gRPC教程与应用
gRPC是是谷歌一个开源的跨语言的RPC框架,面向移动和 HTTP/2 设计。
grpc中文网
在 gRPC 里客户端应用可以像调用本地对象一样直接调用另一台不同的机器上服务端应用的方法,使得您能够更容易地创建分布式应用和服务。
gRPC 也是基于以下理念:定义一个服务,指定其能够被远程调用的方法(包含参数和返回类型)。在服务端实现这个接口,并运行一个 gRPC 服务器来处理客户端调用。
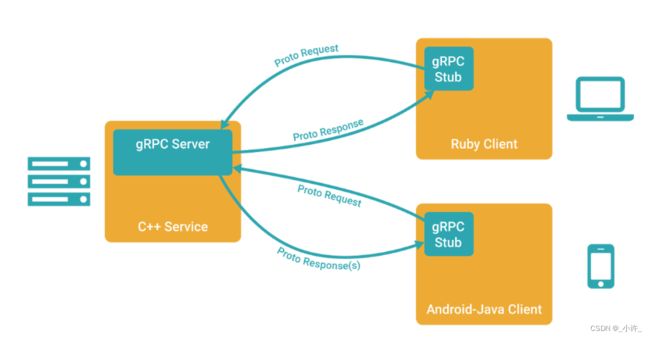
gRPC 默认使用 protocol buffers,这是 Google 开源的一套成熟的结构数据序列化机制。

protocol buffers能够生成RPC服务器,并使用proto文件来预先定义的消息格式。数据包是按照proto文件所定义的消息格式完成二进制码流的编码和解码。从而使基于RPC的服务器提供相关的接口,那么客户端通过服务端提供接口就可以访问服务器端的方法。
gRPC通过服务端-客户端方法来实现客户端直接访问服务端的方法。并以用户自定义的消息格式,完成字节的编码和解码。
gRPC 官方文档中文版
gRPC官网
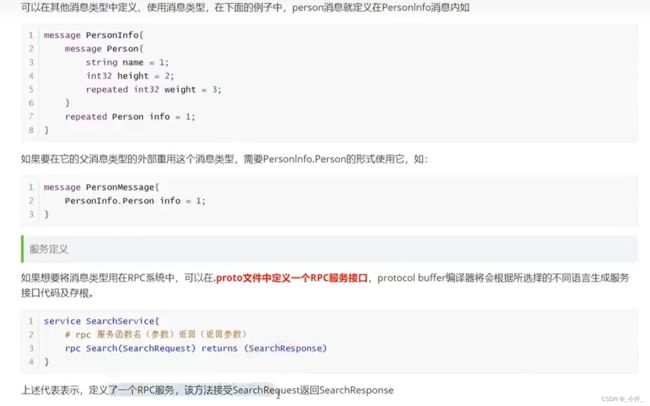
gRPC 通过 protocol buffers来定义接口,将方法或者类注册到服务中,客户端也是使用同样的接口,只要接口连接成功就可以调用注册进服务的接口。
protocol buffers =是跨语言的,有自己的语法,通过自身语法定义接口定义语言来定义服务方法,并整合到其他语言,将程序的方法绑定protocol buffers的接口,实现跨语言访问。
protocol buffers教程
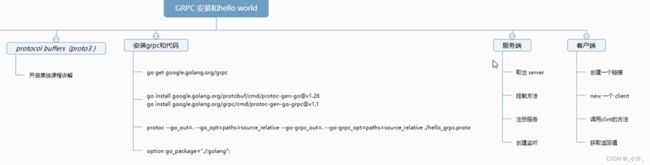
安装protocol compiler插件
以下步骤跟着教程来即可
本项目的gitee地址
go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@v1.28
go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@v1.2
如下图所示,在本机的GOPATH目录下下载了插件:
这两个插件是protocol buffer文件要使用的,用户将编译成对应语言的代码。这里是编译成go的代码。
了解rmi的可以知道该rpc只能在java中使用,这是由于rmi使用了java程序的接口,缺少扩展性,而protocol buffer则使用自身语法定义接口,并将接口绑定其他语言的方法,这样实现了语言的扩展性。
安装rpc服务器
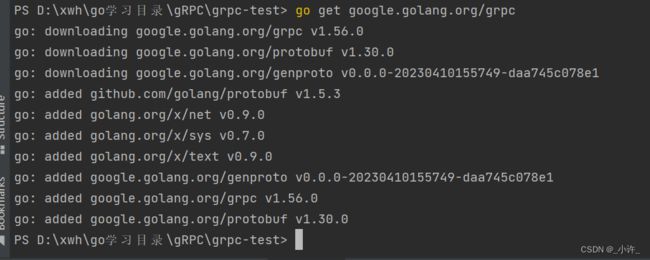
go get google.golang.org/grpc
安装go语言的rpc服务器
gRPC 在 Go 语言中的安装与简单实践
rpc服务的实现可能有很多库,很多实现方式,如官方rpc官网上也提供了github的库。如下,
编写protobuf规则
//proto语法版本
syntax = "proto3";
//编译为对应语言
//第一个参数是目录位置分号隔开,第二个参数是服务名称
//option java_package = "io.grpc.examples";
option go_package = "./;golang";
package helloworld;
// The greeter service definition.
