SpringBoot源码解析: SpringApplication构造器解析
@SpringBootApplication注解解析完之后,SpringBoot项目启动需要我们使用SpringApplication类去调用run方法并将启动类名放入参数中传递
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class);
}
}
复制代码接下来进入run方法看这个类做了什么事
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
复制代码run方法new了一个SpringApplication类然后调用了重载的run方法,这一章我们先解析SpringApplication的构造方法都做了什么
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
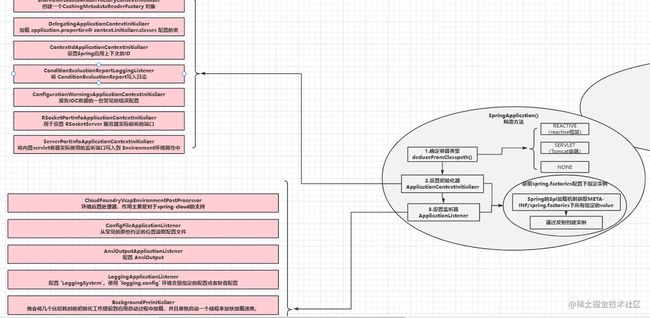
//1.判断web容器环境类型 Reactive(NIO) Servlet() NONE
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//2.创建初始化器并设置进上下文中(在容器刷新之前执行)
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//3.创建监听器器并设置进上下文中
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//4.确定主配置类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
复制代码这里传入的两个参数resourceLoader为null,primarySources为启动类 ,这里会将启动类保存进Set集合中。
下面对 SpringApplication 的构造方法进行解析:
一、WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
这个方法会判断当前容器启动的环境
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
//如果包含DispatcherHandler类并且不包含DispatcherServlet(MVC控制器)和ServletContainer(Servlet容器)则为reactive环境
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
//如果不包含Servlet或者ConfigurableWebApplicationContext类则为普通环境
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
//否则为Servlet环境
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
复制代码1.1 REACTIVE
反应式web应用,这个是一种比较新的web 构架,无阻塞的应用,实际就是web客户端和后端会有一个管道,后端将改变数据不断的推送到客户端,而不是传统的WEB应用将后端数据获得后发送给客户端显示,这样前端就被阻塞必须等待后端数据处理完成才能显示,反应式编程是依据观察者和订阅者模式来实现的,这样提高了客户端的响应时间,单因为客户端的不确定是,可能前端很容易就被后端推送的数据压垮,所以有了被压(back pressure)概念,直到Jdk 9才对reactive有了支持,spring 5的flux就是一个reactive框架。
1.2 SERVLET
基于web的应用,Tomcat框架
1.3 NONE
非servlet应用
二、setInitializers
初始化器会在容器刷新之前进行接口回调initialize方法。
设置初始化器
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
复制代码获取所有初始化器
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type, Class[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
//通过Spring的Spi机制获取META-INF/spring.factories下所有key为org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的值
Set names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
复制代码 2.1 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)
通过Spi机制获取META-INF/spring.factories下所有key为org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的值
Set names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
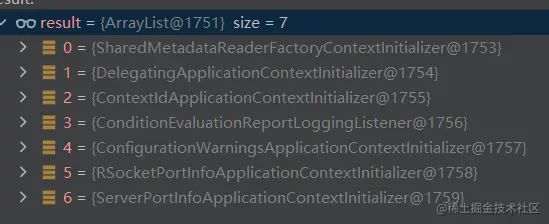
复制代码 这里默认的初始化器有7个
- SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer:创建一个 SpringBoot 和 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor共用的 CachingMetadataReaderFactory 对象
- DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer:加载 application.properties中 context.initializer.classes 配置的类
- ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer:设置Spring应用上下文的ID
- ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener:将 ConditionEvaluationReport写入日志
- ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer:报告IOC容器的一些常见的错误配置
- RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer:用于设置 RSocketServer 服务器实际侦听的端口
- ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer:将内置servlet容器实际使用的监听端口写入到 Environment环境属性中
2.2 createSpringFactoriesInstances
使用反射创建所有初始化器
private List createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type, Class[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set names) {
List instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
复制代码 三、setListeners
设置监听器,用于监听IOC容器中发布的各种事件
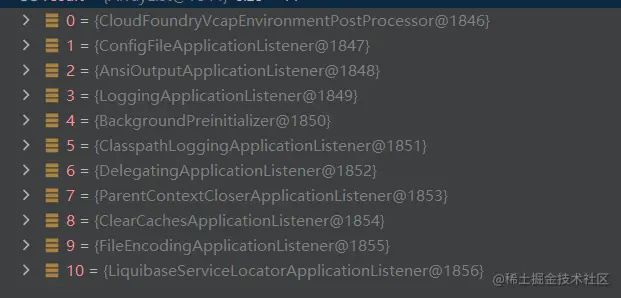
- ClearCachesApplicationListener:应用上下文加载完成后对缓存做清除工作
- ParentContextCloserApplicationListener:监听双亲应用上下文的关闭事件并往自己的子应用上下文中传播
- FileEncodingApplicationListener:检测系统文件编码与应用环境编码是否一致,如果系统文件编码和应用环境的编码不同则终止应用启动
- AnsiOutputApplicationListener:根据
spring.output.ansi.enabled参数配置 AnsiOutput - ConfigFileApplicationListener:从常见的那些约定的位置读取配置文件
- DelegatingApplicationListener:监听到事件后转发给
application.properties中配置的context.listener.classes的监听器 - ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener:对环境就绪事件
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent和应用失败事件ApplicationFailedEvent做出响应 - LoggingApplicationListener:配置
LoggingSystem。使用logging.config环境变量指定的配置或者缺省配置 - LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener:使用一个可以和 SpringBoot 可执行jar包配合工作的版本替换 LiquibaseServiceLocator
- BackgroundPreinitializer:使用一个后台线程尽早触发一些耗时的初始化任务
四、设置主应用程序类
这里根据栈获取执行main方法的类,就能找到启动类
private Class deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
复制代码总结
- SpringApplication维护了启动类
- 通过Spring的Spi机制获取了META-INF/spring.factories下所有ApplicationContextInitializer(容器刷新执行)实现类
- 通过Spring的Spi机制获取了META-INF/spring.factories下所有ApplicationListener(监听事件)实现类