SpringMVC学习笔记三:Controller注解以及restful风格
4、Controller注解以及restful风格
4.1、控制器Controller
控制器复杂提供访问应用程序的行为,通常通过接口定义或注解定义两种方法实现。
控制器负责解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型。
在Spring MVC中一个控制器类可以包含多个方法
在Spring MVC中,对于Controller的配置方式有很多种。
下面介绍接口定义和注解定义两种方式来定义Controller
4.2、实现Controller接口
Controller是一个接口,在org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc包下,接口中只有一个方法:
public interface Controller {
//用于返回一个模型和视图
@Nullable
ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
配置SpringMVC
配置文件只留下视图解析器和路径映射。
<bean id="internalResourceViewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
bean>
<bean id="/t1" class="com.princehan.controller.MyController"/>
配置web.xml
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
编写控制器
public class MyController implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
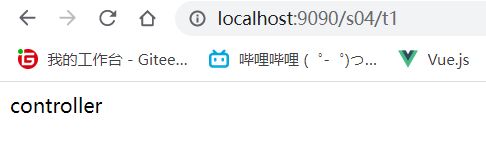
modelAndView.addObject("msg", "controller");
modelAndView.setViewName("test");
return modelAndView;
}
}
编写测试页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>controllertitle>
head>
<body>
${msg}
body>
html>
- 实现接口Controller定义控制器是较老的办法
- 缺点是:一个控制器中只有一个方法,如果要多个方法则需要定义多个Controller;定义的方式比较麻烦;
4.3、注解实现 @Controller
@Controller注解类型用于声明Spring类的实例是一个控制器(在讲IOC时还提到了另外3个注解);
Spring可以使用扫描机制来找到应用程序中所有基于注解的控制器类,为了保证Spring能找到你的控制器,需要在配置文件中声明组件扫描。
配置SpringMVC
<context:component-scan base-package="com.princehan.controller"/>
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
新建一个Controller,使用注解实现
@Controller
public class MyController2 {
@RequestMapping("/t2")
public String Controller1(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "helloController");
return "test";
}
@RequestMapping("/t3")
public String Controller2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "helloController");
return "test";
}
}
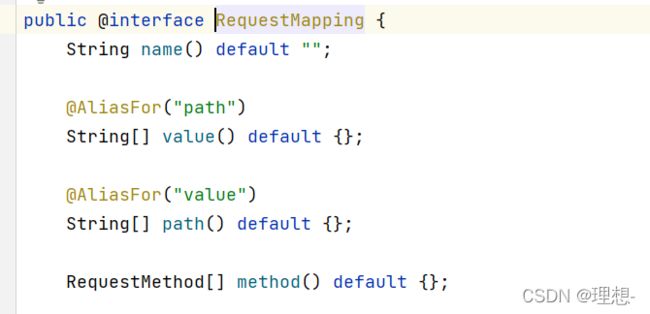
其中@RequestMapping表示映射的路径,可以放于方法的声明之上,表示映射的路径,也可以放在一个类名上,该类方法的映射名前将会自动加上类上的映射。例如:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/t")
public class MyController2 {
@RequestMapping("/t1")
public String Controller1(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "helloController");
return "test";
}
}
映射路径为/t/t1。
4.4、RestFul风格
概念
Restful就是一个资源定位及资源操作的风格。不是标准也不是协议,只是一种风格。基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存等机制。
功能
- 资源:互联网所有的事物都可以被抽象为资源
- 资源操作:使用POST、DELETE、PUT、GET,使用不同方法对资源进行操作。
- 分别对应 添加、 删除、修改、查询。
传统方式操作资源 :通过不同的参数来实现不同的效果!方法单一,post 和 get
http://127.0.0.1/item/queryItem.action?id=1 查询,GET
http://127.0.0.1/item/saveItem.action 新增,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/updateItem.action 更新,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item/deleteItem.action?id=1 删除,GET或POST
使用RESTful操作资源 : 可以通过不同的请求方式来实现不同的效果!如下:请求地址一样,但是功能可以不同!
