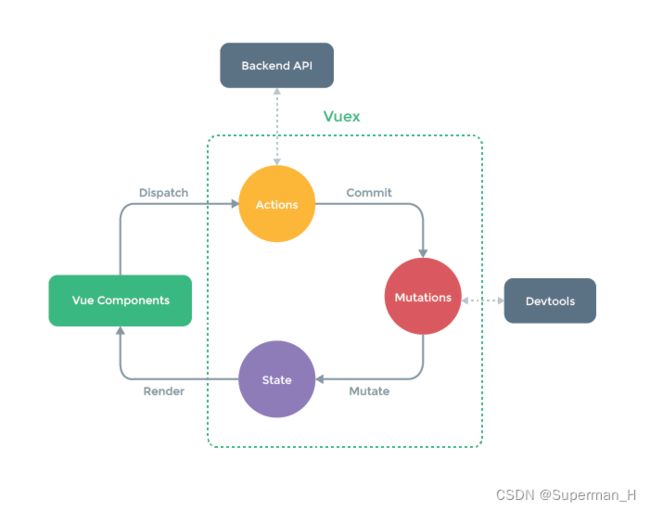
State (状态):存储数据。存储的数据用于 Render(渲染) Vue Components(组件)
-
Vue Components (组件):就是页面显示的内容。与用户交互,将数据 Dispatch(发送) 给 Actions
-
Actions (行动):处理交互行为,包括 [同步] & [异步]。将数据 Commit(提交) 到 Mutations
Backend API (后端 API):与前端进行数据交互
-
Mutations (变化):修改 State 中的数据,尽可能不做逻辑处理,只处理 [同步] 操作
如果只有 [同步] 操作,则 Vue Components 可以直接操作 Mutations,进而修改 State 里面的数据Devtools (开发者工具):记录 Mutations 的动作
Vuex 的使用
1. 下载 vuex 插件:
npm i vuex
- vuex3 对应 vue2、vuex4 对应 vue3
- 下载指定版本:
npm i vuex@3
2. 创建 store 文件
- 创建 @/store/index.js 文件
- 配置 store 文件,即 @/store/index.js 文件:
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
// 该指令必须在 store 创建之前执行
Vue.use(Vuex);
// Actions(行动): 处理交互行为
const actions = {
// context: 简化版的 store; value: 发送过来的数据
changeDispatch(context, value) {
console.log("actions", context, value);
// 将数据 commit 给 mutations
// 设置 2 个实参: commit 中的方法名 & 发送的数据
context.commit("changeCommit", value);
},
};
// Mutations(变化): 修改 state 中的数据
const mutations = {
// state: 存储的数据; value: 发送的数据
changeCommit(state, value) {
console.log("mutations", state, value);
// 修改 state 中存储的数据
state.name = value;
// 修改后,页面会重新渲染
},
};
// State: 用于存储数据
const state = { name: "superman" };
// 创建并导出 store
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
});
- Vue 中 代码的执行顺序:先执行
import进来的文件,然后再执行当前文件!!!
就是说,即使import语句在后面,也会优先执行!!
