verilog状态机设计——实现1011和101序列检测器
文章目录
- 1 检测1011序列
-
- 1.1不重叠检测和重叠检测
- 1.2 verilog实现不重叠检测
- 1.3 verilog实现重叠检测
- 2 检测101序列
1 检测1011序列
题目:
用Moore型状态机实现序列“1101”从右到左的不重叠检测。
1、请画出状态转移图,其中状态用S1,S2,…来标识。
2、针对这个具体设计,如何衡量验证的完备性?
功能正确; 覆盖所有的可能状态以及跳转条件;
确保不会进入死循环和未知状态,如果由于某些扰动进入非设计状态,也能很快的恢复到正常状态;
清晰易懂,便于后续维护,便于EDA工具进行更好地分析和优化;
可综合,不能使用folk,function这些关键字;
Moore型:状态机的状态变化仅和当前状态有关。
1.1不重叠检测和重叠检测
直接拿1101的左到右进行分析,看下图即可:
![]()
题目分析:
从右到左不重叠检测1101,也就是从左到右不重叠检测1011,因此我们可画出状态图:
![]()
1.2 verilog实现不重叠检测
//序列检测器1011,不重叠检测
module test(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input d, //序列输入
output reg done //检测完成
);
parameter S1 = 3'd1,S2 = 3'd2,S3 = 3'd3,S4 = 3'd4,S5 = 3'd5;
reg [2:0] state,next_state;
//三段式状态机
//第一段,状态寄存器
always@(posedge clk)
if(!rst_n)
state <= S1;
else
state <= next_state;
//第二段,组合逻辑描述状态转移
always @ (*)begin
case(state)
S1: next_state = d ? S2:S1;
S2: next_state = d ? S2:S3;
S3: next_state = d ? S4:S1;
S4: next_state = d ? S5:S3;
S5: next_state = d ? S2:S1;
default: next_state = S1;
endcase
end
//第三段,状态输出
always@(*)
done = (state == S5) ;
endmodule
tb仿真文件:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module test_tb;
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
reg d; //序列输入
wire done ; //检测完成
test u1 (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.d(d), //序列输入
.done(done) //检测完成
);
//
initial clk = 0;
always #1 clk = ~clk;
//
initial begin
rst_n = 0;
#1;
rst_n = 1;
end
//
initial begin
d = 0;
#2;
d = 1;
#2;
d = 0;
#2;
d = 1;
#2;
d = 1;
#2;
d = 0;
#2;
d = 1;
#2;
d = 1;
#3;
d= 0;
#20;
$stop;
end
endmodule
波形:
可看到当检测到1011的时候,done变成高电平。
![]()
由于是不重叠序列检测,因此可看到,如下1011时done没有变成高电平,因此设计正确。
![]()
1.3 verilog实现重叠检测
//1011重叠检测
module Sys_Rst(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input d,
output reg done
);
parameter IDLE = 3'd0,
S0 = 3'd1,
S1 = 3'd2,
S2 = 3'd3,
S3 = 3'd4;
reg [2:0] cur_state,next_state;
//第一段,描述状态寄存器
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
cur_state <= 4'b0;
else
cur_state <= next_state;
//第二段,组合逻辑描述状态转移
always @(*)begin
case (cur_state)
IDLE: next_state <= d ? S0 : IDLE;
S0: next_state <= d ? S0 : S1;
S1: next_state <= d ? S2 : IDLE;
S2: next_state <= d ? S3 : S1;
S3: next_state <= d ? S0 : S1;
default: next_state = S0;
endcase
end
//第三段,状态输出
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
done <= 0;
else if(next_state == S3)
done <= 1;
else
done <= 0;
endmodule
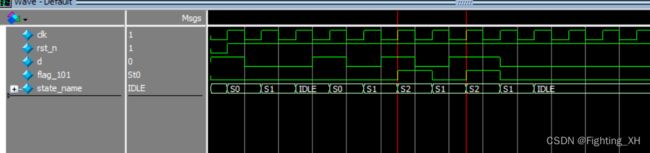
tb和之前一样,直接看波形,可看到,检测到1011后done拉高,这时候1被重叠检测,再次检测到1011的时候又拉高了done

2 检测101序列
通过百度百科的查阅:状态机由状态寄存器和组合逻辑电路构成,能够根据控制信号按照预先设定的状态进行状态转移,是协调相关信号动作、完成特定操作的控制中心。有限状态机简写为FSM(Finite State Machine),主要分为2大类:
关于两种状态机详解
第一类,若输出只和当前状态有关而与输入无关,则称为Moore状态机。
第二类,输出不仅和状态有关而且和输入有关系,则称为Mealy状态机。
状态机的小实例
设计重叠序列检测器:有“101”序列输入时输出为1,其他输入情况下,输出为0。画出状态转移图,并用Verilog描述。要求:用Moore型状态机进行设计,因此该状态机的输出只和当前状态有关,因此在定义状态的时候需要多定义一个,多定义的状态相当于中间状态,用来产生输出。
题目分析:101采用Moore型状态机的话,我们要定义四个状态。包括IDLE,S0,S1,S2,这里的S2就相当于多定义的一个产生输出的中间状态。
因此:flag_101 = (state == S2)? 1’b1: 1’b0;

Verilog代码
module Dectect_101(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input data,
output flag_101
);
parameter IDLE = 0,
S0 = 1,
S1 = 2,
S2 = 3;
reg [1:0] state;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(rst_n == 1'b0)begin
state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
case(state)
IDLE:
if(data == 1)
state <= S0;
else
state <= IDLE;
S0:
if(data == 0)
state <= S1;
else
state <= S0;
S1:
if(data == 1)
state <= S2;
else
state <= IDLE;
S2:
if(data == 1)
state <= S0;
else
state <= S1;
endcase
end
end
assign flag_101 = (state == S2)? 1'b1: 1'b0;
endmodule
testbench
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module Sys_Rst_tb;
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
reg d; //序列输入
wire flag_101 ; //检测完成
Sys_Rst u1 (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.data(d), //序列输入
.flag_101(flag_101) //检测完成
);
parameter IDLE = 0,
S0 = 1,
S1 = 2,
S2 = 3;
//4字符16位
reg [31:0] state_name ;
always@(*)begin
case(u1.state)
IDLE: state_name = "IDLE";
S0: state_name = "S0";
S1: state_name = "S1";
S2: state_name = "S2";
default: state_name = "IDLE";
endcase
end
//
initial clk = 0;
always #1 clk = ~clk;
//
initial begin
rst_n = 0;
#1;
rst_n = 1;
end
//
initial begin
d = 1;
#2;
d = 0;
#2;
d = 0;
#2;
d = 1;
#2;
d = 0;
#2;
d = 1;
#2;
d = 0;
#2;
d = 1;
#3;
d= 0;
#20;
$stop;
end
endmodule