深入研究webrtc平滑发送(paced sender)
webrtc处理音视频的共同过程大致为:采集数据-数据编码-rtp打包-平滑发送-通道socket发送。
本文讨论平滑发送(paced sender)作用:如果音视频数据编码后立即发送到网络,那么短时间内网络上会有大量的数据,从而会导致网络拥塞,严重的话引起网络瘫痪。因此webrtc引入了paced sender模块,其主要的作用就是根据网络带宽估计模块计算的发送码率将数据均匀的分布在等时间段的时间片中,达到了平滑发送,在弱网的环境运行时,pacer sender是个非常重要的模块,本文详细讲解其工作原理。
paced sender示意图如下:
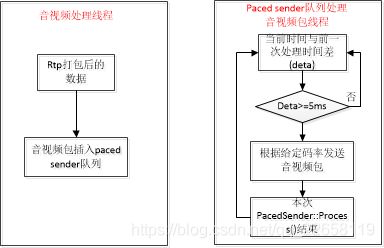
一、数据入队列
音视频打包后的rtp数据插入paced sender队列是在一个线程中,从paced sender队列中取出数据发送在另一个模块线程中,通过同一个临界区 rtc::CritScope cs(&critsect_)保证数据写入和读取安全。
void PacedSender::EnqueuePackets(
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend>> packets) {
rtc::CritScope cs(&critsect_);//保证写入时线程安全
for (auto& packet : packets) {
pacing_controller_.EnqueuePacket(std::move(packet));//将包一个个写入pacing_controller实例的队列管理中
}
}
void PacingController::EnqueuePacketInternal(
std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend> packet,
int priority) {
prober_.OnIncomingPacket(packet->payload_size());//判断发送包是否能激活码率探测条件
Timestamp now = CurrentTime();
prober_.OnIncomingPacket(packet->payload_size());
// TODO(sprang): Make sure tests respect this, replace with DCHECK.
if (packet->capture_time_ms() < 0) {
packet->set_capture_time_ms(now.ms());
}
packet_queue_.Push(priority, now, packet_counter_++, std::move(packet));
}
RoundRobinPacketQueue packet_queue_;//PacingController实例中管理包队列的实例
PacedSender中有PacingController实例,PacingController实例决定了何时发送包的逻辑,但是实际的处理时机是外部提供的,如PacedSender。而且数据包准备发送时的转发也通过外部PacedSendingController::PacketSender接口处理。待发送的数据包队列也由PacingController实例管理。
PacingController数据包队列管理由实例中RoundRobinPacketQueue 实例管理,数据入队列前将数据包封装成QueuedPacket包,该包记录了数据包的入队列时间,数据大小,捕获时间等。
void RoundRobinPacketQueue::Push(int priority,
Timestamp enqueue_time,
uint64_t enqueue_order,
std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend> packet) {
uint32_t ssrc = packet->Ssrc();
uint16_t sequence_number = packet->SequenceNumber();
int64_t capture_time_ms = packet->capture_time_ms();
DataSize size =
DataSize::bytes(send_side_bwe_with_overhead_
? packet->size()
: packet->payload_size() + packet->padding_size());
auto type = packet->packet_type();
RTC_DCHECK(type.has_value());
rtp_packets_.push_front(std::move(packet));//原始包写入存储队列
Push(QueuedPacket(
priority, *type, ssrc, sequence_number, capture_time_ms, enqueue_time,
size, *type == RtpPacketToSend::Type::kRetransmission, enqueue_order,
enqueue_times_.insert(enqueue_time), rtp_packets_.begin()));//将原始包封装QueuedPacket后写入队列
}
void RoundRobinPacketQueue::Push(QueuedPacket packet) {
auto stream_info_it = streams_.find(packet.ssrc());//查找对应ssrc对应的stream实例,因为可能存在多个人流的情况,不同的流必定有不一样的ssrc
if (stream_info_it == streams_.end()) {//默认情况是空的,所以有新的流时会根据ssrc创建新的stream实例。
stream_info_it = streams_.emplace(packet.ssrc(), Stream()).first;//std::map streams_;
stream_info_it->second.priority_it = stream_priorities_.end();