//service定义接口(方法)
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
//message定义结构体或者类
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
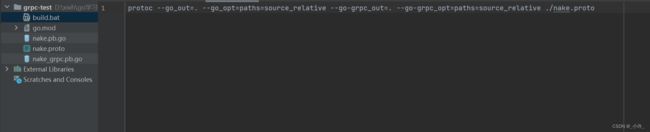
切换到proto文件目录并生成代码
protocol buffer文件以proto为后缀,切换到对应目录,执行插件。
protoc --go_out=. --go_opt=paths=source_relative --go-grpc_out=. --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative ./grpc-test/make.proto
protoc是插件命令,grpc-test/make.proto是proto文件位置。
到此go-rpc的服务端代码已经自动生成了(根据自定义的规则proto文件生成),接下来就是启动rpc服务器实例,将方法注册到服务器实例即可。
注意生成的文件一个是grpc.pb,一个是.pb前者是接口,后者是rpc服务器。
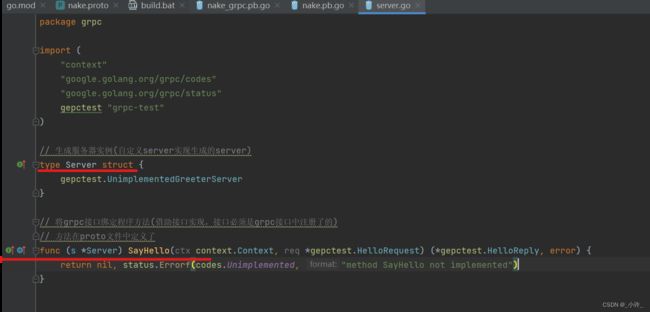
根据grpc.pc提供的类实现服务器实例:

只需要实现该结构体即可,实现其SayHello方法。自定义Server实现方法。
实现后注意前面有继承关系的ICON才算成功。
方法注册到服务器
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"grpc-test/pb"
"net"
)
// 生成服务器实例(自定义server实现生成的server)
type Server struct {
pb.UnimplementedGreeterServer
}
// SayHello 将grpc接口绑定程序方法(借助接口实现,接口必须是grpc接口中注册了的)
// 方法在proto文件中定义了
func (s *Server) SayHello(context.Context, *pb.HelloRequest) (*pb.HelloReply, error) {
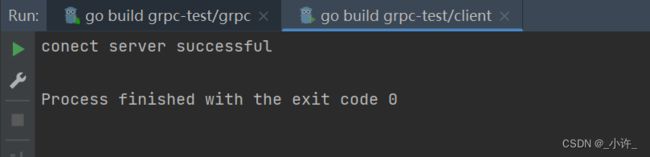
return &pb.HelloReply{Message: "conect server successful"}, nil
}
// 运行服务
func main() {
//基于tcp实现
listen, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1099")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("failed to listen", err)
}
//创建grpc服务
server := grpc.NewServer()
//*************** 关键 **********
//注册自定义方法
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(server, &Server{})
// *********************************
//启动服务
err = server.Serve(listen)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("failed to serve", err)
return
}
}
客户端连接服务端
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials/insecure"
"grpc-test/pb"
)
func main() {
//配置连连接参数(无加密)
dial, _ := grpc.Dial("localhost:1099", grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
defer dial.Close()
//创建客户端连接
client := pb.NewGreeterClient(dial)
//通过客户端调用方法
res, _ := client.SayHello(context.Background(), &pb.HelloRequest{Name: "xiaoxu"})
fmt.Println(res.GetMessage())
}
客户端连接后直接通关接口调用方法,服务器端也需要存在如下的两个文件。

客户端调用的是如下文件提供的接口,而改接口被rpc服务器封装,并在服务器端与服务器端方法绑定,grpc封装了传输的细节,因此使用是来就想调用本地方法一样方便。
案例gitee地址
原理剖析
grpc是rpc的一种具体实现方式,采用服务端和客户端通讯的方式,和HTTP的不同在于规避了许多无关部分,例如HTTP的b/c架构需要借助浏览器,因此远程调用时在程序中必须模拟浏览器访问再解析数据。而grpc直接实现了新的服务器,并允许用户自定义接口,在服务器中暴露这些接口,在程序中整合grpc服务器,然后将接口绑定到程序的方法,客户端在连接rpc服务器是调用接口,则会直接指向服务器程序的方法,因此就行在本地调用一样。
protocol buffer配置文件,定义接口规则,用于生成自定义的接口:
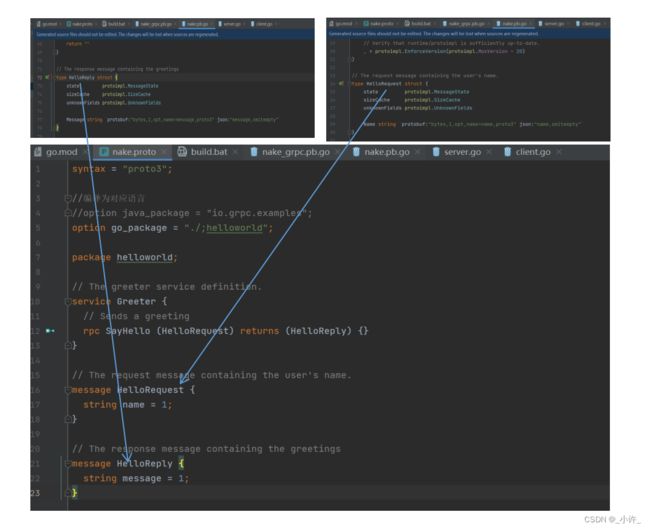
在.proto文件定义生成规则,在.pb文件生成定制化接口。
gprc的跨语言性
grpc是使用期本身的语法定义接口的,在上面的例子中使用了go语言,将接口绑定到go语言的接口中,那么如果将grpc的接口绑定到其他语言中也是可以使用的。
由于Go语言都是基于源码进行的,在其他语言中需要下载protobuf的工具包,帮助将proto的接口转换为对应语言的接口。
转换其他语言的接口主要在于命令不同:
option java_package = "com.zy.tutor"; // 生成的java文件的包名
option java_outer_classname = "xunjianProtos"; // 生成的java文件的类名
//插件生成命令
protoc --java_out . plateDetection.proto
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobufgroupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-javaartifactId>
<version>3.19.1version>
dependency>
grpc支持很多语言,不在一一赘述。
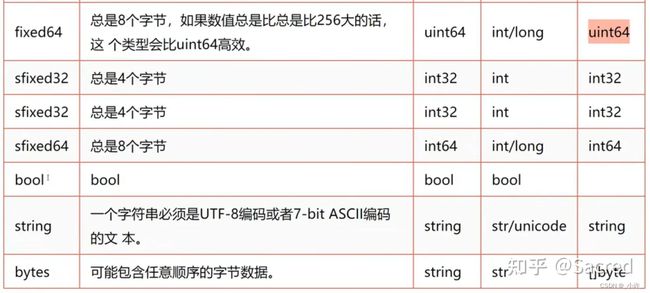
propto数据类型
每种语言都有自己的独特的数据类型,如java的了类,go的结构体,显然protobuf是无法满足所有的语言的数据结构的,因此一些特殊的数据结构需要转化。proto直接的数据结构如下:
参考自:proto文件详解感谢作者@Sacred
那么最复杂的数据类型只能序列化为STRING再反序列化了。
案例
- 下载protobuf插件和grpc工具包
略
- 定义proto文件约定接口
syntax = "proto3";
//编译为对应语言
//option java_package = "io.grpc.examples";
option go_package = "./;protoInterface";
package protoInterface;
// 定义接口
service Interface {
// 方法1
rpc GetProduct (Request) returns (Response) {}
// 方法2
rpc GetOrder (Request) returns (Response) {}
}
// 定义数据类型
message Request {
string paramString = 1;
}
//
message Response {
string messageString = 1;
}
- 插件命令将proto文件转为接口与服务
protoc --go_out=. --go_opt=paths=source_relative --go-grpc_out=. --go-grpc_opt=paths=source_relative ./build.proto
插件命令若是windows则在bat文件下,若是linux则在sh文件下。
- 服务层逻辑
package service
import "encoding/json"
type Product struct {
Id int64 `json:"id" xorm:"not null pk autoincr comment('主键 id') BIGINT"`
CustomerId int64 `json:"customer_id" xorm:"comment('客户 id') BIGINT(20)"`
ProductName string `json:"product_name" xorm:"comment('产品名称') VARCHAR(20)"`
AvailableAreaId int `json:"available_area_id"` // 可用区id
ResourcePoolId int `json:"resource_pool_id"` //资源池id
ProductId int64 `json:"product_id"` //产品id
CardType string `json:"card_type"` //显卡型号
CardNum int `json:"card_num"` //显卡数量
ContainerName string `json:"container_name"` // 容器名称
ContainerId string `json:"container_id"` // 容器id
CreatedAt string `json:"created_at" xorm:"comment('创建时间') DATETIME created"`
UpdatedAt string `json:"updated_at" xorm:"comment('修改时间') DATETIME updated"`
}
func (Product) DefaultProduct() Product {
return Product{
Id: 1,
CustomerId: 1,
ProductName: "xiaoxu",
AvailableAreaId: 1,
ResourcePoolId: 1,
ProductId: 1,
CardType: "bike",
CardNum: 1,
ContainerName: "xiaoxu",
ContainerId: "1",
CreatedAt: "2023",
UpdatedAt: "2023",