3. 在入口文件 main.js 中注册 store 文件
import Vue from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import store from "./store"; // 引入 store 文件
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
store, // 注册 store
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount("#app");
注册完 store 文件后,组件实例身上就会有 $store 属性,可通过 $store 属性获取并修改 store 中存储的数据啦
<template>
<div>
<p>name: {{ $store.state.name }}p>
<button @click="changeName">点击修改 state 中的数据button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
changeName() {
// 在组件中 将数据 dispatch 给 Actions
// 传入 2 个实参: dispatch 中的方法名 & 发送的数据
this.$store.dispatch("changeDispatch", "superVue");
},
},
};
script>
建议 [this.]$store.state.XXX 放在计算属性中:
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>name: {{ getName }}p>
<button @click="changeName">点击修改 state 中的数据button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
changeName() {
// 在组件中 将数据 dispatch 给 Actions
// 传入 2 个实参: dispatch 中的方法名 & 发送的数据
this.$store.dispatch("changeDispatch", "superVue");
},
},
computed: {
getName() {
return this.$store.state.name;
},
},
};
script>
对于同步操作
- 如果只有同步操作,Vue Components 可以直接将数据 commit 到 Mutations,进而处理 State 里面存储的数据
- 当然,也可以一步一步来:Vue Components — Dispatch → Actions — Commit → Mutations
<template>
<div id="app">
<p>name: {{ getName }}p>
<button @click="changeName">点击修改 state 中的数据button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
changeName() {
// 在组件中 将数据 commit 给 Mutations
// 传入 2 个参数: commit 中的方法名 & 发送的数据
this.$store.commit("changeCommit", "superVue");
},
},
computed: {
getName() {
return this.$store.state.name;
},
},
};
script>
一些个 summary
- 如果每个组件中操作数据的逻辑代码一样,可以将代码直接写在 Vuex 的 Actions 中
- Vue Components 中获取 State 中的数据:
{{$store.state.属性名}}||this.$store.state.属性名 - Vue Components 通过
this.$store.dispatch("actions事件名"[, 数据])执行同步 / 异步操作 - 同步代码修改 state 中的数据:
Actions 中:通过context.commit("mutations事件名"[, 数据])执行同步操作
Vue Components 中:也可通过this.context.commit("mutations事件名"[, 数据])执行同步操作
getters
- 用于对 state 中的数据进行加工,类似组件中的计算属性 computed
- Vue Components 获取 getters 中的数据:
[this.]$store.getters.属性名 - 当前仓库的 state 会作为 getters 方法的第 1 参数传入
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const actions = { };
const mutations = { };
// 设置 getters 对象
const getters = {
// state 会作为第 1 参数传入!!!
gettersArr(state) {
return state.arr.filter(item => {
if (item.id % 2 == 0) return item;
});
},
};
const state = {
arr: [
{ id: 0, name: "JS" },
{ id: 1, name: "Java" },
{ id: 2, name: "Python" },
{ id: 3, name: "C++" },
],
};
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
getters,
});
<template>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item of computedArr" :key="item.id">
{{ item.id }}--{{ item.name }}
li>
ul>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
computedArr() {
// 在组件中获取 getters 中的数据
return this.$store.getters.gettersArr;
},
},
};
script>
辅助函数
每次在模板中访问 store 文件中的数据 / 方法时,都需要用一大串代码获取 (eg: [this.]$store.dispatch()),非常不方便,此时我们可以使用辅助函数
mapState
- mapState 可以帮助我们生成计算属性,方便我们获取 state 中的数据
- mapState 的参数可以是 [对象] / [数组]
<template>
<div class="app">
<p>name: {{ staName }}p>
<p>gender: {{ staGender }}p>
<p>age: {{ staAge }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState } from "vuex"; // 引入 mapState
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
// 参数是对象: 属性名为相当于 computed 的属性名,属性值为 state 对象的属性名
...mapState({ staName: "name", staGender: "gender", staAge: "age" }),
// 因为 mapState 返回的是一个对象,所以要用 ... 将其与 computed 合并
},
};
script>
- mapState 的参数是对象,当该对象的属性值与属性名一样时,可以使用数组作为参数
<template>
<div class="app">
<p>name: {{ name }}p>
<p>gender: {{ gender }}p>
<p>age: {{ age }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState } from "vuex"; // 引入 mapState
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
// 使用数组作为参数
...mapState(["name", "gender", "age"]),
// 相当于
