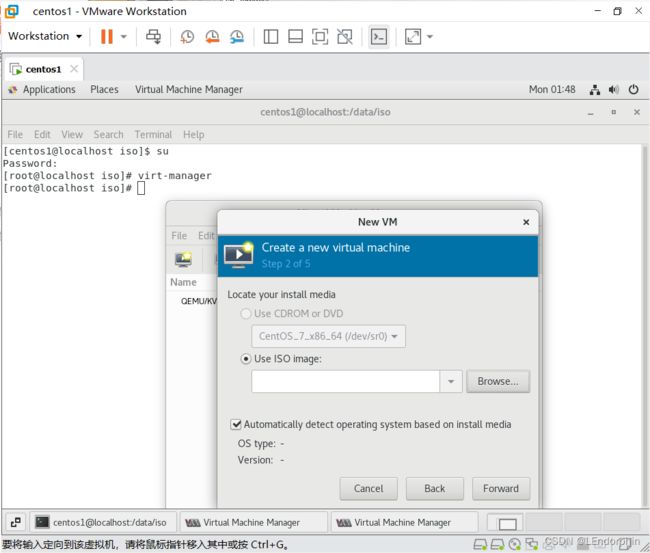
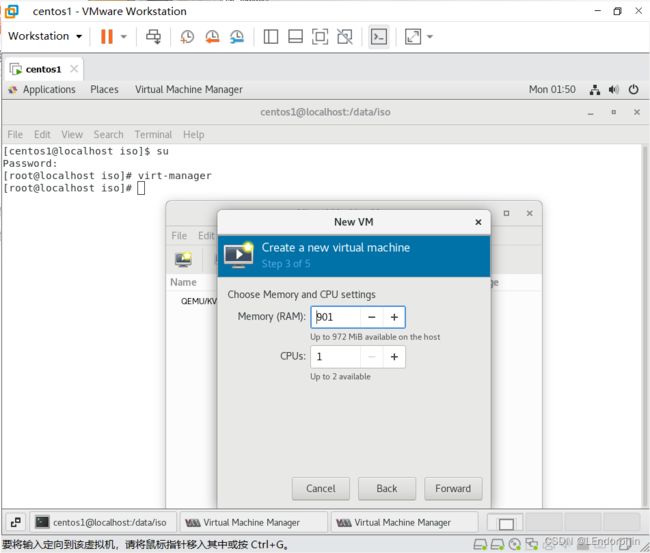
KVM虚拟化安装的两种方式
现在说一下什么叫嵌套虚拟化,就是虚拟机里面再虚拟化(出来机器),就叫嵌套虚拟化。
因为嵌套虚拟化需要使用图形化界面,所以安装机器时最好在安装时勾选上对应的框。

