Pytorch搭建UNet网络
Pytorch搭建UNet网络
- 前言
-
- 原理
- 代码实现
前言
学习一下经典的语义分割网络U-Net
原理
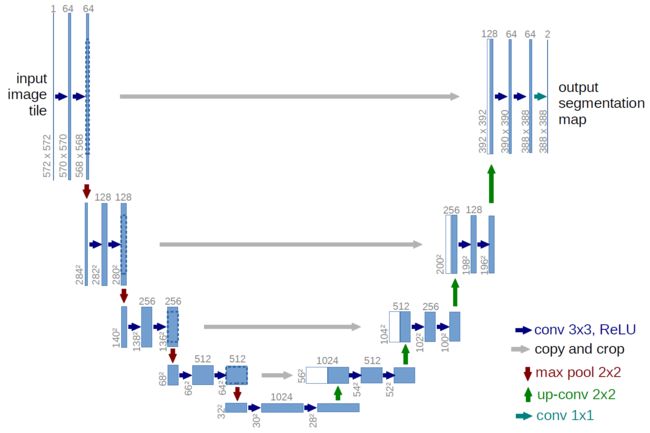
介绍一下UNet的网络结构:
UNet是一个U型的网络结构,左侧的半个U是特征提取网络也就是编码网络,右侧的半个U是解码网络。在左侧和右侧之间将对应的特征图按照通道进行连接(concatenate),从而实现不同层次特征图之间的一种信息融合。
特征提取网络是经典的VGG风格的网络,通过两或三个重复堆叠的3×3卷积层+ReLU层形成vgg_block,共5个vgg_block,每个vgg_block之间通过最大池化层进行下采样,使宽高减半。
解码网络的每一层先通过一个kernel_size为2×2,stride为2的转置卷积层进行上采样,使通道数减半、宽高加倍;接着与特征提取网络中对应的特征层按照通道进行连接;然后经过两个3×3卷积层+ReLU层。共4次上采样。
最后输出层通过1×1卷积层将通道数映射为所需类数,用softmax激活函数输出概率图。
UNet的好处:①浅层卷积关注纹理特征,深层网络关注本质的语义特征,UNet通过连接的方式兼顾两者②特征提取下采样会丢失一些边缘信息,而这无法通过上采样学习到,通过连接可以实现找回边缘信息,使边缘预测更精确。
代码实现
首先是下采样块,类似vgg_block。注意一般情况下图片和标签尺寸是一样的,所以这里卷积层里都用的padding=1,与图上略有不同。
class DownBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_convs, inchannels, outchannels, pool=True):
super(DownBlock, self).__init__()
blk = []
if pool:
blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
for i in range(num_convs):
if i == 0:
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(inchannels, outchannels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
else:
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(outchannels, outchannels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
blk.append(nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.layer = nn.Sequential(*blk)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layer(x)
接着是上采样块,先通过一个kernel_size为2×2,stride为2的转置卷积层进行上采样;接着与特征提取网络中对应的特征层进行连接;然后经过两个3×3卷积层+ReLU层。
class UpBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inchannels, outchannels):
super(UpBlock, self).__init__()
self.convt = nn.ConvTranspose2d(inchannels, outchannels, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inchannels, outchannels, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(outchannels, outchannels, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x1, x2):
x1 = self.convt(x1)
x = torch.cat([x2, x1], dim=1)
x = self.conv(x)
return x
整体UNet网络,5次下采样,4次上采样。
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nchannels=1, nclasses=1):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.down1 = DownBlock(2, nchannels, 64, pool=False)
self.down2 = DownBlock(3, 64, 128)
self.down3 = DownBlock(3, 128, 256)
self.down4 = DownBlock(3, 256, 512)
self.down5 = DownBlock(3, 512, 1024)
self.up1 = UpBlock(1024, 512)
self.up2 = UpBlock(512, 256)
self.up3 = UpBlock(256, 128)
self.up4 = UpBlock(128, 64)
self.out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, nclasses, kernel_size=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.down1(x)
x2 = self.down2(x1)
x3 = self.down3(x2)
x4 = self.down4(x3)
x5 = self.down5(x4)
x = self.up1(x5, x4)
x = self.up2(x, x3)
x = self.up3(x, x2)
x = self.up4(x, x1)
return self.out(x)