stream_info_it->second.ssrc = packet.ssrc();
}
Stream* stream = &stream_info_it->second;
if (stream->priority_it == stream_priorities_.end()) {
// 如果SSRC当前没有流优先级,则加入stream_priorities_
RTC_CHECK(!IsSsrcScheduled(stream->ssrc));
stream->priority_it = stream_priorities_.emplace(
StreamPrioKey(packet.priority(), stream->size), packet.ssrc());
} else if (packet.priority() < stream->priority_it->first.priority) {
//如果流的优先级变高了,我们就把旧的低优先级的删掉,然后用新的高优先级重新创建StreamPrioKey加入中stream_priorities_
//注意此处的|priority_|是值越小,优先级越高
stream_priorities_.erase(stream->priority_it);
stream->priority_it = stream_priorities_.emplace(
StreamPrioKey(packet.priority(), stream->size), packet.ssrc());
}
RTC_CHECK(stream->priority_it != stream_priorities_.end());
//为了计算不是暂停状态下包在队列中的时间花销,我们减去队列处于停止状态到目前为止的总时间,以及包pop出来后队列停留的总时间
UpdateQueueTime(packet.enqueue_time());
packet.SubtractPauseTime(pause_time_sum_);
size_packets_ += 1;//统计在本次临界区有效时入队列包个数
size_ += packet.size();//统计在本次临界区有效时队列码流数
stream->packet_queue.push(packet);//插入ssrc对应流的QueuedPacket队列
}
封装QueuedPacket 包后,查找数据包ssrc对应的流实例,程序初始化时流实例都时空的,因此开始是查找不到对应的stream实例,则创建ssrc对应的实例。之后统计本次锁控有效期间数据包个数size_packets_ 以及入队列数据码流总大小size_ ,然后插入到对应ssrc流实例中的队列中stream->packet_queue.push(packet);,至此数据入队列完成。
二、取队列数据发送过程
队列包处理是线程固定时间循环处理的,webrtc中固定5ms处理一次队列数据。通过TimeUntilNextProcess()来判断是否开始处理队列Process() ,看如下代码和注释
void PacedSender::Process() {//从队列中取出数据包发送至网络的处理方法
rtc::CritScope cs(&critsect_);
pacing_controller_.ProcessPackets();
}
TimeDelta PacingController::TimeElapsedSinceLastProcess() const {//返回当前时间与上一次执行PacedSender::Process()的时间差
return CurrentTime() - time_last_process_;
}
int64_t PacedSender::TimeUntilNextProcess() {
rtc::CritScope cs(&critsect_);
//如果paced sender处理停止状态,我们将间隔500ms发送padding包,以确保我们在paced sender处于停止状态时由于收不到反馈包而陷入暂停状态
TimeDelta elapsed_time = pacing_controller_.TimeElapsedSinceLastProcess();
if (pacing_controller_.IsPaused()) {
return std::max(PacingController::kPausedProcessInterval - elapsed_time,
TimeDelta::Zero())//PacingController::kPausedProcessInterval=500ms
.ms();
}
auto next_probe = pacing_controller_.TimeUntilNextProbe();
if (next_probe) {
return next_probe->ms();
}
const TimeDelta min_packet_limit = TimeDelta::ms(5);//约定固定5ms执行一次PacedSender::Process()
return std::max(min_packet_limit - elapsed_time, TimeDelta::Zero()).ms();//返回时间差,如果返回0则表示5ms时间到,可以执行
//PacedSender::Process(),如果返回非0,如值为deta,表是离下一次执行PacedSender::Process()还差时间deta
}
接下来看下平滑处理控制pacing_controller_中.ProcessPackets()函数,具体每一重要步骤,都写了注释,可以根据注释理解:
void PacingController::ProcessPackets() {
Timestamp now = CurrentTime();
TimeDelta elapsed_time = UpdateTimeAndGetElapsed(now);//计算当前时间和上一次进入函数处理时的时间差
if (ShouldSendKeepalive(now)) {//判断是否需要发送保活,以下三个条件中的一个满足:paced sender处于暂停状态、发送padding打破陷入暂停和拥塞状态
//要需要发送保活进入次分支
