积分图像、图像分割、Harris角点检测
目录
1、积分图像
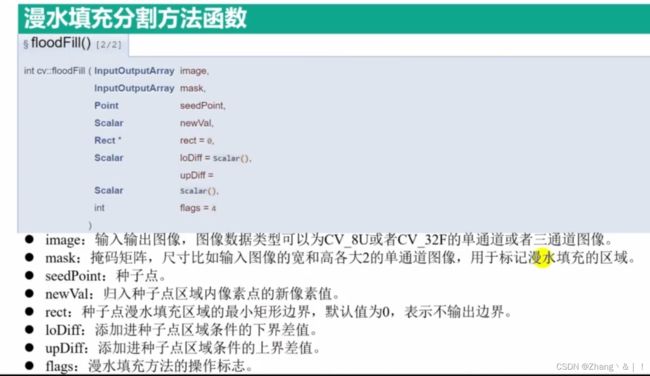
2、图像分割--漫水填充
3、图像分割--分水岭法
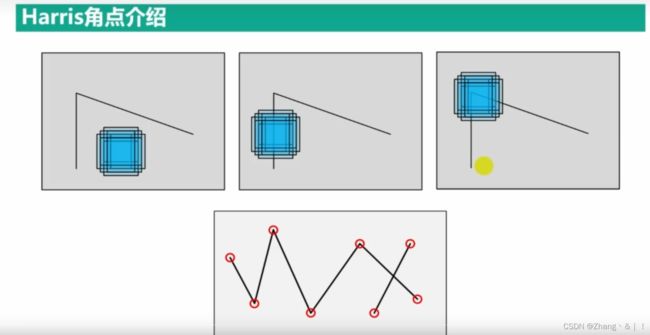
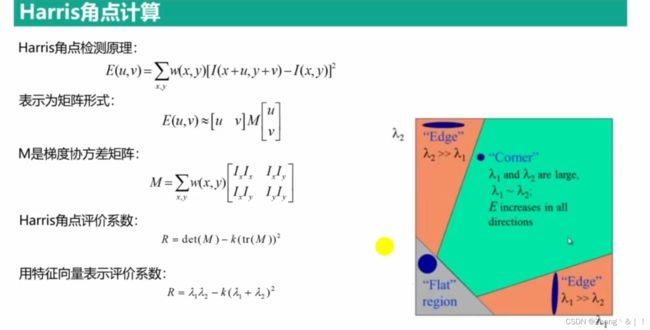
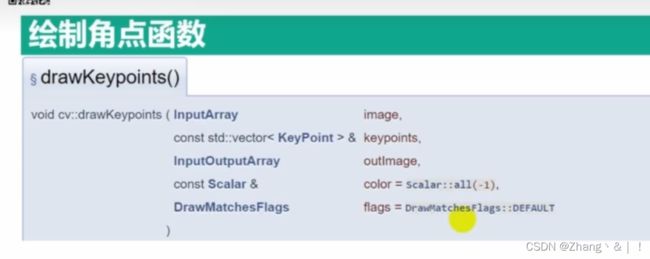
4、Harris角点检测
1、积分图像
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//积分图像
int test()
{
//创建一个16×16全为1的矩阵,因为256=16×16
Mat img = Mat::ones(16, 16, CV_32FC1);
//在图像中加入随机噪声
RNG rng(10086);
for (int y = 0; y < img.rows; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < img.cols; x++)
{
float d = rng.uniform(-0.5, 0.5);
//使用.at的形式读出x,y位置像素来进行操作
img.at(y, x) = img.at(y, x) + d;
}
}
//计算标准求和积分
Mat sum;
integral(img, sum);
//为了便于显示,转成CV_8U格式
Mat sum8U = Mat_(sum);
namedWindow("sum8U", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("sum8U", sum8U);
//计算平方求和积分
Mat sqsum;
integral(img, sum, sqsum);
//为了便于显示,转成CV_8U格式
Mat sqsum8U = Mat_(sqsum);
namedWindow("sqsum8U", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("sqsum8U", sqsum8U);
//计算倾斜求和积分
Mat tilted;
integral(img, sum, sqsum, tilted);
//为了便于显示,转成CV_8U格式
Mat tilted8U = Mat_(tilted);
namedWindow("tilted8U", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("tilted8U", tilted8U);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 2、图像分割--漫水填充
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//图像分割--漫水填充
int test()
{
system("color 02");
Mat img = imread("E:/testMap/lena.png");
if (!(img.data))
{
cout << "读取图像错误,请确认图像文件是否正确" << endl;
return -1;
}
RNG rng(10086);//随机数,用于随机生成像素
//设置操作标志flags
int connectivity = 4;//连通邻域方式
int maskVal = 255;//掩码图像的数值
int flags = connectivity | (maskVal << 8) | FLOODFILL_FIXED_RANGE;//漫水填充操作方式标志
//设置与选中像素点的差值
Scalar loDiff = Scalar(20, 20, 20);
Scalar upDiff = Scalar(20, 20, 20);
//声明掩模矩阵变量,尺寸比输入图像宽高各大2
Mat mask = Mat::zeros(img.rows + 2, img.cols + 2, CV_8UC1);
while (true)
{
//随机产生图像中某一像素点
int py = rng.uniform(0, img.rows - 1);
int px = rng.uniform(0, img.cols - 1);
Point point = Point(px, py);
//彩色图像中填充的像素值
Scalar newVal = Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255));
//漫水填充函数
int area = floodFill(img, mask, point, newVal, &Rect(), loDiff, upDiff, flags);
//输出像素点和填充的像素数目
cout << "像素点x: " << point.x << " y : " << point.y << "填充像素数目:" << area << endl;
//输出填充的图像结果
imshow("填充的彩色图像", img);
imshow("掩模图像", mask);
//判断是否结束程序
int c = waitKey();
if ((c & 255) == 27)
{
break;
}
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 3、图像分割--分水岭法
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//图像分割--分水岭法
int test()
{
Mat img, imgGray, imgMask, img_;
Mat maskWaterShed; //watershed()函数的参数
img = imread("E:/testMap/lenaw.png"); //含有标记的图像
img_ = imread("E:/testMap/lena.png"); //原图像
cvtColor(img, imgGray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(imgGray, imgMask, 235, 255, THRESH_BINARY);//二值化
Mat k = getStructuringElement(0, Size(3, 3));//生成结构元素
morphologyEx(imgMask, imgMask, MORPH_OPEN, k);//开运算
imshow("含有标记的图像", img);
imshow("原图像", img_);
vector> contours;
vector hierarchy;//轮廓索引编号
findContours(imgMask, contours, hierarchy, RETR_CCOMP, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
