C++基础入门(四)—— 程序流程结构(下)
C++系列内容的学习目录 → \rightarrow →C++学习系列内容汇总。
- 1. 程序流程结构概述
- 2. 选择结构
- 3. 循环结构
-
- 3.1 while循环语句
- 3.2 do...while循环语句
- 3.3 for循环语句
- 3.4 嵌套循环
- 4. 跳转语句
-
- 4.1 break语句
- 4.2 continue语句
- 4.3 goto语句
- 5. 总结
程序流程结构分为两个篇章。
1、2部分的内容见C++基础入门(四)—— 程序流程结构(上)
3、4、5部分的内容见C++基础入门(四)—— 程序流程结构(下)
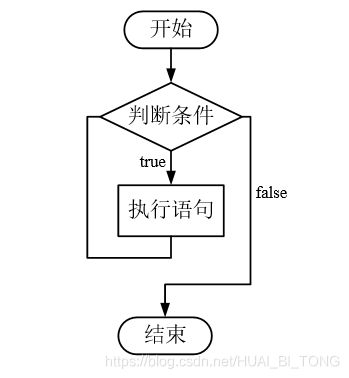
1. 程序流程结构概述
2. 选择结构
程序流程结构简介和选择结构部分的详细内容见C++基础入门(四)—— 程序流程结构(上)。
3. 循环结构
3.1 while循环语句
while循环语句的作用: 满足循环条件,执行循环语句。
while循环语句的语法:while(循环条件){ 循环语句 }
解释: 只要循环条件的结果为真,就执行循环语句。
#include0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
要注意的是,在执行循环语句时候,程序必须提供跳出循环的出口,否则出现死循环。
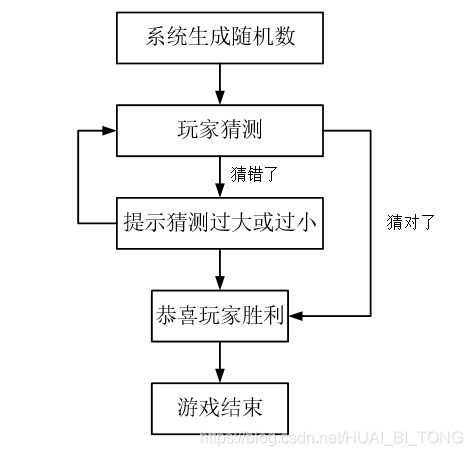
while循环练习案例: 猜数字。
案例描述: 系统随机生成一个1到100之间的数字,玩家进行猜测,如果猜错,提示玩家数字过大或过小,如果猜对恭喜玩家胜利,并且退出游戏。
#include请玩家输入一个猜测的数字:
50
猜测过大!
请玩家输入一个猜测的数字:
25
猜测过大!
请玩家输入一个猜测的数字:
13
恭喜您猜对了!
3.2 do…while循环语句
do…while循环语句的作用: 满足循环条件,执行循环语句。
do…while循环语句的语法: do{ 循环语句 } while(循环条件);
do…while循环语句与while的区别在于,不管条件的值如何,do…while都会先执行一次循环语句,再判断循环条件。
#include0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
do…while循环练习案例: 水仙花数。
案例描述: 水仙花数是指一个 3 位数,它的每个位上的数字的 3次幂之和等于它本身,例如:1^3 + 5^3+ 3^3 = 153。请利用do…while语句,求出所有3位数中的水仙花数。
练习案例的代码如下所示。
#include153
370
371
407
3.3 for循环语句
for循环语句的作用: 满足循环条件,执行循环语句。
for循环语句的语法:for(起始表达式;条件表达式;末尾循环体) { 循环语句; }
要注意的是,for循环中的表达式,要用分号进行分隔。
实例如下所示。
#include0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
详解:

总结: while , do…while, for都是开发中常用的循环语句,for循环结构比较清晰,比较常用。
for循环语句的练习案例: 敲桌子。
案例描述: 从1开始数到数字100, 如果数字个位含有7,或者数字十位含有7,或者该数字是7的倍数,我们打印敲桌子,其余数字直接打印输出。
练习案例的代码如下所示。
#include1
2
3
4
5
6
敲桌子
.
.
.
95
96
敲桌子
敲桌子
99
100
3.4 嵌套循环
嵌套循环的作用: 在循环体中再嵌套一层循环,解决一些实际问题。
例如我们想在屏幕中打印如下图片,就需要利用嵌套循环。
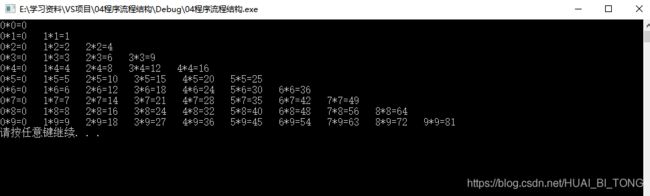
#include 嵌套循环的练习案例: 乘法口诀表。
案例描述: 利用嵌套循环,实现九九乘法表。
#include结果如下所示。
4. 跳转语句
4.1 break语句
break语句的作用: 用于跳出选择结构或者循环结构。
break语句使用的时机:
- 出现在switch条件语句中,作用是终止case并跳出switch;
- 出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前的循环语句;
- 出现在嵌套循环中,跳出最近的内层循环语句。
switch条件语句中使用break语句的实例如下所示。
#include请选择副本难度:
1.普通
2.中等
3.困难
请输入您认为的副本难度:
2
您选择的是中等难度!
循环语句中使用break语句的实例如下所示。
#include0
1
2
3
4
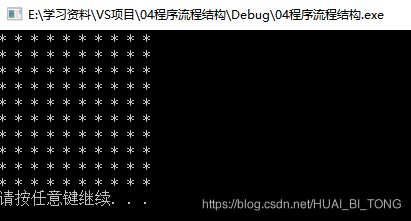
嵌套循环中使用break语句的实例如下所示。
#include * * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
4.2 continue语句
continue语句的作用: 在循环语句中,跳过本次循环中余下尚未执行的语句,并继续执行下一次循环。
continue并没有使整个循环终止,只是跳出本次循环;而break则会跳出整个循环。
实例如下所示。
#include1
3
5
7
9
4.3 goto语句
goto语句的作用: 从goto语句无条件跳转到同一函数内的另一条语句。
goto语句的语法: goto 标记;
解释: 如果标记的名称存在,执行到goto语句时,会跳转到标记的位置。
在程序中不建议使用goto语句,以免造成程序流程混乱。
实例如下所示。
#include1.xxxx
2.xxxx
4.xxxx