DataSize keepalive_data_sent = DataSize::Zero();
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend>> keepalive_packets =
packet_sender_->GeneratePadding(DataSize::bytes(1));//创建保活包,相当于心跳包
for (auto& packet : keepalive_packets) {
keepalive_data_sent +=
DataSize::bytes(packet->payload_size() + packet->padding_size());
packet_sender_->SendRtpPacket(std::move(packet), PacedPacketInfo());
}
OnPaddingSent(keepalive_data_sent);
}
if (paused_)
return;
if (elapsed_time > TimeDelta::Zero()) {//这个if条件下是计算5ms间隔内,通过队列中包的字节数和包在队列中停留时间计算码率,然后与带宽估计输出的目标码率比较,取最大的码率作为发送码率
DataRate target_rate = pacing_bitrate_;
DataSize queue_size_data = packet_queue_.Size();
if (queue_size_data > DataSize::Zero()) {
//
packet_queue_.UpdateQueueTime(CurrentTime());
if (drain_large_queues_) {//
TimeDelta avg_time_left =
std::max(TimeDelta::ms(1),
queue_time_limit - packet_queue_.AverageQueueTime());
DataRate min_rate_needed = queue_size_data / avg_time_left;
if (min_rate_needed > target_rate) {//最终的发送码率选择码率估计模块输出的码率和pacer队列中计算的码率中的最大
target_rate = min_rate_needed;
RTC_LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "bwe:large_pacing_queue pacing_rate_kbps="
<< target_rate.kbps();
}
}
}
media_budget_.set_target_rate_kbps(target_rate.kbps());
UpdateBudgetWithElapsedTime(elapsed_time);//计算本次间隔目标码率下需要发送的字节
}
bool first_packet_in_probe = false;
bool is_probing = prober_.IsProbing();
PacedPacketInfo pacing_info;
absl::optional<DataSize> recommended_probe_size;
if (is_probing) {
pacing_info = prober_.CurrentCluster();
first_packet_in_probe = pacing_info.probe_cluster_bytes_sent == 0;
recommended_probe_size = DataSize::bytes(prober_.RecommendedMinProbeSize());
}
DataSize data_sent = DataSize::Zero();
// The paused state is checked in the loop since it leaves the critical
// section allowing the paused state to be changed from other code.
while (!paused_) {
if (small_first_probe_packet_ && first_packet_in_probe) {
// If first packet in probe, insert a small padding packet so we have a
// more reliable start window for the rate estimation.
auto padding = packet_sender_->GeneratePadding(DataSize::bytes(1));
// If no RTP modules sending media are registered, we may not get a
// padding packet back.
if (!padding.empty()) {
// Insert with high priority so larger media packets don't preempt it.
EnqueuePacketInternal(std::move(padding[0]), kFirstPriority);
// We should never get more than one padding packets with a requested
// size of 1 byte.
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(padding.size(), 1u);
}
first_packet_in_probe = false;
}
auto* packet = GetPendingPacket(pacing_info);//从队列中取出音视频包
if (packet == nullptr) {//如果队列中没有数据包了,且发送码字数不满足发送的目标码率,则需要通过添加padding弥补
// No packet available to send, check if we should send padding.
