探究ThreadLocal和ThreadPoolExecutor中的内存泄露风险与防范策略
探究ThreadLocal和ThreadPoolExecutor中的内存泄露风险与防范策略
本文将探讨ThreadLocal和ThreadPoolExecutor中可能存在的内存泄露问题,并提出相应的防范策略。
ThreadPoolExecutor的内存泄露问题
ThreadPoolExecutor是一个线程池类,它可以管理和复用线程,从而提高程序的性能和稳定性。但是,如果使用不当,ThreadPoolExecutor也会导致内存泄露问题。
首先来说,如果我们在使用ThreadPoolExecutor时没有正确地关闭线程池,就会导致线程一直存在,从而占用大量的内存。为了避免这种情况的发生,我们可以在程序结束时手动关闭线程池。具体来说,我们可以在finally块中调用shutdown方法,从而确保线程池一定会被关闭。
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS, workQueue);
try {
// do something
} finally {
executor.shutdown();
}
不过在实际生产过程中,大多数时候并不能关闭线程池,为了在无法关闭线程池的运行生产环境中防止内存泄漏
- 限制线程池的大小:确保线程池的大小适合工作负载和可用系统资源。过大的线程池可能导致过多的内存消耗,同时尽可能复用线程池,避免在项目中过多的创建线程池
- 使用有界队列:考虑使用有界队列(例如ArrayBlockingQueue)而不是无界队列。有界队列可以控制任务的排队数量,避免无限制的内存增长。
- 优化任务的执行时间:尽量减少任务的执行时间,避免长时间的任务阻塞线程池的线程。
- 定期监控线程池的状态:通过监控线程池的活动线程数、队列大小和任务执行情况,及时发现异常情况并进行调整。
ThreadLocal的内存泄露问题
ThreadLocal是一个多线程编程中常用的工具类,它允许我们在每个线程中存储和获取对象,而不必担心线程安全问题。但是,如果使用不当,ThreadLocal也会导致内存泄露问题。
通常情况下,我们会在使用完ThreadLocal后将其置为null,以便垃圾回收器可以回收它所占用的内存。但是,如果我们在某些情况下没有将其置为null,那么它就会一直占用内存,直到程序结束。
为了避免这种情况的发生,我们可以使用ThreadLocal的remove方法手动删除已经不再需要的变量。具体来说,我们可以在finally块中调用remove方法,从而确保变量一定会被删除。
ThreadLocal实际项目中在线程池中使用ThreadLocal导致内存溢出的案例,背景是在线程池中发送数据到kafka,并自定义了拒绝策略,在拒绝策略中把拒绝的相关信息打印出来。模拟相关业务代码
public class ThreadPoolUtil {
private static ThreadLocal<ThreadLocalMemoryEntity>threadLocal= new ThreadLocal<>();
//处理业务的线程池 核心参数设置小保证能进入拒绝策略
private static final ThreadPoolExecutorcompensateBatchPool= new ThreadPoolExecutor(
10, 10, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue(1)
, new LogPolicy());
//模拟客户端发送请求的线程池
private static final ThreadPoolExecutorsimulateReqPool= new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1000, 1000, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue(1000));
public static ThreadPoolExecutor getCompensateBatchPool() {
returncompensateBatchPool;
}
public static ThreadPoolExecutor getSimulateReqPool() {
returnsimulateReqPool;
}
public static ThreadLocal<ThreadLocalMemoryEntity> getThreadLocal() {
returnthreadLocal;
}
// 拒绝策略
public static class LogPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
ThreadLocalMemoryEntity threadLocalMemoryEntity =threadLocal.get();
// 模拟记录内容
System.out.println("执行拒绝策略:"+ threadLocalMemoryEntity.getName());
}
}
}
业务实体
@Data
public class ThreadLocalMemoryEntity {
private String name;
private byte[] data = new byte[1024*1024];
}
idea配置堆内存空间 Xms512m -Xmx512m
业务代码
public class ThreadLocalMemoryLeakExample {
private static ThreadLocal<ThreadLocalMemoryEntity> threadLocal = ThreadPoolUtil.getThreadLocal();
private static ThreadPoolExecutor compensateBatchPool = ThreadPoolUtil.getCompensateBatchPool();
private static ThreadPoolExecutor SimulateReqPool = ThreadPoolUtil.getSimulateReqPool();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
ThreadLocalMemoryEntity threadLocalMemoryEntity = new ThreadLocalMemoryEntity();
threadLocalMemoryEntity.setName("test" + i);
//模拟发送请求 实际生产中每一个请求都会有一个线程
SimulateReqPool.execute(() -> {
threadLocal.set(threadLocalMemoryEntity);
//模拟执行业务逻辑
compensateBatchPool.execute(() -> {
//模拟发送kafka消息
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("发送kafka数据:" + threadLocalMemoryEntity.getName());
});
});
}
} finally {
compensateBatchPool.shutdown();
SimulateReqPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
直接运行mian方法,结果如下
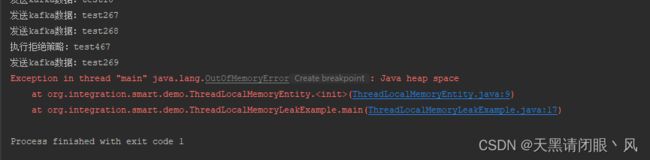
虽然GC会不断回收new的ThreadLocalMemoryEntity对象,但是由于不断将ThreadLocalMemoryEntity放入ThreadLocal中,导致内存溢出异常抛出。
如何防范ThreadLocal内存溢出
优化后的业务代码
public class ThreadLocalMemoryLeakExample {
private static ThreadLocal<ThreadLocalMemoryEntity> threadLocal = ThreadPoolUtil.getThreadLocal();
private static ThreadPoolExecutor compensateBatchPool = ThreadPoolUtil.getCompensateBatchPool();
private static ThreadPoolExecutor SimulateReqPool = ThreadPoolUtil.getSimulateReqPool();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
ThreadLocalMemoryEntity threadLocalMemoryEntity = new ThreadLocalMemoryEntity();
threadLocalMemoryEntity.setName("test" + i);
//模拟发送请求 实际生产中每一个请求都会有一个线程
SimulateReqPool.execute(() -> {
try {
threadLocal.set(threadLocalMemoryEntity);
//模拟执行业务逻辑
compensateBatchPool.execute(() -> {
//模拟发送kafka消息
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("发送kafka数据:" + threadLocalMemoryEntity.getName());
});
} finally {
//防止内存泄露
threadLocal.remove();
}
});
}
} finally {
compensateBatchPool.shutdown();
SimulateReqPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
注意需要在threadLocal.set 所在的线程 进行 remove才有效,因此在使用ThreadLocal的时候可以遵守这个编程规范
try {
threadLocal.set(xxx);
}finally {
threadLocal.remove();
}
总结
在多线程编程中,ThreadLocal和ThreadPoolExecutor是两个常用的工具类,但是它们也会带来内存泄露的风险。为了避免这种情况的发生,我们可以在使用完毕后手动删除变量或关闭线程池。希望本文能够对您有所帮助。