复习C语言:王道C语言督学营OJ记录
初级
Week1
Day1
#include Day 2
//#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include 但第二天也讲了进制转换的一部分简单内容。
十进制数转化为二进制数,再将二进制数转化为十六进制数。
Day 3
00 00 00 7b
x86架构是小端存储(英特尔还是AMD),低位在前,高位在后。
为什么内存数据要用十六进制去看?
高效简洁,两个字符表示一个字节,如7b就是一个字节。
1位 即1 bit 存储0或者1
1字节 即 1Byte = 8 bit
1Kb = 1024字节
1Mb = 1024 Kb
1Gb = 1024 Mb
int i就是四个字节
float f占四个字节
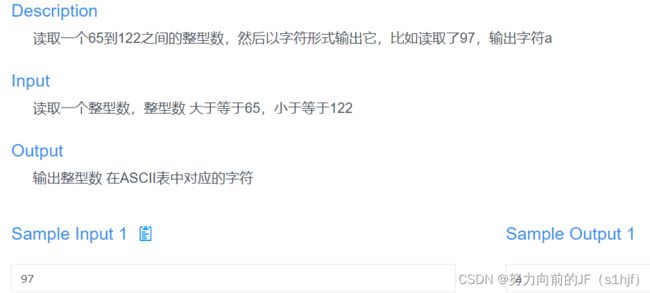
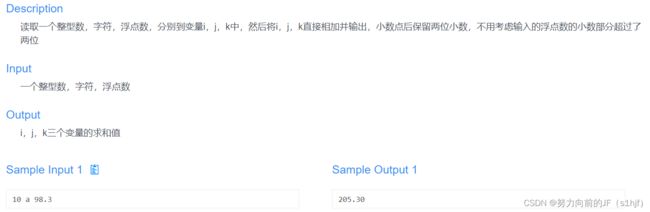
因为输入在计算机内存中都是以二进制存储的(无论是整形,浮点型还是字符型),输出的时候选择合适的输出类型即可。
#includeone time had already accepted
Week 2
Day 4
‘a’为字符型常量。
“a”、“How are you?”双引号包围的是字符串常量,C语言中并没有字符串变量。
不能将字符串型常量赋值给字符型变量。

#includeone time had already accepted
Day 5
#includej=int(j)不能编译通过吗?在DEV上是可以编译的呀,再找找资料。
two accepted
Day 6
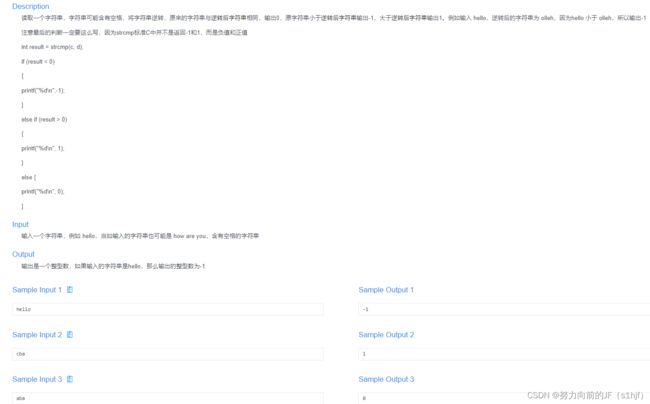
#include一次提交AC
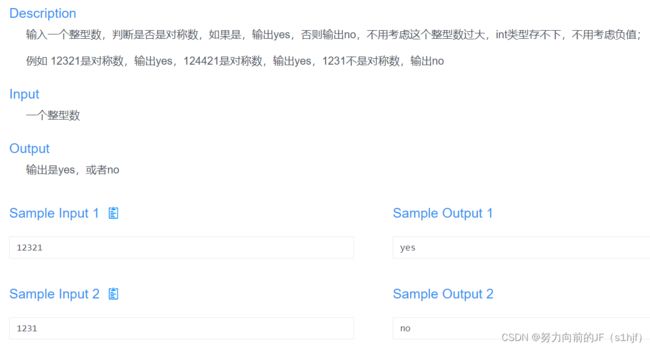