DataSize padding_to_add = PaddingToAdd(recommended_probe_size, data_sent);
if (padding_to_add > DataSize::Zero()) {
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend>> padding_packets =
packet_sender_->GeneratePadding(padding_to_add);
if (padding_packets.empty()) {
// No padding packets were generated, quite send loop.
break;
}
for (auto& packet : padding_packets) {
EnqueuePacket(std::move(packet));
}
// Continue loop to send the padding that was just added.
continue;
}
// Can't fetch new packet and no padding to send, exit send loop.
break;
}
std::unique_ptr<RtpPacketToSend> rtp_packet = packet->ReleasePacket();
RTC_DCHECK(rtp_packet);
packet_sender_->SendRtpPacket(std::move(rtp_packet), pacing_info);//paced sender发送数据包出去
data_sent += packet->size();
// Send succeeded, remove it from the queue.
OnPacketSent(packet);//统计本次5ms间隔发送的码字,以及更新剩余发送码率和padding码率
if (recommended_probe_size && data_sent > *recommended_probe_size)
break;
}
if (is_probing) {
probing_send_failure_ = data_sent == DataSize::Zero();
if (!probing_send_failure_) {
prober_.ProbeSent(CurrentTime().ms(), data_sent.bytes());
}
}
}
设置目标码率以及计算本次5ms时间间隔内需要发送的码率
void IntervalBudget::set_target_rate_kbps(int target_rate_kbps) {//设置目标码率
target_rate_kbps_ = target_rate_kbps;
max_bytes_in_budget_ = (kWindowMs * target_rate_kbps_) / 8;
bytes_remaining_ = std::min(std::max(-max_bytes_in_budget_, bytes_remaining_),
max_bytes_in_budget_);
}
//设置本次5ms时间间隔内需要发送的码率
void PacingController::UpdateBudgetWithElapsedTime(TimeDelta delta) {
delta = std::min(kMaxProcessingInterval, delta);
media_budget_.IncreaseBudget(delta.ms());
padding_budget_.IncreaseBudget(delta.ms());
}
void IntervalBudget::IncreaseBudget(int64_t delta_time_ms) {
int64_t bytes = target_rate_kbps_ * delta_time_ms / 8;//计算目标码率下需要发送的字节数
if (bytes_remaining_ < 0 || can_build_up_underuse_) {
// We overused last interval, compensate this interval.
bytes_remaining_ = std::min(bytes_remaining_ + bytes, max_bytes_in_budget_);
} else {
// If we underused last interval we can't use it this interval.
bytes_remaining_ = std::min(bytes, max_bytes_in_budget_);//max_bytes_in_budget_最大字节数是刚刚好5ms时间的最大发送字节
}
}
每成功发送一次包,都需要统计发送的码字,以及将发送成功的数据包移出相应的队列
void PacingController::OnPacketSent(
RoundRobinPacketQueue::QueuedPacket* packet) {
Timestamp now = CurrentTime();
if (!first_sent_packet_time_) {
first_sent_packet_time_ = now;
}
bool audio_packet = packet->type() == RtpPacketToSend::Type::kAudio;
if (!audio_packet || account_for_audio_) {
//更新媒体发送
UpdateBudgetWithSentData(packet->size());
last_send_time_ = now;
}
packet_queue_.FinalizePop();//发送成功后,从队列中移除,更新码字统计
padding_failure_state_ = false;
}
//更新媒体数据发送
void PacingController::UpdateBudgetWithSentData(DataSize size) {
outstanding_data_ += size;
media_budget_.UseBudget(size.bytes());//更新媒体数据发送剩余字节
padding_budget_.UseBudget(size.bytes());//更新padding发送剩余字节
}
//更新bytes_remaining_ ,本次5ms需要发送的总字节数bytes_remaining_ 减去本次发送包的字节数
void IntervalBudget::UseBudget(size_t bytes) {
bytes_remaining_ = std::max(bytes_remaining_ - static_cast<int>(bytes),
-max_bytes_in_budget_);
}
三 paced sender的目标码率如何计算
目标码率的计算是通过 GoogCcNetworkController根据网络状态带宽估计,丢包率来计算发送码率。初始化 RtpTransportControllerSend时开启了重复任务来监测网络状态,评估发送码率,代码如下:
