python 实现模糊聚类
python模糊聚类细节与实现
- 前言
- 数学逻辑
- 代码框架
- Python实现
-
- 数据预处理 preProcess
- 获得相似矩阵 getSimilarityMatrix
- 获取传递闭包 transitiveClosure
- 模糊运算 fuzzMatrixProduct
- 实现聚类 mergeProcess
- 实例演示
- 完整代码
- 代码未完成部分
前言
作为数学系的学生,我对于模糊数学并不是很认可,一方面确实是知识的缺失,并没有真正去接触到其底层支持机制,目前我并不认为它是对的或是错的;另一方面,大学时间有限,对于模糊数学我并没有花过多精力在上面。该文的写作来源于好友的毕业需求。
数学逻辑
数据预处理(归一化) ==>相似关系建立 ==>动态聚类
Tip:
- 这里的第三步使用的是传递闭包法,该法解决的问题是:由第二步相似关系建立得到的相似矩阵只满足自反性和对称性,但并不满足传递性(实际上我也不知道为什么)
- 摒弃某些资料提到的 λ-截矩阵 概念,我的理解是:本质不就是设置阈值么
代码框架
- preProcess: (mat: np.matrix, method=‘min_max’) -> np.matrix ……预处理函数
- getSimilarityMatrix:(mat: np.matrix) -> np.matrix ……获得相似矩阵
- transitiveClosure: (mat: np.matrix) -> np.matrix……获得相似函数的传递闭包
- fuzzMatrixProduct: (mat: np.mat) -> np.mat……模糊运算(%)
- mergeProcess:(mat: np.mat) -> list……聚类过程
(%):
R 1 ∘ R 2 = R 3 , R 1 ∈ R m × s , R 2 ∈ R s × t R 3 [ i , j ] = max k = 1 , … , s min ( R 1 [ i , k ] , R 2 [ k , j ] ) R_1 \circ R_2 = R_3,~~~R_1 \in \mathbb{R}^{m\times s},~~ R_2 \in \mathbb{R}^{s\times t}\\\\ R_3[i,~j]=\max_{k=1,\dots,s}\min(R_1[i, ~k], R_2[k, ~j]) R1∘R2=R3, R1∈Rm×s, R2∈Rs×tR3[i, j]=k=1,…,smaxmin(R1[i, k],R2[k, j])
其中, i ∈ [ 1... m ] , j ∈ [ 1... t ] i\in[1...m],~j\in[1...t] i∈[1...m], j∈[1...t]
Python实现
并没有使用机器学习那一套现成框架,所以代码难免会冗长和欠缺考虑。
【温馨提示】
本文采用的矩阵形式为:行数为待聚类样本数,具体可见后面实例
- 需要借助numpy包进行矩阵操作
- 需要借助heapq包进行 优先队列 操作
- 需要借助copy包进行 深拷贝 操作
- 需要借助turtle包进行画图操作(用其他画图工具或现成包可能更好,该文并未在可视化上下大功夫)
import numpy as np
import heapq as pq
import copy
import turtle as tu
数据预处理 preProcess
def preProcess(mat: np.matrix, method='min_max') -> np.matrix:
# 转置,这一步的目的是为了后面求和好写,最后还要换回来
mat = np.mat(np.transpose(mat))
# 提供了两种归一化方法: 极差 和 z_score
if method.lower() != 'min_max' and method.lower() != 'z_score':
print("Invaild Operation")
return mat
# 将默认的int类型换成浮点类型,否则后面可能除法会出错
mat = mat.astype(np.float32)
row = mat.shape[0]
if method.lower() == 'min_max':
for i in range(row):
# 采用行数为待聚类样本数的优点就显示出来了
curMax = np.max(mat[i])
curMin = np.min(mat[i])
if curMin == curMax:
continue
# 核心数学公式1:
mat[i] = (mat[i] - curMin) / (curMax - curMin)
else:
for i in range(row):
curMean = np.mean(mat[i])
curStd = np.std(mat[i])
if curStd == 0:
continue
# 核心数学公式2
mat[i] = (mat[i] - curMean) / curStd
# 最后记得转置回去
return np.mat(np.transpose(mat))
获得相似矩阵 getSimilarityMatrix
def getSimilarityMatrix(mat: np.matrix) -> np.matrix:
row = mat.shape[0]
similarityMatrix = np.zeros((row, row), dtype=float)
# 最后要保证落在【0,1】,该标志位指示是否有负数出现
# 如果有负数出现,采用的处理方式是整个矩阵的元素都加一再除2
isexistNegtive = False
for i in range(1, row):
for j in range(i):
similarityMatrix[i][j] = np.sum(np.multiply(mat[i], mat[j]))
if similarityMatrix[i][j] < 0:
isexistNegtive = True
tmp = np.max(similarityMatrix)
if tmp == 0:
print("Operation Error!")
