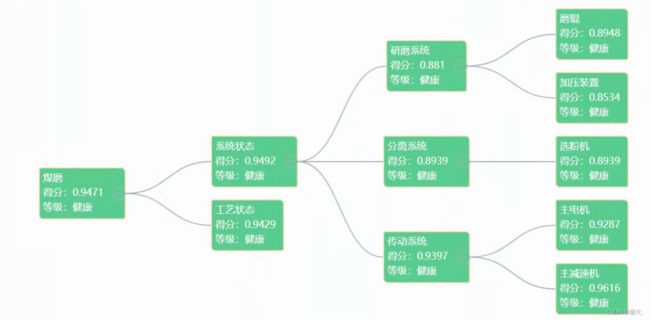
基于设备状态测点进行健康度评估的算法
示例算法:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
# 设备健康度评价算法
import json
import numpy as np
import math
# 归一化Normalized-健康度评价
from numpy import array, around
np.set_printoptions(precision=4, suppress=False)
# 最小阈值、最大阈值、标准值、实时值、数据指标类型
# 标准化 基于指标类型计算
def normalization(minValue, maxValue, tandardValue, value, type):
if minValue == None or maxValue == None or tandardValue == None or value == None or type == None:
return None
# 标准值指标
if type == 3:
if minValue <= value < tandardValue:
return (value - minValue) / (tandardValue - minValue)
elif tandardValue <= value <= maxValue:
return (maxValue - value) / (maxValue - tandardValue)
else:
return 0.0
# 正向指标(越大越好)
elif type == 2:
health_value = (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue)
if health_value > 1:
health_value = 1
return health_value
# 逆向指标(越小越好)
elif type == 1:
health_value = 1 - (value - minValue) / (maxValue - minValue)
if health_value > 1:
health_value = 1
return health_value
# 指标健康度
def indicator_health(args):
data_array = array(args['data'])
rows = data_array.shape[0]
health_list = []
for i in range(0, rows):
# 指标数据(最小阈值,最大阈值,标准值,测量值,报警值,指标类型)
health = normalization(data_array[i][0], data_array[i][1], data_array[i][2], data_array[i][3], data_array[i][5])
# print('指标测量数据:{0}----{1}'.format(data_array[i], health))
if health == None:
health_list.append(None)
else:
if health < 0:
health = 0
health_list.append(round(health, 4))
print('指标健康度:{0}'.format(health_list))
return array(health_list).tolist()
# 层次权重
def hierarchy_weight(args):
data_array = array(args['data'])
# 特征值计算
lamda = np.linalg.eig(data_array)
# for i in range(len(lamda[0])):
# print('特征值:{0}\n对应的特征向量:\n{1}\n'.format(lamda[0][i], np.transpose([lamda[1][:, i]])))
index = np.argmax(lamda[0])
lamda_max = np.real(lamda[0][index])
vector = lamda[1][:, index]
# 特征向量
vector_final = np.transpose((np.real(vector)))
# 归一化
one_final = vector_final / np.sum(vector_final)
print('层次权重:{0}'.format(one_final.tolist()))
print()
# print('最大特征值为:{0}\n对应的特征向量:\n{1}\n特征归一化权重值:{2}'.format(lamda_max, vector_final, one_final))
return around(one_final, 4).tolist()
# 熵权化
# 定义熵值法函数
def entropy_weight(args):
data_array = array(args['data'])
print("data_array: ", data_array)
'''熵值法计算变量的权重'''
# 行列转换
x = data_array.T
'''
如果数据实际不为零,则赋予最小值
if x==0:
x=0.00001
else:
pass
'''
# 求k
rows = x.shape[0] # 行
cols = x.shape[1] # 列
if rows == cols == 1:
return [1]
k = 1.0 / math.log(rows)
print("x: ", x)
# 矩阵计算--
# 信息熵
x = array(x)
lnf = [[None] * cols for i in range(rows)]
lnf = array(lnf)
for i in range(0, rows):
for j in range(0, cols):
if x[i][j] == None or (x[j] == None).any():
lnfij = 0.0
else:
print("x[i][j]: ", x[i][j])
print("x[i]: ", x[i])
# if (x[j] == None).any():
# lnfij = 0.0
if (x[j] < 0).any() or x[i][j] <= 0:
lnfij = 0.0
else:
p = x[i][j] / x.sum(axis=0)[j]
lnfij = math.log(p) * p
print("lnfij: ", lnfij)
lnf[i][j] = lnfij
E = lnf
print("lnf: ", lnf)
# 将nan空值转换为0
ej = -k * (E.sum(axis=0))
# 计算每种指标的信息熵
d = (1 - ej) / np.sum(1 - ej)
# 计算冗余度
# d = 1 - E.sum(axis=0)
print("d: ", d)
# 计算各指标的权重
w = [[None] * 1 for i in range(cols)]
for j in range(0, cols):
wj = d[j] / sum(d)
w[j] = round(wj, 4)
# 计算各样本的综合得分,用最原始的数据
print('熵权法权重:{0}'.format(w))
return w
# 组合常权重
def combination_weight(args):
data_array = array(args['data'])
# 行列转换
x = data_array.T
# 层次权重
hierarchyData = x[0]
# 熵权重
entropyData = x[1]
# hierarchyData = array(args['hierarchyData'])
# entropyData = array(args['entropyData'])
# 权重排序
weight_sort = hierarchyData[np.argsort(hierarchyData)]
print("weight_sort:", weight_sort)
n = np.size(weight_sort)
p = 0
for i in range(n):
p += (i + 1) * weight_sort[i]
print("p:", p)
# 线性系数
a = 1
if n != 1:
a = round(2 / (n - 1) * p - (n + 1) / (n - 1), 4)
print('线性系数:{0}'.format(a))
combination_data = hierarchyData * a + entropyData * (1 - a)
print('组合常权重:{0}'.format(combination_data))
return around(combination_data, 4).tolist()
# 变权权重(权重,均衡系数)
def variable_weight(args):
data_array = array(args['data'])
# 行列转换
x = data_array.T
# 权重
weight = x[0]
# 均衡系数
equalization = x[1]
# weight = array(args['weight'])
# equalization = array(args['equalization'])
n = np.size(weight)
w_weight = []
for i in range(n):
p = 0
for j in range(n):
p += equalization[j] * weight[j]
w_weight.append(around(p, 4))
print('变权商:{0}'.format(w_weight))
# 变权权重
x = []
for i in range(n):
x.append(around(equalization[i] * weight[i] / w_weight[i], 4))
print('变权权重:{0}'.format(x))
# print(x.sum)
return x
# [0.1928, 0.4692, 0.2657, 0.0723]
# 指标均衡系数
def indicator_equilibrium(args):
data_array = array(args['data_array'])
print(data_array)
k = array(args['k'])
rows = data_array.shape[0]
coefficient_list = []
for i in range(0, rows):
# 指标数据(最小阈值,最大阈值,标准值,测量值,报警值)
coefficient = equilibrium_coefficient(data_array[i][0], data_array[i][1], data_array[i][2], data_array[i][3], k)
# print('指标测量数据:{0}----{1}'.format(data_array[i], health))
coefficient_list.append(round(coefficient, 4))
print('指标均衡系数向量:{0}'.format(coefficient_list))
return coefficient_list
# 均衡系数(最小值、最大值、惩戒阈值、测量值、系数)
def equilibrium_coefficient(min_data, max_data, threshold, data, k):
if (min_data == None or max_data == None or threshold == None or data == None):
return 1
else:
return round(math.exp(abs((data - threshold) / (max_data - min_data)) * k), 4)
# 健康度计算
def health_calculation(weight, health_data):
n = np.size(weight)
p = 0
for i in range(n):
p += weight[i] * health_data[i]
print('健康度:{0}'.format(p))
return round(p, 4)
# 白化权函数
def gray_cloud_cluster(args):
health_data = array(args['data'])
weight = array(args['weight'])
n = np.size(health_data)
# 聚类系数向量
health_cluster = []
# 白化权值
whitening_weight = []
for i in range(n):
x = health_data[i]
x_health = []
if 0 <= x <= 0.3:
x_health.append(math.exp(pow(x, 2) / (2 * pow(0.1, 2))))
else:
x_health.append(0)
if 0.1 <= x <= 0.5:
x_health.append(math.exp(pow((x - 0.3), 2) / (2 * pow(0.067, 2))))
else:
x_health.append(0)
if 0.3 <= x <= 0.7:
x_health.append(math.exp(pow((x - 0.5), 2) / (2 * pow(0.067, 2))))
else:
x_health.append(0)
if 0.5 <= x <= 0.9:
x_health.append(math.exp(pow((x - 0.7), 2) / (2 * pow(0.067, 2))))
else:
x_health.append(0)
if 0.7 <= x <= 1.0:
x_health.append(math.exp(pow((x - 1.0), 2) / (2 * pow(0.1, 2))))
else:
x_health.append(0)
whitening_weight.append(x_health)
whitening_weight = np.array(whitening_weight)
print('白化权值:{0}'.format(whitening_weight))
rows = whitening_weight.shape[0] # 行
cols = whitening_weight.shape[1] # 列
for j in range(0, cols):
data = 0
for i in range(0, rows):
data += whitening_weight[i][j] * weight[i]
health_cluster.append(data)
# health_cluster= whitening_weight*weight
print('聚类系数向量:{0}'.format(health_cluster))
return health_cluster
# 向量归一化
def vector_normalization(args):
data = array(args['data'])
var = np.mat(data)
# 创建向量集合
res = np.zeros_like(var)
norm = np.sum(var)
for i in range(var.shape[0]):
for j in range(var.shape[1]):
res[i, j] = var[i, j] / norm
print('归一化向量:{0}'.format(res))
return res.tolist()
# index_data3 = {"data": [[0.3209, 0.3209, 0.3209], [0.4928, 0.4928, 0.4928], [0.8597, 0.8597, 0.8597]]}
# index_data3 = {"data": [[0.9288,0.9743, 0.8543], [0.9333, 0.9000, 0.7333], [0.8800, 0.8400, 0.8000]]}
# index_data3 = {"data": [[0.5396, 0.1924], [0.2970, 0.7077], [0.1634, 0.0999]]}
# # (0.5396, 0.2970, 0.1634)
# print(combination_weight(index_data3))
#(最小阈值,最大阈值,标准值,测量值,报警值,指标类型)
index_data3 ={"data":[[0.8324,0.8324,0.8324],[0.9857,0.9857,0.9857]]}
entropy_weight(index_data3)