或者
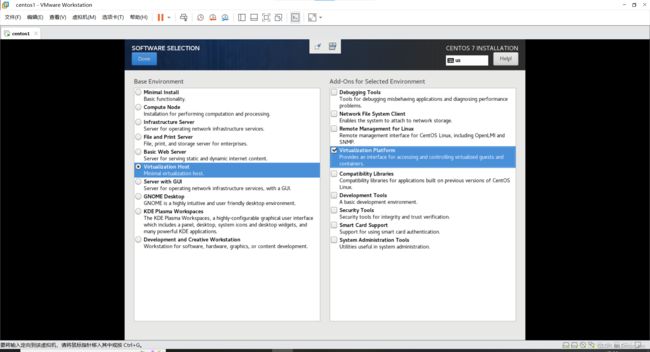
(如果安装忘记勾选,在后面也有使用命令行安装成功的办法。)
然后,我们现在继续
[root@localhost ~]# yum grouplist
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.njupt.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.njupt.edu.cn
Installed Environment Groups:
Server with GUI
Available Environment Groups:
Minimal Install
Compute Node
Infrastructure Server
File and Print Server
Basic Web Server
Virtualization Host
GNOME Desktop
KDE Plasma Workspaces
Development and Creative Workstation
Available Groups:
Compatibility Libraries
Console Internet Tools
Development Tools
Graphical Administration Tools
Legacy UNIX Compatibility
Scientific Support
Security Tools
Smart Card Support
System Administration Tools
System Management
Done
#上面显示已经下载,如果没有下载,可以使用下面命令下载
[root@localhost ~]# yum groupinstall "Server with GUI"
然后,修改机器,让机器能在启动的时候进入图形化界面,方便后面我们在使用服务端登录的时候能进入图形化界面
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl set-default graphical.target
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/default.target to /usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.target.
[root@localhost ~]# lscpu
#如果下面出现Virtualization: VT-x 说明这台机器已经支持虚拟化
#或
[root@localhost ~]# egrep 'svm|vmx' /proc/cpuinfo
#如果下面出现svm或者vmx光亮字,说明也支持虚拟化了
如果以上命令下面没有出现相关显示,说明不支持虚拟化
接下来,继续安装KVM软件
[root@localhost ~]# yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img libvirt
[root@localhost ~]# yum install virt-install libvirt-python virt-manager python-virtinst libvirt-client
#libvirt 关于虚拟机管理的
#virt 关于虚拟机安装克隆的
#qemu-kvm 关于管理虚拟机磁盘的
#virt-install 是关于KVM命令行的
#virt-manage 是关于图形化的
#libirt-lient 是关于客户端的
然后reboot重启
这样虚拟化环境就准备好了。
下面开始创建虚拟机
首先,准备一块硬盘,准备存放ISO镜像和虚拟机文件。
分区,格式化,挂载
[root@localhost centos1]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 30G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 300M 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
└─sda3 8:3 0 27.7G 0 part /
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
sr0 11:0 1 4.4G 0 rom /run/media/centos1/CentOS 7 x86_64
[root@localhost centos1]# gdisk /dev/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Partition table scan:
MBR: not present
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: not present
Creating new GPT entries.
Command (? for help): n
Partition number (1-128, default 1):
First sector (34-41943006, default = 2048) or {+-}size{KMGTP}:
Last sector (2048-41943006, default = 41943006) or {+-}size{KMGTP}:
Current type is 'Linux filesystem'
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300):
Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem'
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): EAEEFB33-F262-4012-BC01-B7904EA294DE
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 2014 sectors (1007.0 KiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 41943006 20.0 GiB 8300 Linux filesystem
Command (? for help): wq
Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING
PARTITIONS!!
Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y
OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdb.
The operation has completed successfully.
[root@localhost centos1]# mkdir /data
#全部格式化,一直按回车,最后保存
[root@localhost centos1]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1
meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=1310655 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=5242619, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
[root@localhost centos1]# mkdir /data
blkid /dev/sdd
echo 'UUID="6949c146-8f65-472b-a958-88191be0b6b8" /data xfs defaults 0 0' >> /etc/fstab
[root@localhost centos1]# mount -a
[root@localhost centos1]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 471M 0 471M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 15M 472M 4% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda3 28G 4.4G 24G 16% /
/dev/sda1 297M 152M 145M 52% /boot
tmpfs 98M 32K 98M 1% /run/user/1000
/dev/sr0 4.4G 4.4G 0 100% /run/media/centos1/CentOS 7 x86_64
/dev/sdb1 20G 33M 20G 1% /data
创建虚拟机,得有ISO镜像,把ISO镜像上传上去才行
[root@localhost centos1]# mkdir /data/iso
[root@localhost centos1]# cd /data/iso
[root@localhost iso]# ll
total 4601856
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4712300544 Aug 29 01:43 CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-2009.iso
可以选择找一个镜像传上去也可以,mini的也行
第一种安装嵌套虚拟机方式,图形化界面