}
}
func (Product) ToJSON(product Product) string {
marshal, err := json.Marshal(product)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return string(marshal)
}
func (Product) ToSTRUCT(product string) Product {
var pro Product
err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(product), &pro)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return pro
}
- grpc服务注册服务层逻辑
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"grpc-demo/protobuf"
"grpc-demo/service"
"net"
)
// Server 实现服务类
type Server struct {
protoInterface.UnimplementedInterfaceServer
}
// GetProduct
func (Server) GetProduct(context.Context, *protoInterface.Request) (*protoInterface.Response, error) {
//获取程序中的返回值
param := service.Product{}
product := param.DefaultProduct()
json := param.ToJSON(product)
return &protoInterface.Response{
MessageString: json,
}, nil
}
// GetOrder
func (Server) Util(context.Context, *protoInterface.Request) (*protoInterface.Response, error) {
return nil, nil
}
// 运行服务
func main() {
//基于tcp实现
listen, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":1099")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("failed to listen", err)
}
//创建grpc服务
server := grpc.NewServer()
//注册自定义方法
protoInterface.RegisterInterfaceServer(server, &Server{})
//启动服务
err = server.Serve(listen)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("failed to serve", err)
return
}
}
- 客户端调用
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials/insecure"
"grpc-demo/protobuf"
"grpc-demo/service"
)
func main() {
//配置连连接参数(无加密)
dial, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:1099", grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if err != nil {
println("failed grpc connect", err)
}
defer dial.Close()
//创建客户端连接
client := protoInterface.NewInterfaceClient(dial)
//通过客户端调用方法
res, err := client.GetProduct(context.Background(), &protoInterface.Request{
ParamString: "hello",
})
if err != nil {
println("failed grpc recive err", err)
}
//打印接受的字符
fmt.Printf("%v", res)
/*
//获取带product结构体在反序列化
param := service.Product{}
product := param.ToSTRUCT(res.MessageString)
fmt.Println(product)
*/
}
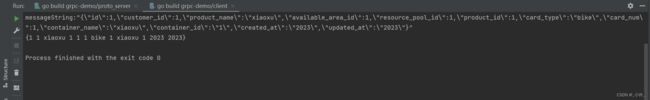
启动grpc服务后,启动客户端请求,如下返回的字符流。
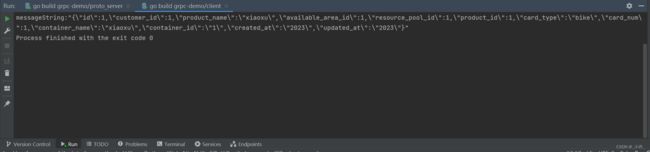
反序列化后得到结构体
//获取带product结构体在反序列化
param := service.Product{}
product := param.ToSTRUCT(res.MessageString)
fmt.Println(product)
因此只要在客户端封装grpc客户端就可以使用该客户端调用方法,就先高调用本地方法一样。
go-grpc