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 查询,GET
http://127.0.0.1/item 新增,POST
http://127.0.0.1/item 更新,PUT
http://127.0.0.1/item/1 删除,DELETE
上手测试
新建一个Controller
@Controller
public class RestfulController {
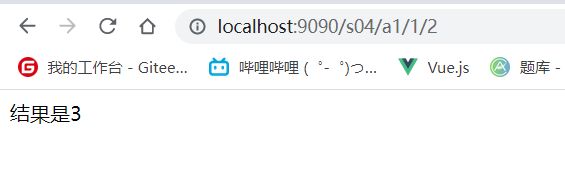
@RequestMapping("/a1/{a}/{b}")
public String test1(@PathVariable int a, @PathVariable int b, Model model) {
int res = a + b;
model.addAttribute("msg", "结果是" + res);
return "test";
}
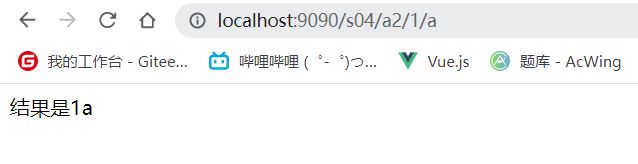
@GetMapping("/a2/{a}/{b}")
public String test2(@PathVariable int a, @PathVariable String b, Model model) {
String res = a + b;
model.addAttribute("msg", "结果是" + res);
return "test";
}
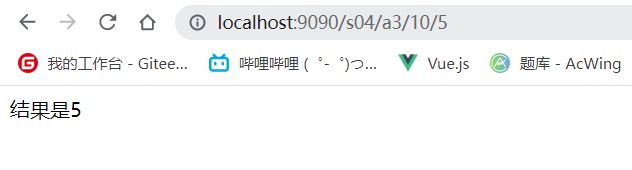
@RequestMapping(value = "/a3/{a}/{b}", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String test3(@PathVariable int a, @PathVariable int b, Model model) {
int res = a - b;
model.addAttribute("msg", "结果是" + res);
return "test";
}
}
配置Tomcat并测试
- RestFul风格更加洁。
- 获得参数更加方便,框架会自动进行类型转换。
- 通过路径变量的类型可以约束访问参数,如果类型不一样,则访问不到对应的请求方法。
注意:使用浏览器地址栏进行访问默认是Get请求,如果使用的是其他方式的请求,会报错
使用
@RequestMapping设置请求类型
用value 或者path属性表示请求路径。method 表示请求类型。
@RequestMapping(value = "/a3/{a}/{b}", method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public String test3(@PathVariable int a, @PathVariable int b, Model model) {
int res = a - b;
model.addAttribute("msg", "结果是" + res);
return "test";
}
}
小结:
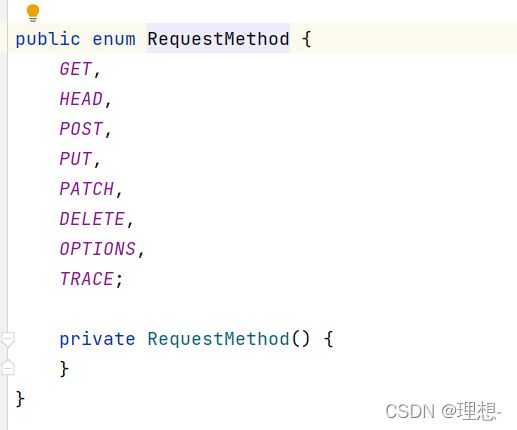
Spring MVC 的@RequestMapping 注解能够处理 HTTP 请求的方法, 比如 GET, PUT, POST, DELETE 以及 PATCH。
所有的地址栏请求默认都会是 HTTP GET 类型的。
方法级别的注解变体有如下几个: 组合注解
@GetMapping
@PostMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping
@PatchMapping
@GetMapping是一个组合注解
它相当于@RequestMapping(method =RequestMethod.GET)的一个快捷方式。
补充:
若一个类用@RestController注解修饰,则这类中的所有的请求都会被视图解析器忽略。
若不想视图解析器忽略掉所有的请求,可以不加@RestController,用@ResponseBody修饰方法,也可以起到同样的效果。