分享几个不常用的web api
分享几个不常用的web api
屏幕捕获
顾名思义,屏幕捕获 API 允许我们捕获屏幕内容,从而使构建屏幕录制的过程变得轻而易举。
在示例中我们使用video标签来显示捕获屏幕内容。
<video id="preview" autoplay>
不支持HTML5
video>
<button id="start" class="btn">开始录制button>
<script>
const previewElem = document.getElementById("preview");
const startBtn = document.getElementById("start");
async function startRecording() {
previewElem.srcObject =
await navigator.mediaDevices.getDisplayMedia({
video: true,
audio: true,
});
}
startBtn.addEventListener("click", startRecording);
script>
内容分享
该API允许将网页中的文本、链接甚至文件共享给设备上安装的其他应用程序。
async function shareHandler() {
navigator.share({
title: "share title",
text: "share text",
url: "share url",
});
}
注意: 要使用Share API,需要用户的交互。例如,按钮单击或触摸事件。
剪切板
这个API允许我们在剪贴板中读取和写入数据。这对于实现复制到剪贴板功能非常有用。
async function copyHandler() {
const text = "text";
navigator.clipboard.writeText(text);
}
全屏
我们通常都是使用F11按钮来实现网页全屏,不过我们也可以使用js来实现。
async function enterFullscreen() {
await document.documentElement.requestFullscreen();
}
async function exitFullscreen() {
await document.exitFullscreen();
}
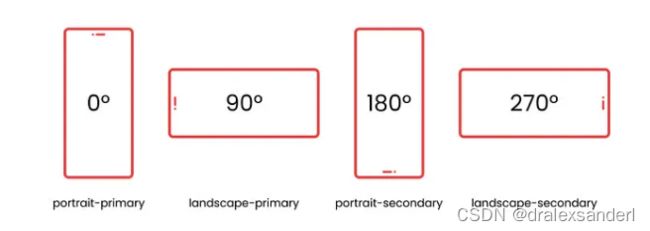
屏幕方向
该API允许检查屏幕的当前方向,甚至将其锁定到特定方向。
// 锁定方向
async function lockHandler() {
await screen.orientation.lock("portrait");
}
function releaseHandler() {
screen.orientation.unlock();
}
// 获取屏幕方向
function getOrientation() {
return screen.orientation.type;
}
屏幕方向有以下几个值:
屏幕唤醒锁定
屏幕唤醒锁定 API 提供了一种在应用程序需要继续运行时防止设备变暗或锁定屏幕的方法。
默认情况下,大多数设备会在指定时间后关闭屏幕,以延长硬件的使用寿命。现代设备这样做是为了节省电池电量。虽然这是一个有用的功能,但某些应用程序需要屏幕保持唤醒状态才能发挥最大作用。
let wakeLock = null;
async function lockHandler() {
wakeLock = await navigator.wakeLock.request("screen");
}
async function releaseHandler() {
await wakeLock.release();
wakeLock = null;
}
注意: 仅当页面已在屏幕上可见时,您才能使用屏幕唤醒锁定 API 。否则,它会抛出错误。
观察特定元素
这个API允许检测元素何时进入或离开视口。这对于实现无限滚动非常有用。
const box1 = document.querySelector("#box1");
const box2 = document.querySelector("#box2");
const box1Status = document.querySelector("#box1-status");
const box2Status = document.querySelector("#box2-status");
const box1Observer = new IntersectionObserver(
(entries) => {
entries.forEach((item) => {
// `intersectionRatio`为目标元素的可见比例,大于`0`代表可见
if (item.intersectionRatio > 0) {
box1Status.innerText = "visible";
} else {
box1Status.innerText = "invisible";
}
});
},
{ root: document }
);
const box2Observer = new IntersectionObserver(
(entries) => {
entries.forEach((item) => {
// `intersectionRatio`为目标元素的可见比例,大于`0`代表可见
if (item.intersectionRatio > 0) {
box2Status.innerText = "visible";
} else {
box2Status.innerText = "invisible";
}
});
},
{ root: box1 }
);
box1Observer.observe(box1);
box2Observer.observe(box2);
<section class="flex top-fixed">
<div class="flex">BOX1:div>
<div class="flex" id="box1-status">invisiblediv>
<div class="flex"> BOX2:div>
<div class="flex" id="box2-status">invisiblediv>
section>
<div class="box1-placeholder">div>
<div id="box1">
<div class="box2-placeholder">div>
<div id="box2">div>
<div class="box2-placeholder">div>
div>
<div class="box1-placeholder">div>