Fater RCNN 试着加入注意力机制模型
最近一直状态不好,从什么时候开始的呢,自己也忘啦,积极的调整和永远的相信自己可以~废话不多说
一、源码中给出的resnet50_fpn_backbone,解析
1.backbone的body层,也就是resnet层提取的输出
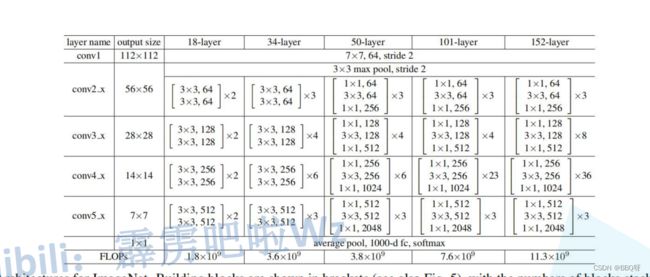
Resnet中的基本组成单元residual结构,分为左右两种,50用的是后面一种bottleneck结构50 101 152的区别其实就是每组layer里面bottleneck的个数不同。
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, blocks_num, num_classes=1000, include_top=True, norm_layer=None):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self._norm_layer = norm_layer
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64#通过Maxpooling之后的得到的特征矩阵的深度
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)#224*224*3 -> 112*112*64
self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)#56*56*64
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)#一张3*224*224的图像经过layer4之后会变为2048*7*7
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
#Bottleneck, block_num = [3, 4, 6, 3],channel代表该层的第一个conv的输出通道数,channel * block.expansion代表该层的输出通道数,stride代表该总的layer是否会stride
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
norm_layer = self._norm_layer#batch norm
downsample = None
#self.in_channel代表每层输入的通道数,channel * block.expansion就是该层输出通道数
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
norm_layer(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel, downsample=downsample,
stride=stride, norm_layer=norm_layer))
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel, norm_layer=norm_layer))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)#将索引为 start_dim 和 end_dim 之间(包括该位置)的数量相乘,其余位置不变。因为默认 start_dim=0,end_dim=-1,所以 torch.flatten(t) 返回只有一维的数据
x = self.fc(x)
return x
resnet_backbone = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],#50Layer得Resnet
include_top=False)从源码可以看到它的结构,[3,4,6,3]从而选择了为50层的结构。这里和之前单层baakbone不同的是,因为要的是多层输出,所以returnlayers这个字典会有多组值。
return_layers = {'layer1': '0', 'layer2': '1', 'layer3': '2', 'layer4': '3'}#这个是用来告诉要提取哪些层的输出然后这里又构造了一个类,类不重要,里面的第一步分内容是这个,
body = IntermediateLayerGetter(backbone, return_layers=return_layers)#类似于pytoch自带的create_feature_extractor,但是这个只能定位到子模块第一层其实和上节课的create_feature_extractor函数作用差不多。这样我们就提取到了resnet50的四个特征层的输出。
2.backbone的fpn层层,也就是resnet层提取的输出之后,进行特征融合和backbone的最后输出
如图,也就是初始化函数中8个卷积层,forward()函数中再加3次上采样和一次Maxpool.