//process_interval_初始化为25ms,固定25ms重复任务来监测网络状况来计算网络发送码率
if (process_interval_.IsFinite()) {
controller_task_ = RepeatingTaskHandle::DelayedStart(
task_queue_.Get(), process_interval_, [this]() {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(&task_queue_);
UpdateControllerWithTimeInterval();
return process_interval_;
});
void RtpTransportControllerSend::UpdateControllerWithTimeInterval() {
RTC_DCHECK(controller_);
ProcessInterval msg;
msg.at_time = Timestamp::ms(clock_->TimeInMilliseconds());
if (add_pacing_to_cwin_)
msg.pacer_queue = pacer()->QueueSizeData();
PostUpdates(controller_->OnProcessInterval(msg));//更新网络状态
}
NetworkControlUpdate GoogCcNetworkController::OnProcessInterval(
ProcessInterval msg) {
NetworkControlUpdate update;
if (initial_config_) {//第一次初始化参数,后续忽略次步骤
update.probe_cluster_configs =
ResetConstraints(initial_config_->constraints);
update.pacer_config = GetPacingRates(msg.at_time);
if (initial_config_->stream_based_config.requests_alr_probing) {
probe_controller_->EnablePeriodicAlrProbing(
*initial_config_->stream_based_config.requests_alr_probing);
}
absl::optional<DataRate> total_bitrate =
initial_config_->stream_based_config.max_total_allocated_bitrate;
if (total_bitrate) {
auto probes = probe_controller_->OnMaxTotalAllocatedBitrate(
total_bitrate->bps(), msg.at_time.ms());
update.probe_cluster_configs.insert(update.probe_cluster_configs.end(),
probes.begin(), probes.end());
max_total_allocated_bitrate_ = *total_bitrate;
}
initial_config_.reset();
}
if (congestion_window_pushback_controller_ && msg.pacer_queue) {
congestion_window_pushback_controller_->UpdatePacingQueue(
msg.pacer_queue->bytes());
}
bandwidth_estimation_->UpdateEstimate(msg.at_time);
absl::optional<int64_t> start_time_ms =
alr_detector_->GetApplicationLimitedRegionStartTime();
probe_controller_->SetAlrStartTimeMs(start_time_ms);
auto probes = probe_controller_->Process(msg.at_time.ms());
update.probe_cluster_configs.insert(update.probe_cluster_configs.end(),
probes.begin(), probes.end());
if (rate_control_settings_.UseCongestionWindow() &&
use_downlink_delay_for_congestion_window_ &&
last_packet_received_time_.IsFinite() && !feedback_max_rtts_.empty()) {
UpdateCongestionWindowSize(msg.at_time - last_packet_received_time_);
}
if (congestion_window_pushback_controller_ && current_data_window_) {
congestion_window_pushback_controller_->SetDataWindow(
*current_data_window_);
} else {
update.congestion_window = current_data_window_;
}
MaybeTriggerOnNetworkChanged(&update, msg.at_time);
return update;
}
根据计算的网络参数设置到pace中
void RtpTransportControllerSend::PostUpdates(NetworkControlUpdate update) {
if (update.congestion_window) {
pacer()->SetCongestionWindow(*update.congestion_window);
}
if (update.pacer_config) {//GoogCcNetworkController模块中带宽估计计算的目标码率设置到pace中
pacer()->SetPacingRates(update.pacer_config->data_rate(),
update.pacer_config->pad_rate());
}
for (const auto& probe : update.probe_cluster_configs) {
pacer()->CreateProbeCluster(probe.target_data_rate, probe.id);
}
if (update.target_rate) {
control_handler_->SetTargetRate(*update.target_rate);
UpdateControlState();
}
}
具体GoogCcNetworkController如何进行带宽估计并计算码率的算法,由于时间限制,后续详细研究。