模版方法模式在 JDK 及 spring 源码中的引用
模版方法模式
模板方法模式是一种行为设计模式, 它在超类中定义了一个算法的框架, 允许子类在不修改结构的情况下重写算法的特定步骤。
更多有关于模版方法模式的介绍详见:https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/template-method
模版方法模式在 JDK 源码中的引用
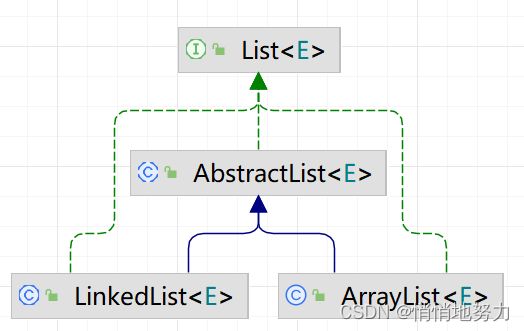
- 定义 List 接口,定义一些规范。
- 抽象类 AbstractList 实现 List 接口,写一些通用的实现。
- 子类 ArrayList, LinkedList 继承抽象类 AbstractList,写自己的具体实现。
List 接口
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
E get(int index);
E set(int index, E element);
void add(int index, E element);
E remove(int index);
// ...... 省略其他内容
}
List 接口的部分内容如上所示,定义了一些列表容器的规范,比如:获取容器中元素个数、是否为空、是否包含某个元素、获取某个索引位置对应元素、移除元素等方法。
AbstractList
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {
public boolean add(E e) {
add(size(), e);
return true;
}
abstract public E get(int index);
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// ...... 省略其他内容
}
ArrayList
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
private int size;
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
// ...... 省略其他内容
}
模板方法模式在 spring 源码中的应用
- 定义 Servlet 接口,定义一些规范。
- 抽象类 GenericServlet 实现 Servlet 接口,写一些通用的实现。
- 抽象类 HttpServlet 继承 GenericServlet 类,写一些有关 Http 请求的通用实现。
- 自定义子类继承抽象类 HttpServlet ,根据自己的业务处理 http 请求。

Servlet
public interface Servlet {
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
public String getServletInfo();
public void destroy();
}
GenericServlet
将 ServletConfig 由局部变量变为全局变量
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig,
java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private transient ServletConfig config;
public GenericServlet() {
// NOOP
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
// NOOP by default
}
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return getServletConfig().getServletContext();
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return config;
}
// 省略其他代码......
}
HttpServlet
重写核心的 service 方法,完成通用逻辑的编写:根据请求方式调用相应的 doGet, doPost 等方法。
定义 doGet, doPost 等方法,让子类重写。如果请求方式为 GET,但子类没有重写 doGet 方法,则会执行父类(即该类 HttpServlet)的 doGet 方法:通用逻辑为返回 400 或 405 异常。
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
// ...... 省略部分代码
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
// 省略其他代码......
}
自定义类 HelloServlet
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Writer writer = resp.getWriter();
writer.write("hello SimpleServletHandlerAdapter!");
writer.flush();
}
}