//在maskWaterShed上绘制轮廓,用于输入分水岭算法
maskWaterShed = Mat::zeros(imgMask.size(), CV_32S);
for (int index = 0; index < contours.size(); index++)
{
//其中第一个参数image表示目标图像,第二个参数contours表示输入的轮廓组,每一组轮廓由点vector构成,
//第三个参数contourIdx指明画第几个轮廓,如果该参数为负值,则画全部轮廓,第四个参数color为轮廓的颜色,
//第五个参数thickness为轮廓的线宽,如果为负值或CV_FILLED表示填充轮廓内部,第六个参数lineType为线型,
//第七个参数为轮廓结构信息, 第八个参数为maxLevel
drawContours(maskWaterShed, contours, index, Scalar::all(index + 1), -1, 8, hierarchy, INT_MAX);
}
//分水岭算法需要对原图像进行处理
watershed(img_, maskWaterShed);
vector colors;// 随机生成几种颜色
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
int b = theRNG().uniform(0, 255);
int g = theRNG().uniform(0, 255);
int r = theRNG().uniform(0, 255);
colors.push_back(Vec3b((uchar)b, (uchar)g, (uchar)r));
}
Mat resultImg = Mat(img.size(), CV_8UC3); // 显示图像
for (int i = 0; i < imgMask.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < imgMask.cols; j++)
{
//绘制每个区域的颜色
int index = maskWaterShed.at(i, j);
if (index == -1)//区域间的值被置为 - 1(边界)
{
resultImg.at(i, j) = Vec3b(255, 255, 255);
}
else if (index <= 0 || index > contours.size())//没有标记清楚的区域被置为0
{
resultImg.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
}
else//其他每个区域的值保持不变: 1,2,…,contours.size()
{
resultImg.at(i, j) = colors[index - 1];//把些区域绘制成不同颜色
}
}
}
imshow("resultImg", resultImg);
resultImg = resultImg * 0.8 + img_*0.2;
//addWeighted(resultImg,0.8,img_, 0.2,0, resultImg);
imshow("分水岭结果", resultImg);
//绘制每个区域的图像
for (int n = 1; n <= contours.size(); n++)
{
Mat resImagel = Mat(img.size(), CV_8UC3);//声明一个最后要显示的图像
for (int i = 0; i < imgMask.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < imgMask.cols; j++)
{
int index = maskWaterShed.at(i, j);
if (index == n)
resImagel.at(i, j) = img_.at(i, j);
else
resImagel.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
}
}
//显示图像
imshow(to_string(n), resImagel);
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 4、Harris角点检测
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//Harris角点检测
int test()
{
Mat img = imread("E:/testMap/lena.png", IMREAD_COLOR);
if (!img.data)
{
cout << "读取图像错误,请确认图像文件是否正确" << endl;
return -1;
}
//转成灰度图像
Mat gray;
cvtColor(img, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//计算Harris系数
Mat harris;
int blockSize = 2; //邻域半径
int apertureSize = 3;
cornerHarris(gray, harris, blockSize, apertureSize, 0.04);//角点检测
//归一化便于进行数值比较和结果显示
Mat harrisn;
normalize(harris, harrisn, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
//将图像的数据类型变成CV_8U
convertScaleAbs(harrisn, harrisn);
//寻找Harris角点
vector keyPoints;
for (int row = 0; row < harrisn.rows; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < harrisn.cols; col++)
{
int R = harrisn.at(row, col);
if (R >125)
{
//向角点存入KeyPoint中
KeyPoint keyPoint;
keyPoint.pt.y = row;
keyPoint.pt.x = col;
keyPoints.push_back(keyPoint);
}
}
}
//绘制角点与显示结果
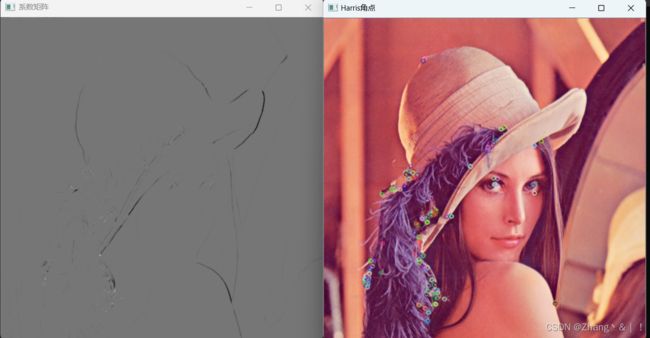
drawKeypoints(img, keyPoints, img);
imshow("系数矩阵", harrisn);
imshow("Harris角点", img);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}