经过fpn的输出其实和body输出一样是字典的形式,只不过多了一个"pool"
FPN的八个卷积核,左边四个的输入输出,输入为in_channels_list,输出只有一个为
out_channels,后面四个卷积核输入输出都为out_channels。
3.将得到的baakbone作为参数传入FasterRCNN作为其中一个形参创建FasterRCNN模型。
model = FasterRCNN(backbone=backbone, num_classes=21)二、换MobileNet V3+FPN(MBCONV)
1.MBCONV模块
2.代码第一部分:截取主干网络
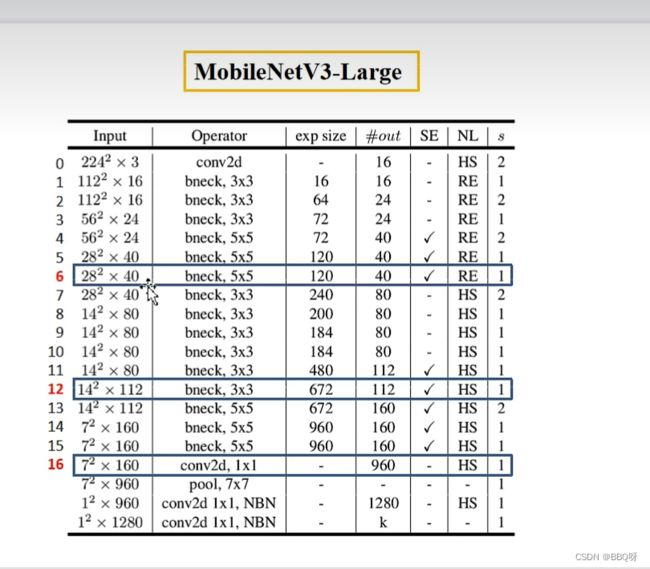
monile_v3_backbone = torchvision.models.mobilenet_v3_large()
return_layers = {"features.6": "0" , "features.12": "1" , "features.16": "2"}
monile_v3_backbone = create_feature_extractor(monile_v3_backbone, return_nodes=return_layers)InvertedResidualConfig模块:
class InvertedResidualConfig:
# Stores information listed at Tables 1 and 2 of the MobileNetV3 paper
def __init__(self, input_channels: int, kernel: int, expanded_channels: int, out_channels: int, use_se: bool,
activation: str, stride: int, dilation: int, width_mult: float):
self.input_channels = self.adjust_channels(input_channels, width_mult)
self.kernel = kernel
self.expanded_channels = self.adjust_channels(expanded_channels, width_mult)
self.out_channels = self.adjust_channels(out_channels, width_mult)
self.use_se = use_se
self.use_hs = activation == "HS"
self.stride = stride
self.dilation = dilation
@staticmethod
def adjust_channels(channels: int, width_mult: float):
return _make_divisible(channels * width_mult, 8)
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module):
# Implemented as described at section 5 of MobileNetV3 paper
def __init__(self, cnf: InvertedResidualConfig, norm_layer: Callable[..., nn.Module],
se_layer: Callable[..., nn.Module] = partial(SElayer, scale_activation=nn.Hardsigmoid)):
super().__init__()
if not (1 <= cnf.stride <= 2):
raise ValueError('illegal stride value')
self.use_res_connect = cnf.stride == 1 and cnf.input_channels == cnf.out_channels
layers: List[nn.Module] = []
activation_layer = nn.Hardswish if cnf.use_hs else nn.ReLU
# expand
if cnf.expanded_channels != cnf.input_channels:
layers.append(ConvNormActivation(cnf.input_channels, cnf.expanded_channels, kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer))
# depthwise
stride = 1 if cnf.dilation > 1 else cnf.stride
layers.append(ConvNormActivation(cnf.expanded_channels, cnf.expanded_channels, kernel_size=cnf.kernel,
stride=stride, dilation=cnf.dilation, groups=cnf.expanded_channels,
norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer))
if cnf.use_se:
squeeze_channels = _make_divisible(cnf.expanded_channels // 4, 8)
layers.append(se_layer(cnf.expanded_channels, squeeze_channels))
# project
layers.append(ConvNormActivation(cnf.expanded_channels, cnf.out_channels, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=None))
self.block = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.out_channels = cnf.out_channels
self._is_cn = cnf.stride > 1
def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:
result = self.block(input)
if self.use_res_connect:
result += input
return result self.features = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(lastconv_output_channels, last_channel),
nn.Hardswish(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(last_channel, num_classes),
)
2.确定FPN层
in_channels_list = [40,112,960]
out_channels = 256
backbone = fpn.BackboneWithFPN(monile_v3_backbone,return_layers,in_channels_list,out_channels)3.确定anchor_generator
