Java---阶段项目----五子棋
Java---阶段项目----五子棋
- 需求说明
- 技术实现
- 棋盘制作
- 完整代码

需求说明
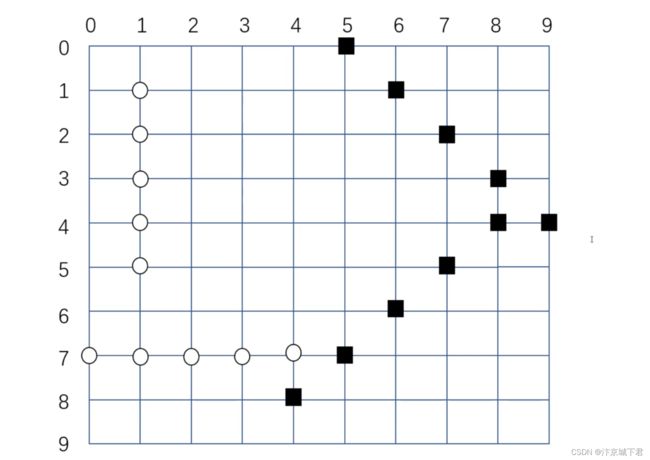
五子棋棋盘为一个10×10的方格,五子棋玩家共为两个(A,B),A在棋盘上落子后,B再落子,依次往复,直到一方胜利或者棋盘空间用完为止,判断胜利的条件就是一条线或者斜线上同时存在A或者B的连续的5颗棋子
如图:
技术实现
静态变量:
- 语法:
public static 数据类型 变量名 = 变量值;
不加static的就是非静态变量
- 解释说明
静态变量只能定义在类中,不能定义在方法中。
静态变量可以在static修饰的方法中使用,也可以在非静态的方法中访问
主要解决在静态方法中不能访问非静态的变量。
public class study { //类
//静态变量只能定义在类中,不能定义在方法中
public static String name = "张三";
public static void main(String[] args) { //方法
System.out.println(name); //可以调用
}
}
静态方法:
- 语法
public static 返回值类型 方法名(){
}
- 解释说明
静态方法就相当于一个箱子,只是箱子里面放的是代码,需要用这些代码的时候,直接把箱子放在指定位置即可
public class study { //类
public static void main(String[] args) { //方法
show();
}
public static void show(){
System.out.println("张三");
System.out.println("男");
System.out.println("20");
}
}
输出:
张三
男
20
棋盘制作
1.制作棋盘
- 使用输入法中的制表符在控制台直接打印出棋盘,然后寻找落子位置的特征
- 利用二维数组重新制作棋盘
public class study {
public static char[][] chess_map={
{'┌','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┐'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'└','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┘'}
};
public static String row = "────";
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9");
for(int i=0;i<chess_map.length;i++) {//外层循环控制行
System.out.print(i);
for(int j=0;j<chess_map[i].length;j++){//内层循环控制列
if(j==chess_map[i].length-1){//最后一行不打印——
System.out.print(chess_map[i][j]);
}else{
System.out.print(chess_map[i][j]+row);
}
}
System.out.println();
if(i<chess_map.length-1){//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
- 棋盘在玩家使用过程中会反复展示,需要使用方法来优化
把棋盘放在一个方法内,直接调用
2.落子
- 玩家A,B会交替落子
- 落子的位置必须是0~100之间的整数,且不能使用已经存在的棋子
public static char pieceA = '○';//玩家A的棋子
public static char pieceB = '■';//玩家B的棋子
public static void main(String[] args) {
draw_map();
int sum = chess_map.length*chess_map[0].length;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<sum;i++){
System.out.println(i%2==0 ? "玩家A落子:":"玩家B落子:");
int position;
while(true){
//保证落子成功
if(sc.hasNextInt()){//判断Scanner中是否有输入的数据
position = sc.nextInt();
if(position >= 0 && position < sum){
char currentpiece = (i%2==0) ? pieceA : pieceB;
int row = position / chess_map.length;//位置除以棋盘数组长度得到行号
int col = position % chess_map[0].length;//位置取模棋盘数组的总列数得到列号
if(chess_map[row][col]==pieceA || chess_map[row][col]==pieceB) {
System.out.println("该位置已经有棋子,请重新输入:");
continue;
}else {
chess_map[row][col] = currentpiece;
break;
}
}else{
System.out.println("非法输入");
}
}else{
System.out.println("非法输入");
sc.next();//将Scanner中的数据取出来,防止死循环
}
}
//落子成功后棋盘需要重新打印
draw_map();
}
}
- 落子完成后,需要校验是否获胜
- 棋盘使用完毕还未分出胜负,需要提示
for (int m = 0; m < chess_map.length; m++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chess_map[0].length; j++) {
//第一种,水平方向
boolean case1 = (j + 4 < chess_map[0].length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 1] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 2] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 3] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 4] == currentpiece;
//第二种,垂直方向
boolean case2 = (m + 4 < chess_map.length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 1][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 2][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 3][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 4][j] == currentpiece;
//第三种,135°角
boolean case3 = (i + 4 < chess_map.length)
&& (j + 4 < chess_map[0].length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 1][j + 1] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 2][j + 2] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 3][j + 3] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 4][j + 4] == currentpiece;
//第四种,45°角
boolean case4 = (m > 4) && (j + 4 < chess_map[0].length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 1][j + 1] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 2][j + 2] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 3][j + 3] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 4][j + 4] == currentpiece;
if (case1 || case2 || case3 || case4) {
System.out.println(m % 2 == 0 ? "玩家A胜利" : "玩家B胜利");
break outer;