// ...mapState({ name: "name", gender: "gender", age: "age" }),
// 注意: 这种情况下,不能使用 ES6 的对象简写,因为属性值是字符串,不是变量
},
};
script>
上例的 store 文件:
import Vuex from "vuex";
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const actions = {};
const mutations = {};
const state = {
name: "superman",
gender: "male",
age: 21,
};
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
});
mapGetters
- mapGetters 可以帮助我们生成计算属性,方便我们获取 getters 中的数据
- mapGetters 的参数可以是 [对象] / [数组]
<template>
<div class="app">
<h1>Apph1>
<ul>
<li v-for="item of computedArr" :key="item.id">
{{ item.id }} -- {{ item.name }}
li>
ul>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from "vuex"; // 引入 mapGetters
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
// 参数是对象:属性名相当于 computed 的属性名,属性值为 getters 对象的属性名
...mapGetters({ computedArr: "computedArr" })
// 因为 mapGetters 返回的是一个对象,所以要用 ... 将其与 computed 合并
},
};
script>
- mapGetters 的参数是对象,当该对象的属性值与属性名一样时,可以使用数组作为参数
computed: {
// 使用数组作为参数
...mapGetters(["computedArr"])
// 相当于
// ...mapGetters({ computedArr: "computedArr" }),
// 注意: 这种情况下,不能使用 ES6 的对象简写,因为属性值是字符串,不是变量
},
上例的 store 文件:
import Vuex from "vuex";
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const actions = {};
const mutations = {};
const getters = {
computedArr(state) {
return state.arr.filter(item => {
if (item.id % 2 == 0) return item;
});
},
};
const state = {
arr: [
{ id: 0, name: "JS" },
{ id: 1, name: "Java" },
{ id: 2, name: "Python" },
{ id: 3, name: "C++" },
],
};
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
getters,
});
mapMutations
- mapMutations 帮助我们生成对应方法,方法中会调用 commit 联系 Mutations
<template>
<div class="app">
<p>num:{{ num }}p>
<button @click="add">addbutton>
<button @click="reduce">reducebutton>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations } from "vuex"; // 引入 mapState、mapMutations
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
...mapState(["num"]),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations({ add: "muAdd", reduce: "muReduce" }),
// if 属性名 == 属性值,参数可以写成数组形式
// ...mapMutations(["add", "reduce"]),
// 相当于
// ...mapGetters({ add: "add", reduce: "reduce" }),
// 注意: 这种情况下,不能使用 ES6 的对象简写,因为属性值是字符串,不是变量
},
};
script>
import Vuex from "vuex";
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const actions = {};
const mutations = {
muAdd(state, val = 1) {
state.num += val;
},
muReduce(state, val = 1) {
state.num -= val;
},
};
const state = { num: 21 };
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
});
此时,如果想传入参数,可以在调用函数时一并传入
<template>
<div class="app">
<p>num: {{ num }}p>
<button @click="add(2)">add 2button>
<button @click="reduce(2)">reduce 2button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
...mapState(["num"]),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations({ add: "muAdd", reduce: "muReduce" }),
},
};
script>
或者,调用自身方法,再调用 mapMutations 的方法、并传入参数
<template>
<div class="app">
<p>num: {{ num }}p>
<button @click="myAdd">add 2button>
<button @click="myReduce">reduce 2button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
...mapState(["num"]),
},
methods: {
// 在自身方法中调用 mapMutations 的方法、并传入参数
myAdd() {
this.add(2)
},
myReduce() {
this.reduce(2)
},
...mapMutations({ add: "muAdd", reduce: "muReduce" }),
},
};
script>
mapActions
- mapActions 帮助我们生成对应方法,方法中会调用 dispatch 联系 Actions
<template>
<div>
<p>num: {{ num }}p>
<button @click="add(2)">add 2button>
<button @click="myReduce">reduce 2button>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
...mapState(["num"]),
},
methods: {
// 在自身方法中,调用 mapActions 中的方法并传入参数
myReduce() {
this.reduce(2);
},
...mapActions({ add: "acAdd", reduce: "acReduce" }),
},
};
script>
import Vuex from "vuex";
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.use(Vuex);
const actions = {
acAdd(context, value) {
context.commit("muAdd", value);
},
acReduce(context, value) {
