Pytorch hook
Basic Knowledge
class Module: class Model(nn.Module):
Base class for all neural network modules. Your models should also subclass this class.
register_forward_hook is a method in this class
The hook will be called every time after :func:forward has computed an output.:
The hook should have the following signature:
hook(module, args, output) -> None or modified output
A hook function receive three parameters —— module, args and output,并返回 None 或修改后的输出。
module: 表示模块对象,即被注册前向钩子的模块,即child.register_forward_hook(hook)里的child模块。
args: 表示模块的输入参数,通常是一个元组或一个包含输入参数的序列。
output: 表示模块的输出结果,可以是任意类型的对象。
The way to use hook
前向钩子是在对象执行前向传播(forward pass)时调用的回调函数。它可以用于在前向传播的不同阶段进行自定义操作,例如获取中间层输出、修改输入或输出等。
感受一下回调函数:
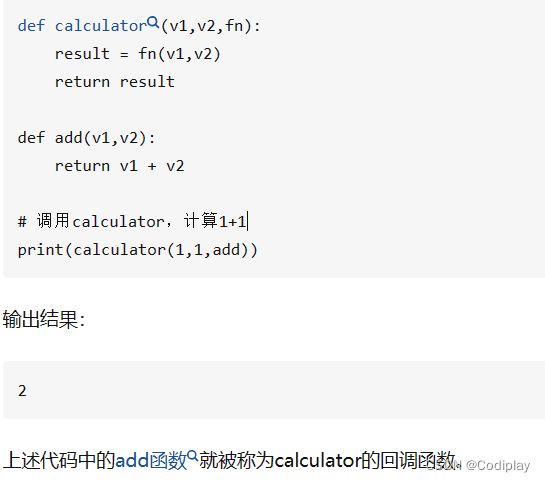
我们自己要写的就是上面的"add"函数。其中要求hook(module, input, output)接受的参数是当前module,input,output,Your mission is to utilize these parameters to construct a callback function, 去记录你想记录的东西。
OK, now we are able to design our individual callback function to save the parameters we care about.
Add a hook is simple:
The principle is finding the layer which output or attributes you care about
In this code, we care about the output of ScaledNeuron (spike) and its inner parameter (v_threshold)
When we print the module, we can know the total modules related to our intersts
def add_IF_hook(model):
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, ScaledNeuron):
# print(f"{name} {module}") 一共15个module(scaledneuron)
module.register_forward_hook(save_spikes_number)
module.register_forward_hook(save_spikes)
The above code successfully adds hooks to the layer we are interested in.
But let’s continue to design our hooks:
We will get three 中间状态的变量——module,input,output
In essence, we try to utilize these three parameters to get what we want. We usually need a dict. or list to store these information. You should firstly consider what information do you want and how to store them.
e.g.
spikes = {}
'''
key是neuron类型
value是tensor
{
ScaledNeuron(
(neuron): IFNode(
v_threshold=1.0, v_reset=None, detach_reset=False
(surrogate_function): Sigmoid(alpha=1.0, spiking=True)
)
): tensor([[[[0.0000, 0.0000],
[0.0000, 0.0000]],
}
'''
def save_spikes(module, inputdata, output):
global spikes
if not module in spikes: # t = 1时第一次inference
# print("dd") 15次,加到spikes里面。
spikes[module] = output.detach().cpu()
else:
# print("hi") 一堆hi 因为 t > 1时,原来已经有了,则把后面的加进来
spikes[module] = torch.cat((spikes[module], output.detach().cpu()),dim=0)
spikes_number = {}
'''
{
layer1: {
1:100 # total_spike_number
2:20 # total_neuron_number
}
}
'''
def save_spikes_number(module, inputdata, output):
global spikes_number
if not module in spikes_number:
spikes_number[module] = {}
spikes_number[module]["1"] = torch.sum(torch.abs(output))
spikes_number[module]["2"] = output.numel()
else:
spikes_number[module]["1"] = spikes_number[module]["1"] + torch.sum(torch.abs(output))