JAVA IO流
r我们对习IO流做一个简单的总结:
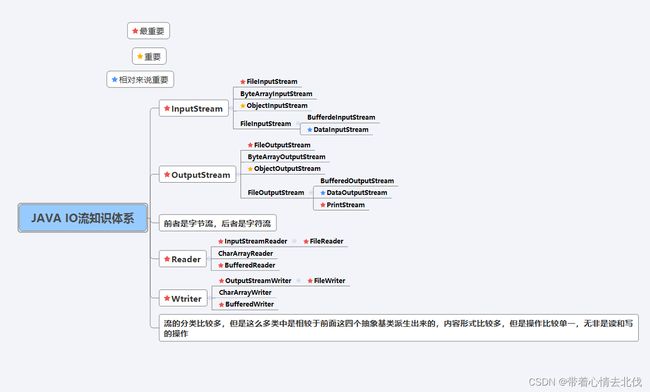
大致流程图如下
以上图片是我们这张知识的大致流程
接下来我们用代码演示其中的操作,我大致的将红色的给写一下,其他的大家在下面进行操作
InputStream的操作演示
public class InputStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
//创建对象
inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\d1.txt");
//传输数据
int read = 0;
//如果文件的数据未读取完毕,继续执行该循环
while ((read = inputStream.read()) !=-1){
//skip跳过并丢弃来自此输入流的 n字节数据
//每个五个输出字母
// inputStream.skip(5);
System.out.println((char)read);
}
// int read = inputStream.read();
// System.out.println((char) read);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}OutputStream的演示操作
public class OutputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("a2.txt");
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
//创建对象
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file,true);
//传输数据
outputStream.write(98);
outputStream.write("www.baidu.com百度".getBytes());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭对象
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
为了节约时间,我将FileInputStream和FileOutputStream进行一起的操作
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/6-04-06-8:53
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*
* 训练要点
* – 理解输入流和输出流类的概念。 – 使用FileInputStream实现读取文本文件。 – 使用FileOutputStream实现向文本文件中写数据
* ▪ 需求说明
* – 文件“我的青春谁做主.txt”位于D盘根目录下,要求将此文件的
* 内容复制到
* – C:\myFile\myPrime.txt中
*
*
* 题意大致是一个复制功能
*
* 无非是对之前知识的一个总结
* 四步骤:
* 选择合适的流
* 创建对象
* 传输数据
* 关闭流对象
*/
public class FileOutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//现将值为空
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//创建字节输入流
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\我的青春谁做主.txt");
//创建字节输出流
fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\io\\myPrime");
//创建字节数据,方便存储
byte [] b = new byte[1024];
int hasRead = 0;
while ((hasRead = fis.read(b))>0){
//每读取一次,即写入文件输入流,读了多少,就写多少
//off是偏移值,即从这个地方开始
fos.write(b,0,hasRead);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
}
printStream的操作演示
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/12-04-12-8:32
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*/
public class PrintStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("a1.txt"));
//看一下基本数据类型是否可以输出
int i =0;
double f = 900.0;
String str = "大家好,我是java小白";
ps.print(i);
ps .print(f);
ps.print(str);
ps.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Reader的演示操作(读取的功能)
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/4-04-04-9:12
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*
* 做一下内容无非是一下四步骤
* 选择合适的流
* 创建对象
* 传输数据
* 关闭对象中的流
*
*
* 显然,这个查询速度比较慢,
*/
public class ReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Reader reader = null;
try {
//创建对象
reader = new FileReader("a2.txt");
int read = 0;
while ((read = reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)read);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关闭流对象
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Wtiter的操作演示(写入的过程)
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/12-04-12-8:48
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*/
public class WriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("b5.txt");
Writer writer = null;
try {
writer = new FileWriter(file,false);
writer.write(100);
writer.write("你好,世界");
//append追加
writer.append(",");
writer.write( new char[]{'4','f','p'});
writer.append('a').append('c').append('e');
writer.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter的操作演示(这是处理流,也是字节流和字符流得桥梁)
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/7-04-07-20:43
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*
*
* 处理流之二:
* 转换流的使用,
* 1.转换流:属于字符流
* InputStreamReader:将一个字节输入流转换为字符的输入流
* OutputStreamWriter: 将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
*
* 2.作用:提供字节流和字符流的转换
*
* 3.解码:字节、字节数组-----》字符数组、字符串
* 编码:字符数组、字符串-----》字节、字节数组
*
* 4.字符集
* ASCII:美国标准信息交换码
* 用一个字节的7位也可以表示
* IS08859-1:拉丁码,欧洲码表
* 用一个字节的8位表示
* GB2312:中国的中文编码表。最多两个字节编码的所有字符
* GBK:中国的中文编码表的升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号,最多两个字节编码
* Unicode: 国际标准码,融合了目前人类使用的所有字符。为每一个字符的分配唯一的字符码,所有的文件
* UTF-8: 变长的编码方式,可用1-4个字节来表示一个字符
*/
public class InputStreamReaderTest {
/*
此时处理异常,任然使用try-catch -finally
*/
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\HelloWord.txt");
//InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用默认的字符集
//参数二指明了字符集,具体使用那个字符集,取决于文件的字符集
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"Utf-8");
char[] chars = new char[20];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(chars))!=-1){
String str = new String(chars,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
}
isr.close();
}
/*
综合的使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWrite
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
//造文件,造流
File file1 = new File("D:\\d1.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:\\di.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
//读写过程
char [] chars = new char[20];
int len;
while ((len =isr.read(chars))!=-1){
osw.write(chars,0,len);
}
//关闭流对象,资源
}
}
BufferedReader的操作演示
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/9-04-09-21:18
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*
* BufferedReader的用法有一个ReadLine()读取一行文字的操作
*
*/
public class BufferedReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fileReader = null;
BufferedReader reader=null;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\hi.txt");
reader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String str = "";
while ((str = reader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
BufferedWriter的操作演示
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/9-04-09-21:12
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*
* 总结:
* bufferedWriter独有的方法换行newLine()
*/
public class BufferedWriteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter("HelloWord.txt");
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
bufferedWriter.write(100);
bufferedWriter.write("www.baidu.com百度");
bufferedWriter.write("www.ailibab.com阿里巴巴".toCharArray());
//写入一行
bufferedWriter.newLine();
bufferedWriter.write(97);
bufferedWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
bufferedWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
File的操作演示
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/4/12-04-12-9:03
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*/
public class FileWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("b2.txt");
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter(file);
//创建字符缓冲区
fw.write(100);//此时的100对应的是d
fw.write("你好");
//......
fw.flush();
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
FileReader的演示
/**
* @Auther:Yuhai
* @Date:2022/3/31-03-31-17:55
* @Description:IntelliJ IDEA
* @version:1.0
*/
//使用FileReader读取文件
public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fis = null;
try {
//创建字节输入流
fis = new FileReader("D:\\Program Files\\IDEA\\IntelliJ IDEA 2019.2.4\\build.txt");
//创建一个长度为1024的竹简
char[] b = new char[1024];
//用于保存的实际字节数
int hasRead = 0;
//使用循环来重复取水的过程
while ((hasRead = fis.read(b))>0){
//取出竹简中的水滴(字节),将数组转换成字符串进型输出
System.out.println(new String(b,0,hasRead));
}
}catch (IIOException | FileNotFoundException e ){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
fis.close();
}
}
}
总结: 学这么多IO流类,其实他们的内容比较复杂,但是形式比较统一,无非是读和写,都是从前面四个抽象基类演变过来的。在我们实际应用中,使用IO流的时候,应当选择适合自己的流来进行操作。