}
}
}
i++;
}
if(i==100){
System.out.println("平局");
}
3.声音特效
- 为落子,非法落子及其获胜添加音效
public static void playAudio(String fileName){
URl url = Gobang.class.getResource(fileName);
AudioClip clip = Applet.newAudioClip(url);
clip.play();
try{
Thread.sleep(50L);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
}
完整代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class study {
public static char[][] chess_map={
{'┌','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┬','┐'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'├','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┼','┤'},
{'└','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┴','┘'}
};
public static String ro = "────";
public static char pieceA = '○';//玩家A的棋子
public static char pieceB = '■';//玩家B的棋子
public static int i = 0;//总次数
public static void main(String[] args) {
draw_map();
int sum = chess_map.length * chess_map[0].length;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
outer:
while(i<sum){
System.out.println(i % 2 == 0 ? "玩家A落子:" : "玩家B落子:");
char currentpiece = (i % 2 == 0) ? pieceA : pieceB;
// int position_row,position_col;
int position;
while (true) {
//保证落子成功
if (sc.hasNextInt()) {//判断Scanner中是否有输入的数据
// System.out.println("请输入行:");
// position_row = sc.nextInt();
// System.out.println("请输入列:");
// position_col = sc.nextInt();
position = sc.nextInt();
// if(position_row >= 0 && position_row < chess_map.length && position_col>=0 && position_col < chess_map[0].length){
if (position >= 0 && position < sum) {
int row = position / chess_map.length;//位置除以棋盘数组长度得到行号
int col = position % chess_map[0].length;//位置取模棋盘数组的总列数得到列号
// int row = position_row;
// int col = position_col;
if (chess_map[row][col] == pieceA || chess_map[row][col] == pieceB) {
System.out.println("该位置已经有棋子,请重新输入:");
continue;
} else {
chess_map[row][col] = currentpiece;
break;
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法输入");
}
} else {
System.out.println("非法输入");
sc.next();//将Scanner中的数据取出来,防止死循环
}
}
//落子成功后棋盘需要重新打印
draw_map();
for (int m = 0; m < chess_map.length; m++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chess_map[0].length; j++) {
//第一种,水平方向
boolean case1 = (j + 4 < chess_map[0].length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 1] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 2] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 3] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m][j + 4] == currentpiece;
//第二种,垂直方向
boolean case2 = (m + 4 < chess_map.length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 1][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 2][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 3][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 4][j] == currentpiece;
//第三种,135°角
boolean case3 = (i + 4 < chess_map.length)
&& (j + 4 < chess_map[0].length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 1][j + 1] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 2][j + 2] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 3][j + 3] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m + 4][j + 4] == currentpiece;
//第四种,45°角
boolean case4 = (m > 4) && (j + 4 < chess_map[0].length)
&& chess_map[m][j] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 1][j + 1] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 2][j + 2] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 3][j + 3] == currentpiece
&& chess_map[m - 4][j + 4] == currentpiece;
if (case1 || case2 || case3 || case4) {
System.out.println(m % 2 == 0 ? "玩家A胜利" : "玩家B胜利");
break outer;
}
}
}
i++;
}
if(i==100){
System.out.println("平局");
}
}
public static void draw_map () {
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9");
for (int i = 0; i < chess_map.length; i++) {//外层循环控制行
System.out.print(i);
for (int j = 0; j < chess_map[i].length; j++) {//内层循环控制列
if (j == chess_map[i].length - 1) {//最后一行不打印——
System.out.print(chess_map[i][j]);
} else {
System.out.print(chess_map[i][j] + ro);
}
}
System.out.println();
if (i < chess_map.length - 1) {//排除最后一行
System.out.println(" │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │");
}
}
}
}
