动态代理(基于接口)的方式实现线程绑定和事务控制(非aop)
基于接口的动态代理的方式实现线程绑定和事务控制
首先我们来看一看实现Service的两种方法
1.本身就是一个实现类
非常常规的配置 耦合性很高
<!-- 本身就是一个实现类 -->
<!-- 业务层对象 配置Service-->
<bean id="accountService" class="bruce.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入dao对象 -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置dao对象 -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="bruce.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入QueryRunner-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
<!-- 注入ConnectionUtils -->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
2.动态代理的方式
这里采用的是基于接口,还有基于子类的,可以参考一下我上一篇动态代理的介绍
<!-- 配置代理的service -->
<bean id="proxyAccountService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getAccountService">
</bean>
<!-- 配置beanfactory -->
<bean id="beanFactory" class="bruce.factory.BeanFactory">
<!-- 注入service -->
<property name="accountService" ref="accountService"></property>
<!-- 注入事务管理器 -->
<property name="txManager" ref="txManager"></property>
</bean>
在这儿介绍的就是动态代理的方式
工具类准备
一、事务控制
为了避免每次方法都需要开启事务,提交事务,回滚事务和释放连接(如下图
写一个事务管理的工具类用于事务控制
事务管理相关的工具类,它包含了,开启事务,提交事务,回滚事务和释放连接
![]()
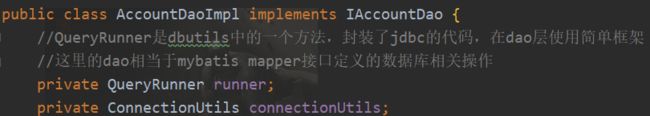
public class TransactionManager {
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public ConnectionUtils getConnectionUtils() {
return connectionUtils;
}
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void commit(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void rollback(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void release(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();//还回连接池
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//线程和连接得解绑 要不然下次拿一个线程上面是由连接的 不能用
}
二、连接的工具类 线程的绑定
为了防止一个方法执行到一半发生错误,但之前的步骤已经执行无法挽回
例如:转账 你花了钱 系统错了 钱没到别人的卡上
连接的工具类,它用于从数据源中获取一个连接,并且实现和线程的绑定
![]()
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
private DataSource dataSource;
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public Connection getThreadConnection() {
//1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
Connection conn = tl.get();
try {
//2.判断当前线程上是否有连接
if (conn == null) {
//3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并且存入ThreadLocal中
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(conn);
}
//4.返回当前线程上的连接
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void removeConnection(){
tl.remove();
}
}
三、基于接口的动态代理
重点!!!!!
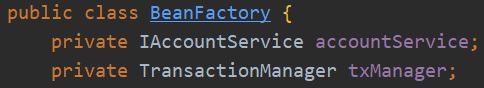
在BeanFactory中实现对Service的动态代理
用于创建Service的代理对象的工厂
一般来说是

但为了实现动态代理
并且
让Service里的所有方法都经过这里面
进行了事务的控制
如下
public IAccountService getAccountService() {
return (IAccountService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(accountService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
accountService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object returnValue = null;
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
returnValue = method.invoke(accountService, args);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
return returnValue;
} catch (Exception e) {
//5.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException();
} finally {
//6.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
});
}
}
这样就完成了动态代理的方式实现线程绑定和事务控制
关于动态代理方法的详细介绍可以看下我上一篇
动态代理的介绍(非aop) 基于接口 基于子类 举例说明
附上杂代码 可能有帮助
Test测试类
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试配置
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
//有多个且没有一个beanId一样
//手动匹配
@Qualifier("proxyAccountService")
private IAccountService as;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
as.transfer("aaa","bbb",100f);
}
}
bean.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 都实现了IAccountService -->
<!-- 1.动态代理 -->
<!-- 配置代理的service -->
<bean id="proxyAccountService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getAccountService">
</bean>
<!-- 配置beanfactory -->
<bean id="beanFactory" class="bruce.factory.BeanFactory">
<!-- 注入service -->
<property name="accountService" ref="accountService"></property>
<!-- 注入事务管理器 -->
<property name="txManager" ref="txManager"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 本身就是一个实现类 -->
<!-- 业务层对象 配置Service-->
<bean id="accountService" class="bruce.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入dao对象 -->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置dao对象 -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="bruce.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入QueryRunner-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
<!-- 注入ConnectionUtils -->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置QueryRunner
默认是单例对象 多个dao在使用同一个对象 可能用完它的时候一个在用另一个还没用完 导致线程互相干扰
多例的话会保证每次使用这个对象都是创建一个新的-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<!-- 注入数据源 QueryRunner是没有set方法和注入 需要使用构造函数注入(前面的都是set方法注入 -->
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源 (导c3p0的包-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!-- 连接数据库的必备信息 -->
<!--mysql的驱动-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<!--连接字符串-->
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springxmlioc?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="530203402"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置Connection的工具类 ConnectionUtils
谁在用呢 是dao在用,需要在上面 dao注入一下ConnectionUtils
-->
<bean id="connectionUtils" class="bruce.utils.ConnectionUtils">
<!-- 注入数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="bruce.utils.TransactionManager">
<!-- 注入ConnectionUtils -->
<property name="connectionUtils" ref="connectionUtils"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
本人菜,希望对你有帮助。
最近愁于考研压力大
我也想体验芜湖~~ 起飞的感觉~~~
可惜 加油