return np.mat(np.zeros(row, row))
similarityMatrix /= tmp
if isexistNegtive:
similarityMatrix = (similarityMatrix + 1) / 2
for i in range(row):
similarityMatrix[i][i] = 1
for j in range(i + 1, row):
# 利用R的对称性
similarityMatrix[i][j] = similarityMatrix[j][i]
return np.mat(similarityMatrix)
获取传递闭包 transitiveClosure
def transitiveClosure(mat: np.matrix) -> np.matrix:
cnt = 1
# 循环知道找到闭包
while False == (fuzzMatrixProduct(mat) == mat).all() and cnt < 10:
mat = fuzzMatrixProduct(mat)
cnt += 1
# cnt设置是为了避免无限循环
if cnt >= 10:
print("Calculate Error")
return np.mat(np.zeros((mat.shape[0], mat.shape[1])))
print(cnt)
return mat
模糊运算 fuzzMatrixProduct
def fuzzMatrixProduct(mat: np.mat) -> np.mat:
size = mat.shape[0]
ret = np.mat(np.zeros((size, size), dtype=float))
for i in range(size):
for j in range(size):
# 核心数学公式3
ret[i, j] = min(mat[i, 0], mat[0, j])
for k in range(1, size):
# 核心数学公式4
ret[i, j] = max(min(mat[i, k], mat[k, j]), ret[i, j])
return ret
实现聚类 mergeProcess
有必要说一下我的思考过程和合并思路

对于这样的一幅图,我们很容易会有合并的思路:7和6先合并啊,然后5和3,再然后……仔细想想我们很容易归纳出我们的合并思路:按序合并相似度高的样本。分析到这里,我们就知道需要一个能够排序的数据结构了,我选择了heapq模块的堆函数(heappush, heappop)。在此之前,先用valtoposi变量记录了每个相似度对应的位置(注意相似度相同的不同样本可能有多对,所以索引出来的结果可能是列表)。得到valtoposi后,将valtoposi的每个元素一一push进我们的优先队列中(变量heap)
但是只有这一条规则是不足以最终得到像上图这样的图形,为什么?设想一种情况,根据heap出列的结果,相似度前三的样本对依次是7和6、5和3、4和6、2和5,依次画图的画就会发现可能会出现交叉的现象,如下图:
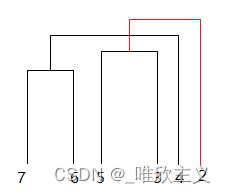
原因在于:4并不是和相邻的样本进行合并!(中间隔了5和3)这也就提示我们:
在合并画图的过程中,我们需要适当调整位置。接下来先介绍我们画图所根据的存储结构——栈
利用栈 objectstack 记录合并顺序,规则如下:
- 如果这个元素是个包含两个数字的列表,则表示合并这两个数字代表的样本
- 如果这个元素是单个数字,则与前面已经部分合并的“大样本”合并
回到上面的错误图形例子,如果不采取任何的调整位置的策略,我们做得到的 objectstack 长这样
[[7, 6], [5, 3], 4, 2]
实际上,我们所希望的 objectstack 是
[[7, 6], 4, [5, 3], 2]
应该采取什么样的策略呢?其实很简单,刚刚说过了出错原因在于 4并不是和相邻的样本进行合并,也就是说,只 要合并的样本在隔壁,那就没有问题!