context.commit("muReduce", value);
},
};
const mutations = {
muAdd(state, value) {
state.num += value;
},
muReduce(state, value) {
state.num -= value;
},
};
const state = { num: 21 };
export default new Vuex.Store({
actions,
mutations,
state,
});
获取页面数据
- 通过钩子函数
mounted调用 Actions 的方法 - 在 Actions 中发送 axios 获取页面所需数据,并调用 Mutations 的方法
- 在 Mutations 中修改 State 的数据,以存储 axios 获取到的数据
模块化 store 文件
- 创建多个 store 文件,每个文件负责指定模块功能的数据及其操作方法
- 将模块化后的 store 文件,导入到主 store 文件,再集中导出
store
---- index.js
---- count.js // 负责数据的增减
---- show.js // 负责数据的显示
count.js
export default {
namespaced: true, // 设置 namespaced,生成命名空间
// 如果不设置 namespaced,state 中只有 [数据] 被分模块
// state 中的 [方法] 以及 [getters 中的数据] 都还是全局数据
mutations: {
add(state, value) {
state.num += value;
},
reduce(state, value) {
state.num -= value;
},
},
state: { num: 0 }
};
show.js
export default {
namespaced: true, // 设置 namespaced 生成命名空间
state: {
show: 1,
name: "superman",
arr: [
{ id: 0, name: "JS" },
{ id: 1, name: "Java" },
{ id: 2, name: "Python" },
{ id: 3, name: "C++" },
],
},
actions: {
acShow(context) {
if (context.state.show) context.commit("muShow", 0);
else context.commit("muShow", 1);
},
},
mutations: {
muShow(state, value) {
state.show = value;
},
},
getters: {
computedArr(state) {
return state.arr.filter(item => {
if (item.id % 2 == 0) return item;
});
},
},
};
index.js
- 将功能模块导入主 store 文件,再在此集中导出
- 注意:只有主 store 文件需要导入 vue 和 vuex
import Vuex from "vuex";
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.use(Vuex);
// 引入模块
import countAbout from "./count";
import showAbout from "./show";
export default new Vuex.Store({
// 模块化
modules: {
countAbout,
showAbout,
},
});
App.vue:
- 获取 state 中的数据:
[this.]$store.state.模块名.属性名 - 获取 getters 中的数据:
[this.]$store.getters['模块名/属性名'] - 调用方法:
this.$store.commit("模块名/方法名"[, 数据])/this.$store.dispatch("模块名/方法名"[, 数据]);
<template>
<div class="app">
<p>num: {{ $store.state.countAbout.num }}p>
<p>num: {{ num }}p>
<button @click="add">add 10button>
<button @click="reduce">reduce 10button>
<hr />
<ul>
<li v-for="item of $store.getters['showAbout/computedArr']" :key="item.id">
{{ item.id }} -- {{ item.name }}
li>
ul>
<button @click="show">隐藏 / 显示button>
<p :style="{ opacity: $store.state.showAbout.show }">
name: {{ $store.state.showAbout.name }}
p>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
num() { return this.$store.state.countAbout.num },
},
methods: {
add() {
this.$store.commit("countAbout/add", 10); // 模块化后,调用方法需要添加模块名!!!!!!
},
reduce() {
this.$store.commit("countAbout/reduce", 10);
},
show() {
this.$store.dispatch("showAbout/acShow");
},
},
};
script>
如果使用辅助函数的话,则第 1 参数为 模块名,第 2 参数才是对应的 属性名:
- 获取 state 中的数据:
mapState("模块名", ["属性名1", "属性名2"]) - 获取 getters 中的数据:
mapGetters("模块名", ["属性名1", "属性名2"]) - 调用方法:
mapMutations("模块名", ["方法名1", "方法名2"])/mapActions("模块名", ["方法名1", "方法名2"])
<template>
<div class="app">
<p>num: {{ num }}p>
<button @click="add(2)">add 2button>
<button @click="reduce(2)">reduce 2button>
<hr />
<ul>
<li v-for="item of computedArr" :key="item.id">
{{ item.id }} -- {{ item.name }}
li>
ul>
<button @click="acShow">隐藏 / 显示button>
<p :style="{ opacity: show }">name: {{ name }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
export default {
name: "App",
computed: {
...mapState("countAbout", ["num", "name"]),
...mapState("showAbout", ["name", "show"]),
...mapGetters("showAbout", ["computedArr"]),
},
methods: {
...mapActions("countAbout", { setData: "setData" }), // 使用对象式写法
...mapMutations("countAbout", ["add", "reduce"]), // 使用数组式写法
...mapActions("showAbout", { acShow: "acShow" }),
},
};
script>
一些报错
Uncaught TypeError: (0 , vue__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_20__.reactive) is not a function版本兼容问题,vue2 使用 vuex3;vue3 使用 vuex4
[vuex] unknown action type: XXX
模块化 store 时,调用 dispatch 等方法,需要添加模块名