Spring Scope
Spring中五种 Scope域
singleton,容器启动时创建(未设置延迟),容器关闭时销毁【单例】prototype,每次使用时创建,不会自动销毁,需要调用 DefaultListableBeanFactory.destroyBean(bean) 销毁【原型】request,每次请求用到此 bean 时创建,请求结束时销毁(每次请求来都会创建一个request域对象放到web request域当中,请求结束会被销毁)session,每个会话用到此 bean 时创建,会话结束时销毁(会话创建时会把session对象创建出来放入web session中,会话结束时销毁,会话有默认销毁时间可以设置,长时间不访问自动销毁)application,web 容器用到此 bean 时创建,容器停止时销毁(ServletContext创建后,首次用bean将其放入ServletContext中,销毁Spring未实现)
单例Bean注入其他Scope Bean不做处理,会出现Scope生效的情况,需要在注入bean对象上添加@Lazy注解
演示:
不同scope域的bean
@Scope("application")
@Component
public class BeanForApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BeanForApplication.class);
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
log.debug("destroy");
}
}
@Scope("session")
@Component
public class BeanForSession {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BeanForSession.class);
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
log.debug("destroy");
}
}
@Scope("request")
@Component
public class BeanForRequest {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BeanForRequest.class);
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
log.debug("destroy");
}
}
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Lazy
@Autowired
private BeanForRequest beanForRequest;
@Lazy
@Autowired
private BeanForSession beanForSession;
@Lazy
@Autowired
private BeanForApplication beanForApplication;
@GetMapping(value = "/test", produces = "text/html")
public String test(HttpServletRequest request, HttpSession session) {
ServletContext sc = request.getServletContext();
String sb = ""
+
"" + "request scope:" + beanForRequest + "" +
"" + "session scope:" + beanForSession + "" +
"" + "application scope:" + beanForApplication + "" +
"";
return sb;
}
}
分析 - singleton 注入其它 scope 失效
以单例注入多例为例
有一个单例对象 E
@Component
public class E {
@Autowired
private F1 f1;
public F1 getF1() {
return f1;
}
}
要注入的对象 F1 期望是多例
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class F1 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(F.class);
public F1() {
log.info("F1()");
}
}
测试:
E e = context.getBean(E.class);
log.debug("{}", e.getF1());
log.debug("{}", e.getF1());
输出:
com.lkl.spring.chapter8.sub.F1@72d1ad2e
com.lkl.spring.chapter8.sub.F1@72d1ad2e
发现它们是同一个对象,而不是期望的多例对象
对于单例对象来讲,依赖注入仅发生了一次,后续再没有用到多例的 F1,因此 E 用的始终是第一次依赖注入的 F
e 创建
e set 注入 f
f 创建
解决
- 仍然使用
@Lazy 生成代理 - 代理对象虽然还是同一个,但当每次使用代理对象的任意方法时,由代理创建新的 f 对象
使用f方法
使用f方法
使用f方法
e 创建
e set 注入 f代理
f 创建
f 创建
f 创建
@Component
public class E {
@Autowired
@Lazy
public void setF(F f) {
this.f = f;
log.info("setF(F f) {}", f.getClass());
}
// ...
}
注意
- @Lazy 也可以加在成员变量上,但加在 set 方法上的目的是可以观察输出,加在成员变量上就不行了
- @Autowired 加在 set 方法的目的类似
E e = context.getBean(E.class);
log.debug("{}", e.getF1().getClass());
log.debug("{}", e.getF1());
log.debug("{}", e.getF1());
输出:
class com.lkl.spring.chapter8.sub.F1$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$278636ac
com.lkl.spring.chapter8.sub.F1@9597028
com.lkl.spring.chapter8.sub.F1@4efbca5a
f 对象的类型是代理类型
解决方法
-
单例注入其它 scope 的四种解决方法
- @Lazy
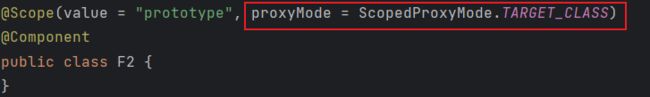
- @Scope(value = “prototype”, proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
- ObjectFactory
- ApplicationContext
-
解决方法虽然不同,但理念上殊途同归:
都是推迟其它 scope bean 的获取
@Component
public class E {
// 方法一
@Lazy
@Autowired
private F1 f1;
// 方法二
@Autowired
private F2 f2;
// 方法三
@Autowired
private ObjectFactory<F3> f3;
// 方法四
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext context;
public F1 getF1() {
return f1;
}
public F2 getF2() {
return f2;
}
public F3 getF3() {
return f3.getObject();
}
public F4 getF4() {
return context.getBean(F4.class);
}
}
前两个使用代理对象解决
第三种通过对象工厂,通过对象工厂获取对象,工厂可以识别对象多例类型
最后一种,直接通过ApplicationContext容器获取多例对象
使用代理对象会有点性能损耗,后面两种方法会好些