最开始的做法是取每一位数,然后倒序加起来,跟输入作比较,但在DEV里面math的幂函数计算不是很懂,就没过第二个Sample。
这一种方法是用数组存每一位,然后跟输入输入每一位作比较,每一位都相等就输出yes,若有一位不相等,直接输出no。
Week 3
Day 7.1
#include一次
Day 7.2
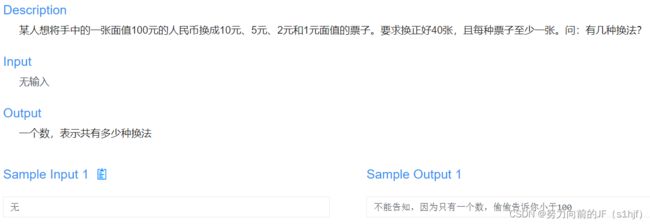
#include每种至少一张,暴力循环最多37次,总面值100,5元最多18次,因为至少有一张10元;10元最多9次。
Day 8
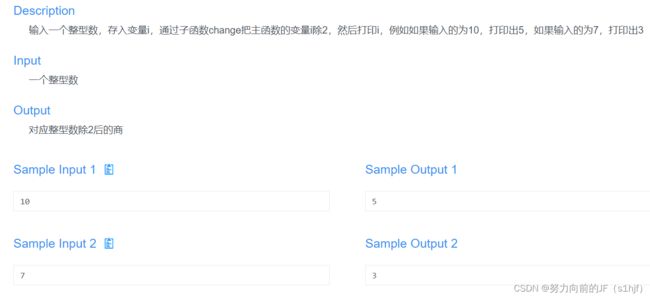
#includeDay 9
#includeWeek 4
Day 10
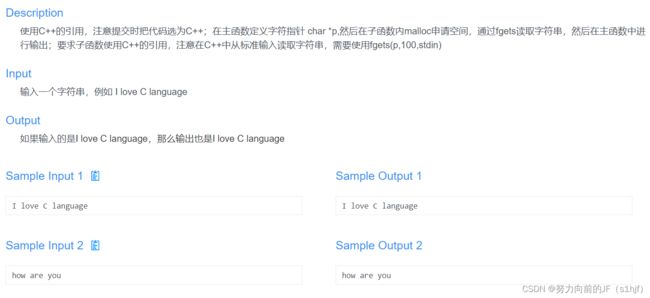
#includeDay 11

在DEV c++里面,malloc函数要调用stdlib库
//注意在scanf和gets中间使用scanf(“%c”,&c),去除换行
一次
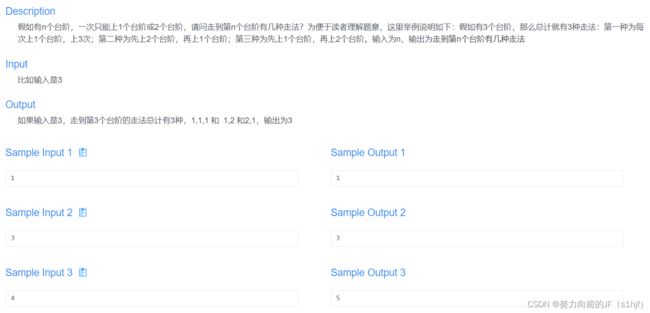
#includeDay12
#include这是一个斐波那契数列,没看出来,直接暴力递归了
斐波那契数列代码如下
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include中级
Week 1
Day 1
#includeDay 2
#includeDay 3
#includeDay 4
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include连续输入两次,再输出两次即可(输入一行输出一行,然后再输入第二行数据,然后进行第二次输出)
Day 5
#include把栈和循环队列的代码放在一起就行了,注意,在视频写的main.cpp中有相同的变量名,注意替换。