我的解决方案是维护一个列表 mergestack,该列表记录了当前的合并情况。当处理到4和6合并时,此时的mergestack内容为:
[[7, 6], [5, 3]]
4和6并不在相邻的样本中,找到4或6出现的位置,进行插入即可,更新后有
objectstack:[[7, 6], 4, [5, 3]]
mergestack: [[7, 6, 4], [5, 3]]
大概思路就是这样了
# 引入了三个栈:objectstack,mergestack 和 scorestack
# objectstack记录合并顺序
# mergestack辅助样本合并
# scorestack记录合并时的相似度
# 结果返回 [objectstack, scorestack]
def mergeProcess(mat: np.mat) -> list:
# 初始化后续所用到的栈等
size = mat.shape[0]
heap = []
picked = []
valtoposi = {}
objectstack = []
mergestack = []
scorestack = []
# 由相似度矩阵得到 valtoposi
# valtoposi是相似度到矩阵位置的一个映射
for i in range(1, size):
for j in range(i):
if mat[i, j] in valtoposi.keys():
valtoposi[mat[i, j]].append([i, j])
else:
valtoposi[mat[i, j]] = [[i, j]]
# 对不同的相似度进行排序
# 由于优先队列出堆顺序是升序排序,而我们需要降序排序,故利用乘负一的方法
for i in valtoposi.keys():
pq.heappush(heap, -i)
while len(picked) < size:
score = pq.heappop(heap) * (-1)
for i in valtoposi[score]:
if i[0] not in picked and i[1] not in picked:
picked.append(i[0])
picked.append(i[1])
objectstack.append(i)
mergestack.append(copy.deepcopy(i))
scorestack.append(score)
elif i[0] in picked and i[1] in picked:
continue
elif i[0] in picked:
picked.append(i[1])
if i[0] in mergestack[-1]:
mergestack[-1] += [int(i[1])]
objectstack.append(i[1])
scorestack.append(score)
continue
for j in range(len(mergestack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[0] in mergestack[j]:
break
mergestack[j] += [int(i[1])]
for j in range(len(objectstack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[0] in objectstack[j]:
break
objectstack.insert(j + 1, i[1])
scorestack.insert(j + 1, score)
else:
picked.append(i[0])
if i[1] in mergestack[-1]:
mergestack[-1] += [int(i[0])]
objectstack.append(i[0])
scorestack.append(score)
continue
for j in range(len(objectstack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[1] in objectstack[j]:
break
objectstack.insert(j + 1, i[0])
scorestack.insert(j + 1, score)
for j in range(len(mergestack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[1] in mergestack[j]:
break
mergestack[j] += [int(i[0])]
if len(picked) == size:
pq.heappush(heap, score * (-1))
# 当所有的样本都被挑中时,合并过程可能并未结束,因为可能形成了几个大类,
# 而这些大类并没有更进一步聚类
while len(mergestack) >= 2:
score = pq.heappop(heap) * (-1)
for j in valtoposi[score]:
i1, i2 = 0, 0
for k in range(len(mergestack)):
if j[0] in mergestack[k] and j[1] in mergestack[k]:
continue
elif j[0] not in mergestack[k] and j[1] not in mergestack[k]:
continue
elif j[0] in mergestack[k]:
i1 = k
else:
i2 = k
if i1 != i2:
mergestack[i1] += mergestack[i2]
del mergestack[i2]
scorestack.append(score)
objectstack.append(j)
return [objectstack, scorestack]
实例演示
>>> Q1
matrix([[0.14876032, 0.3088235 , 0.48584902, 0.07199979, 0.72067046],
[0. , 0. , 0. , 0.55999994, 1. ],
[0.02479339, 0.3823529 , 0.4292453 , 0.51199985, 0.61731845],
