java编程基础总结——26.File对象
File对象
java封装的一个操作文件及文件夹(目录)的对象。
可以操作磁盘上的任何一个文件和文件夹
一、 构造方法
1. 传字符串的路径
2. URI是和网络相关的接口。构建的是网络文件
3. File对象,再加一个子字符串
4. 字符串 字符串(可以把字符串构建成File对象,也可以把File对象用字符串表示)
使用场景:文件和文件夹分离(某个文件的存储目录和文件名称分离),文件名称写子目录也 可以,但没什么意义,直接用第一个就OK了
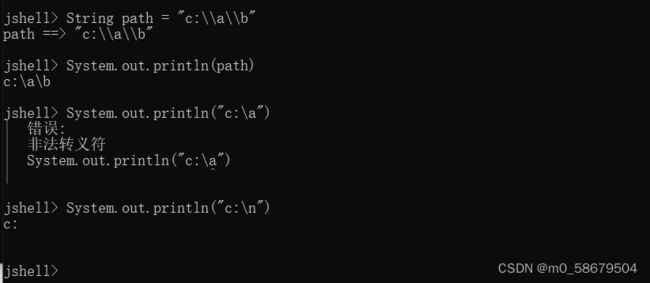
注意:windows支持\,但是一个\在java字符串中有转义的意思,如\r,\n,所以用两个\表示一个\
@Test
void testFileCreate() {
// File file = new File("C:\\a.jpg");第一个构造 绝对路径
// File file = new File(new File("c:\\"), "a.jpg");第三个构造
File file = new File("c:/", "a.jpg");//第四个构造
System.out.println(file.exists());
}
绝对路径和相对路径:
绝对路径:直接可以定位文件的一种路径
window系统:直接使用盘符找找: d:/a/b/c.jpg
linux: /(根) /usr/local/bin/java
网络: http://www.baidu.com/a.jpg
相对路径:相对于某个参照物(相对于文件夹),进行查找
二、常见方法
1. createNewFile()、exists()
exists()判断文件是否存在
createNewFile()文件不存在的时候创建文件,如果已经存在,再次创建不会刷新(覆盖)文件
@Test
void testFileCreate02() throws Exception {
// File f = new File("./a.txt");相对路径
File f = new File("a.txt");
// 判断文件是否存在
if (!f.exists()) {
// 创建文件
f.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功");
}
}@Test
void testFileCreate03() throws Exception {
File f = new File("a.txt");
System.out.println(f.createNewFile());
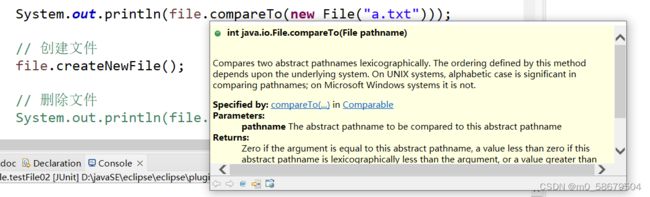
}2. canExecute()、canWrite()、canRead()、compareTo()
返回0是相等
@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
// 是否存在执行权限
System.out.println(file.canExecute());
// 是否有写的权限
System.out.println(file.canWrite());
// 是否有读的权限
System.out.println(file.canRead());
System.out.println(file.compareTo(new File("a.txt")));
}3. delete()、deleteOnExit()
//删除文件(a.txt会被删除)
file.delete()
//已经删除了,再次删除会返回false
System.out.println(file.delete());
// 在JVM退出时删除文件
//比如java自身的缓存文件,程序启动的时候临时缓存在磁盘上,程序运行结束删掉
file.deleteOnExit();
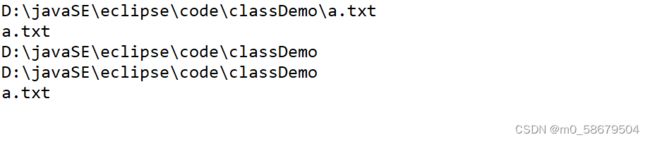
4.getAbsoluteFile()、getAbsolutePath()
@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
file.createNewFile();
// 将文件对象由相对路径转换为绝对路径
File absoluteFile = file.getAbsoluteFile();
System.out.println(absoluteFile);
}@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
file.createNewFile();
// 获取文件的真实路径
String path = file.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println(path);![]()
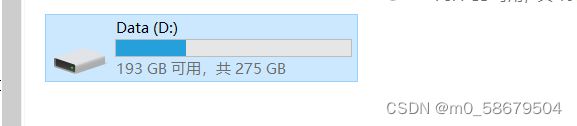
5. getFreeSpace()、getUsableSpace()、getTotalSpace()
@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
// 空闲空间(磁盘空间)
System.out.println((file.getFreeSpace() / 1024 / 1024) +"M");//字节->k->M
// 可有空间
System.out.println((file.getUsableSpace() / 1024 / 1024 / 1024) +"G");
// 总空间
System.out.println((file.getTotalSpace() / 1024 / 1024 / 1024) +"G");
//当前文件占用
System.out.println(file.length());
}6. length()
@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
//当前文件占用
System.out.println(file.length());
}7. getName()、getParent()、getParentFile()、getPath()
名字+目录-->完整的相对路径
getAbsolutePath() = getPath() + getParent()
我们是用相对路径构造的,getParent()拿不到父级的相对路径。转成绝对路径就可以了