有四种安装方式,这里我选择本地安装
第二种是依赖网络环境安装,第三种是PXE安装,也就是集群安装,第四种是导入安装
硬盘可以选择自定义存储,右下角browse浏览,选择本地data目录,然后创建vm目录,左上角起文件名为vm1.qcow2,是一种虚拟机磁盘文件
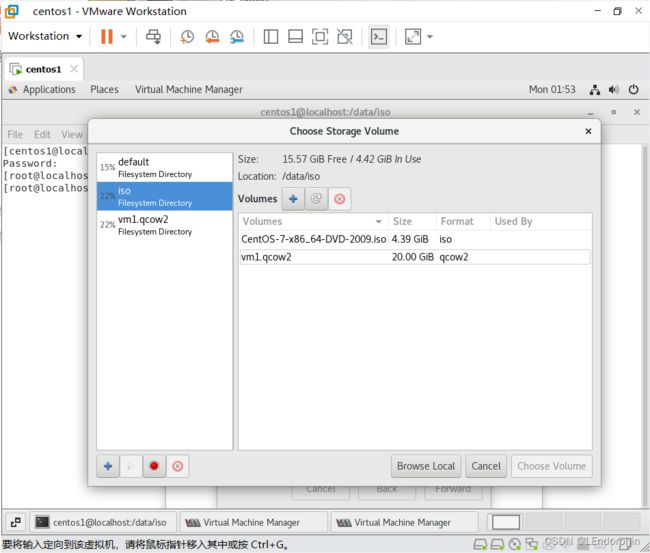
网络使用默认配置,然后完成,接下来跟装一个系统没什么区别
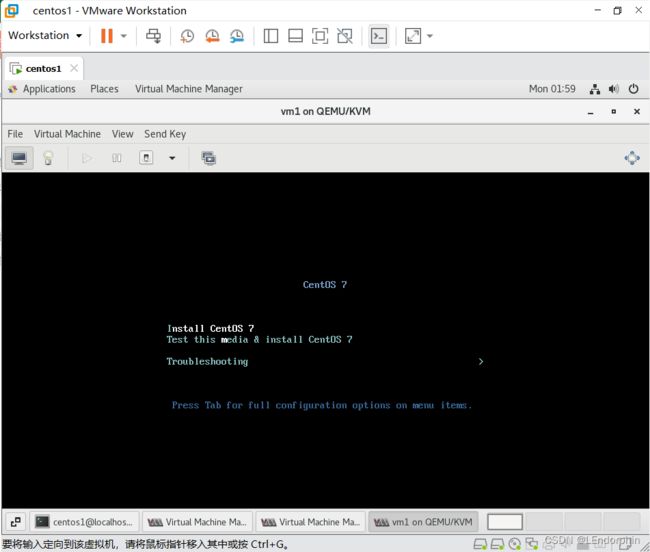
现在记住,这里安装的时候最好勾选上三个框



这里有没有发现多了一个特殊的网卡,virbr0
这实际上是NAT模式。这是跟KVM虚拟机同一个网段的。

点击KVM窗口的view,打开details,就可以清楚知道KVM的情况,还可以据此作出调整
第二种安装方式,命令行安装,优点是效率比图形化高很多(kvm-install)

监听的VNC端口是5940
VCPUS cpu数量
ram 内存
disk 磁盘位置,大小
网络的网卡名字默认是virbro
cdrom 表示安装方式是用磁盘里的文件装KVM
更多详情输入命令virt-install --help
[root@localhost vm2]# virt-install -n winxp --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0,port=5940,keymap=en_us --ram=384 --vcpus=1 --disk path=/data/vm2/winxp.qcow2,size=3,format=qcow2 --bridge=virbr0 --cdrom=/data/iso/winxp_1909.iso
WARNING No operating system detected, VM performance may suffer. Specify an OS with --os-variant for optimal results.
WARNING Unable to connect to graphical console: virt-viewer not installed. Please install the 'virt-viewer' package.
WARNING No console to launch for the guest, defaulting to --wait -1
Starting install...
Allocating 'winxp.qcow2' | 3.0 GB 00:00:00
Domain installation still in progress. Waiting for installation to complete.
#然后等着机器安装成功
然后,复制会话,打开窗口,查看本机5940端口是否在监听
[root@localhost vm2]# netstat -lnutp | grep 5940
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5940 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6263/qemu-kvm
然后,使用vnc工具连接进行安装测试,至此就安装成功了.
这种命令行方式安装,比图形化界面安装高效简洁,而且比较灵活,就是没有图形化界面美观。
这就看个人需求了。