[0.04958678, 0.3382353 , 0.35849056, 0.79999995, 0.56703913],
[1. , 0.28676468, 0.3301887 , 0.536 , 0.678771 ],
[0.09917355, 0.24264704, 0.20283017, 1. , 0.60893863],
[0.677686 , 1. , 1. , 0. , 0. ],
[0.22314051, 0.49264705, 0.73113203, 0.6799998 , 0.27094975],
[0.24793388, 0.36029407, 0.6415094 , 0.43999982, 0.44972068]],
dtype=float32)
相似矩阵:
>>> Q2
matrix([[1. , 0.55344818, 0.59059223, 0.54709302, 0.67309461,
0.50842017, 0.65126281, 0.57075019, 0.59316946],
[0.55344818, 1. , 0.65748321, 0.73821114, 0.71195069,
0.85013822, 0. , 0.47400029, 0.50627011],
[0.59059223, 0.65748321, 1. , 0.7593308 , 0.70517938,
0.77833435, 0.60247369, 0.74411335, 0.6706715 ],
[0.54709302, 0.73821114, 0.7593308 , 1. , 0.7844664 ,
0.94908777, 0.53114982, 0.82722886, 0.70628633],
[0.67309461, 0.71195069, 0.70517938, 0.7844664 , 1. ,
0.86186167, 0.94155703, 0.83943269, 0.80303368],
[0.50842017, 0.85013822, 0.77833435, 0.94908777, 0.86186167,
1. , 0.37286283, 0.82542372, 0.69526072],
[0.65126281, 0. , 0.60247369, 0.53114982, 0.94155703,
0.37286283, 1. , 1. , 0.85078273],
[0.57075019, 0.47400029, 0.74411335, 0.82722886, 0.83943269,
0.82542372, 1. , 1. , 0.81665658],
[0.59316946, 0.50627011, 0.6706715 , 0.70628633, 0.80303368,
0.69526072, 0.85078273, 0.81665658, 1. ]])
传递闭包:
>>> Q3
matrix([[1. , 0.67309461, 0.67309461, 0.67309461, 0.67309461,
0.67309461, 0.67309461, 0.67309461, 0.67309461],
[0.67309461, 1. , 0.77833435, 0.85013822, 0.85013822,
0.85013822, 0.85013822, 0.85013822, 0.85013822],
[0.67309461, 0.77833435, 1. , 0.77833435, 0.77833435,
0.77833435, 0.77833435, 0.77833435, 0.77833435],
[0.67309461, 0.85013822, 0.77833435, 1. , 0.86186167,
0.94908777, 0.86186167, 0.86186167, 0.85078273],
[0.67309461, 0.85013822, 0.77833435, 0.86186167, 1. ,
0.86186167, 0.94155703, 0.94155703, 0.85078273],
[0.67309461, 0.85013822, 0.77833435, 0.94908777, 0.86186167,
1. , 0.86186167, 0.86186167, 0.85078273],
[0.67309461, 0.85013822, 0.77833435, 0.86186167, 0.94155703,
0.86186167, 1. , 1. , 0.85078273],
[0.67309461, 0.85013822, 0.77833435, 0.86186167, 0.94155703,
0.86186167, 1. , 1. , 0.85078273],
[0.67309461, 0.85013822, 0.77833435, 0.85078273, 0.85078273,
0.85078273, 0.85078273, 0.85078273, 1. ]])
完整代码
import numpy as np
import heapq as pq
import copy
import turtle as tu
# data4.xlsx 里的数据
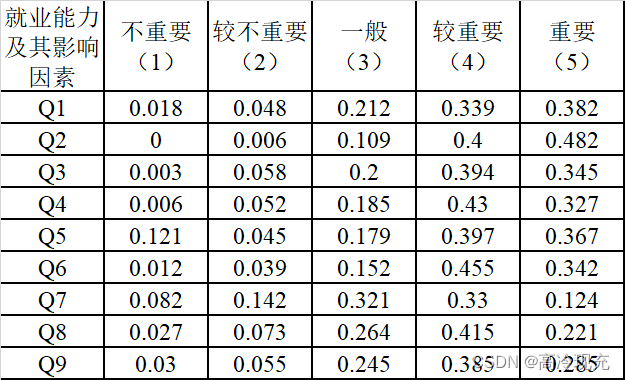
Q = np.mat([
[0.018, 0.048, 0.212, 0.339, 0.382],
[0, 0.006, 0.109, 0.4, 0.482],
[0.003, 0.058, 0.2, 0.394, 0.345],
[0.006, 0.052, 0.185, 0.43, 0.327],
[0.121, 0.045, 0.179, 0.397, 0.367],
[0.012, 0.039, 0.152, 0.455, 0.342],
[0.082, 0.142, 0.321, 0.33, 0.124],
[0.027, 0.073, 0.264, 0.415, 0.221],
[0.03, 0.055, 0.245, 0.385, 0.285]
])
# 数据预处理
def preProcess(mat: np.matrix, method='min_max') -> np.matrix:
# 转置,这一步的目的是为了后面求和好写,最后还要换回来
mat = np.mat(np.transpose(mat))