anchor_sizes=((64,),(128,),(256,),(512,)) # 这里是元组里面的一组,所以是生成3*4=12中anchor
aspect_ratios=((0.5, 1.0, 2.0),)*len(anchor_sizes)
anchor_generator = AnchorsGenerator(sizes=anchor_sizes, # 这里是元组里面的一组,所以是生成3*4=12中anchor
aspect_ratios=aspect_ratios)4.确定roi_pooler
roi_pooler = torchvision.ops.MultiScaleRoIAlign(featmap_names=['0','1','2'], # 在哪些特征层上进行roi pooling
output_size=[7, 7], # roi_pooling输出特征矩阵尺寸
sampling_ratio=2) # 采样率5.生成FasterRCNN
model = FasterRCNN(backbone=backbone,
num_classes=num_classes,
rpn_anchor_generator=anchor_generator,
box_roi_pool=roi_pooler)shen三、
stage4 5 以及最后1*1卷积的输出
#efficientB0
def create_model(num_classes):
monile_v3_backbone = torchvision.models.efficientnet_b0()
return_layers = {"features.3": "0" , "features.5": "1" , "features.8": "2"}
monile_v3_backbone = create_feature_extractor(monile_v3_backbone, return_nodes=return_layers)
img = torch.randn(1,3,224,224)
# outputs = monile_v3_backbone(img)
in_channels_list = [40,112,1280]
out_channels = 256
backbone = fpn.BackboneWithFPN(monile_v3_backbone,return_layers,in_channels_list,out_channels)
anchor_sizes=((64,),(128,),(256,),(512,)) # 这里是元组里面的一组,所以是生成3*4=12中anchor
aspect_ratios=((0.5, 1.0, 2.0),)*len(anchor_sizes)
anchor_generator = AnchorsGenerator(sizes=anchor_sizes, # 这里是元组里面的一组,所以是生成3*4=12中anchor
aspect_ratios=aspect_ratios)
roi_pooler = torchvision.ops.MultiScaleRoIAlign(featmap_names=['0','1','2'], # 在哪些特征层上进行roi pooling
output_size=[7, 7], # roi_pooling输出特征矩阵尺寸
sampling_ratio=2) # 采样率
model = FasterRCNN(backbone=backbone,
num_classes=num_classes,
rpn_anchor_generator=anchor_generator,
box_roi_pool=roi_pooler)
return modelclass MBConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cnf: MBConvConfig, stochastic_depth_prob: float, norm_layer: Callable[..., nn.Module],
se_layer: Callable[..., nn.Module] = SqueezeExcitation) -> None:
super().__init__()
if not (1 <= cnf.stride <= 2):
raise ValueError('illegal stride value')
self.use_res_connect = cnf.stride == 1 and cnf.input_channels == cnf.out_channels
layers: List[nn.Module] = []
activation_layer = nn.SiLU
# expand
expanded_channels = cnf.adjust_channels(cnf.input_channels, cnf.expand_ratio)
if expanded_channels != cnf.input_channels:
layers.append(ConvNormActivation(cnf.input_channels, expanded_channels, kernel_size=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer))
# depthwise
layers.append(ConvNormActivation(expanded_channels, expanded_channels, kernel_size=cnf.kernel,
stride=cnf.stride, groups=expanded_channels,
norm_layer=norm_layer, activation_layer=activation_layer))
# squeeze and excitation
squeeze_channels = max(1, cnf.input_channels // 4)
layers.append(se_layer(expanded_channels, squeeze_channels, activation=partial(nn.SiLU, inplace=True)))
# project
layers.append(ConvNormActivation(expanded_channels, cnf.out_channels, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=None))
self.block = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.stochastic_depth = StochasticDepth(stochastic_depth_prob, "row")
self.out_channels = cnf.out_channels
def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:
result = self.block(input)
if self.use_res_connect:
result = self.stochastic_depth(result)
result += input
return result