@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getParent());
}@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
// 将文件对象由相对路径转换为绝对路径
File absoluteFile = file.getAbsoluteFile();
System.out.println(absoluteFile);
System.out.println(absoluteFile.getName());
// 获取父级的路径等操作,必须使用绝对路径对象
System.out.println(absoluteFile.getParent());
//拿到父类对象
System.out.println(absoluteFile.getParentFile());
System.out.println(file.getPath());
}8. isAbsolute()、isDirectory()、isFile()、isHidden()
@Test
void testFile02() throws Exception {
File file = new File("a.txt");
// 以is开头的几个方法,都是判断是否符合某种规则
//是不是绝对路径构建的对象
System.out.println(file.isAbsolute());
//是不是文件夹
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());
//是不是文件
System.out.println(file.isFile());
//是不是隐藏文件
System.out.println(file.isHidden());
}9. mkdir()、mkdirs()
mkdir()只能创建一层目录
mkdirs()能创建多层目录
@Test
void test03() {
File file = new File("./lib");
//只能创建一层目录
if (file.mkdir()) {
System.out.println("目录创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}@Test
void test03() {
File file = new File("config/resources");
//只能创建一层目录
if (file.mkdir()) {
System.out.println("目录创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}@Test
void test03() {
File file = new File("config/resources");
// 使用递归的方式,完成多层目录的创建
if (file.mkdirs()) {
System.out.println("目录创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}10. renameTo()
@Test
void test04() {
File file = new File("a.txt");
// 剪贴、复制、挪动文件的作用
System.out.println(file.renameTo(new File("d:\\b.txt")));
}11. list()、listFiles()
以字符串数组的形式返回当前目录下的所有文件(只打印第一层)
@Test
void test06() {
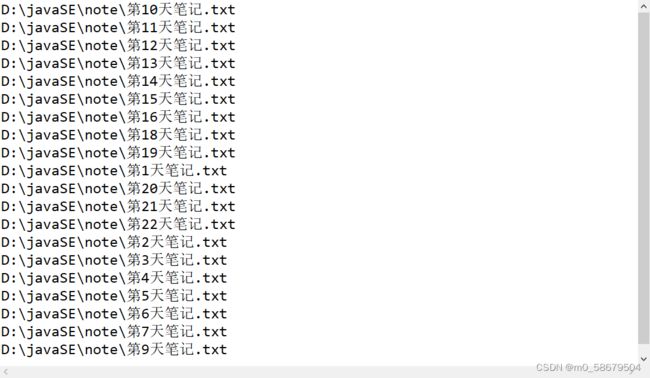
File file = new File("D:\\javaSE\\note");
//获取当前目录下的所有文件名称
String[] names = file.list();
for (String s : names) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}@Test
void test06() {
File file = new File("./");
//获取当前目录下的所有文件对象
File[] names = file.listFiles();
for (File f : names) {
System.out.println(f.getName());
}
}@Test
void test06() {
File file = new File("D:\\javaSE\\note");
// 过滤特定的文件
//lambda表达式
String[] names = file.list((dir, name) -> name.endsWith(".txt"));
for (String s : names) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}@Test
void test07() {
File file = new File("D:\\\\javaSE\\\\note");
// 过滤特定的文件
File[] names = file.listFiles(pathname -> pathname.getName().endsWith(".txt"));
for (File f : names) {
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}应用:
展示磁盘所有文件(递归遍历磁盘 ):
public static void scannFile(String path) {
File file = new File(path);
File[] listFiles = file.listFiles();
for (File f : listFiles) {
if (f.isFile()) {
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
} else if(f.isDirectory()) {
// 文件夹
scannFile(path + File.separatorChar + f.getName());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
scannFile("G:\\");
}