# 提供了两种归一化方法: 极差 和 z_score
if method.lower() != 'min_max' and method.lower() != 'z_score':
print("Invaild Operation")
return mat
# 将默认的int类型换成浮点类型,否则后面可能除法会出错
mat = mat.astype(np.float32)
row = mat.shape[0]
if method.lower() == 'min_max':
for i in range(row):
curMax = np.max(mat[i])
curMin = np.min(mat[i])
if curMin == curMax:
continue
# 核心数学公式1:
mat[i] = (mat[i] - curMin) / (curMax - curMin)
else:
for i in range(row):
curMean = np.mean(mat[i])
curStd = np.std(mat[i])
if curStd == 0:
continue
# 核心数学公式2
mat[i] = (mat[i] - curMean) / curStd
return np.mat(np.transpose(mat))
# 得到相似矩阵
def getSimilarityMatrix(mat: np.matrix) -> np.matrix:
row = mat.shape[0]
similarityMatrix = np.zeros((row, row), dtype=float)
# 最后要保证落在【0,1】,该标志位指示是否有负数出现
isexistNegtive = False
for i in range(1, row):
for j in range(i):
similarityMatrix[i][j] = np.sum(np.multiply(mat[i], mat[j]))
if similarityMatrix[i][j] < 0:
isexistNegtive = True
tmp = np.max(similarityMatrix)
if tmp == 0:
print("Operation Error!")
return np.mat(np.zeros(row, row))
similarityMatrix /= tmp
if isexistNegtive:
similarityMatrix = (similarityMatrix + 1) / 2
for i in range(row):
similarityMatrix[i][i] = 1
for j in range(i + 1, row):
# 利用R的对称性
similarityMatrix[i][j] = similarityMatrix[j][i]
return np.mat(similarityMatrix)
# 得到R的传递闭包
def transitiveClosure(mat: np.matrix) -> np.matrix:
cnt = 1
# 循环知道找到闭包
while False == (fuzzMatrixProduct(mat) == mat).all() and cnt < 10:
mat = fuzzMatrixProduct(mat)
cnt += 1
# cnt设置是为了避免无限循环
if cnt >= 10:
print("Calculate Error")
return np.mat(np.zeros((mat.shape[0], mat.shape[1])))
print(cnt)
return mat
# 计算模糊矩阵
def fuzzMatrixProduct(mat: np.mat) -> np.mat:
size = mat.shape[0]
ret = np.mat(np.zeros((size, size), dtype=float))
for i in range(size):
for j in range(size):
# 核心数学公式3
ret[i, j] = min(mat[i, 0], mat[0, j])
for k in range(1, size):
# 核心数学公式4
ret[i, j] = max(min(mat[i, k], mat[k, j]), ret[i, j])
return ret
def mergeProcess(mat: np.mat) -> list:
size = mat.shape[0]
heap = []
picked = []
valtoposi = {}
objectstack = []
# mergestack = []
mergestack = copy.deepcopy(objectstack)
scorestack = []
for i in range(1, size):
for j in range(i):
if mat[i, j] in valtoposi.keys():
valtoposi[mat[i, j]].append([i, j])
else:
valtoposi[mat[i, j]] = [[i, j]]
for i in valtoposi.keys():
pq.heappush(heap, -i)
while len(picked) < size:
tmp = pq.heappop(heap) * (-1)
for i in valtoposi[tmp]:
if i[0] not in picked and i[1] not in picked:
picked.append(i[0])
picked.append(i[1])
objectstack.append(i)
mergestack.append(copy.deepcopy(i))
scorestack.append(tmp)
elif i[0] in picked and i[1] in picked:
continue
elif i[0] in picked:
picked.append(i[1])
if i[0] in mergestack[-1]:
mergestack[-1] += [int(i[1])]
objectstack.append(i[1])
scorestack.append(tmp)
continue
for j in range(len(mergestack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[0] in mergestack[j]:
break
mergestack[j] += [int(i[1])]
for j in range(len(objectstack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[0] in objectstack[j]:
break
objectstack.insert(j + 1, i[1])
# scorestack.insert(j + 1, tmp)
scorestack.append(tmp)
else:
picked.append(i[0])
if i[1] in mergestack[-1]:
mergestack[-1] += [int(i[0])]
objectstack.append(i[0])
scorestack.append(tmp)
continue
for j in range(len(objectstack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[1] in objectstack[j]:
break
objectstack.insert(j + 1, i[0])
# scorestack.insert(j + 1, tmp)
scorestack.append(tmp)
for j in range(len(mergestack) - 1, -1, -1):
if i[1] in mergestack[j]:
break
mergestack[j] += [int(i[0])]
return [objectstack, scorestack]
def plotCluster(data: list):
obj = data[0]
score = data[1]
tmp = []
cnt = 0
for i in obj:
if type(i) == list:
cnt += len(i)
else:
cnt += 1
width = 700 / (cnt - 1)
height = [_ * 700 - 300 for _ in score][::-1]
tu.setup(1000, 600, -300, -200)
tu.pensize(2)
tu.penup()
tu.goto(-470, -190)
tu.pendown()
cnt2 = -1
for i in obj:
if type(i) == list:
cnt2 += 1
if cnt2 != 0:
tu.seth(0)
tu.penup()
tu.fd(width)
tu.pendown()
tu.penup()
tu.seth(-90)
tu.fd(25)
tu.pendown()
tu.write(str(i[0]), font=('宋体', 15, 'normal'))
tu.penup()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(25)
tu.pendown()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(height[cnt2])
tu.seth(0)
tu.fd(width / 2)
tu.penup()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(15)
tu.pendown()
tu.write(str(round(score[cnt2], 3)), font=('宋体', 10, 'normal'))
tu.penup()
tu.seth(-90)
tu.fd(15)
tu.pendown()
tu.seth(0)
tu.fd(width / 2)
tu.seth(-90)
tu.fd(height[cnt2])
tu.penup()
tu.seth(-90)
tu.fd(25)
tu.pendown()
tu.write(str(i[1]), font=('宋体', 15, 'normal'))
tu.penup()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(25)
tu.pendown()
tmp.append(i)
else:
tu.penup()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(height[cnt2])
tu.seth(180)
tu.fd(width * (len(tmp[-1]) - 1) / 2)
tu.pendown()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(height[cnt2 + 1] - height[cnt2])
cnt2 += 1
tu.seth(0)
tmp_width = width * (len(tmp[-1]) + 1) / 2
tu.fd(tmp_width / 2)
tu.penup()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(15)
tu.pendown()
tu.write(str(round(score[cnt2], 3)), font=('宋体', 10, 'normal'))
tu.penup()
tu.seth(-90)
tu.fd(15)
tu.pendown()
tu.seth(0)
tu.fd(tmp_width / 2)
tu.seth(-90)
tu.fd(height[cnt2])
tu.penup()
tu.seth(-90)
tu.fd(25)
tu.pendown()
tu.write(str(i), font=('宋体', 15, 'normal'))
tu.penup()
tu.seth(90)
tu.fd(25)
tu.pendown()
tmp[-1] += [i]
if len(tmp) > 1:
pass
tu.done()
Q1 = preProcess(Q)
Q2 = getSimilarityMatrix(Q1)
Q3 = transitiveClosure(Q2)
# print(Q3)
Q4 = mergeProcess(Q3)
# print(Q4)
plotCluster(Q4)
代码未完成部分
画图部分是有bug的,时间忙,有空再修改