面试之Spring的启动原理
引入
为什么突然说一下Spring启动原理呢,因为之前面试的时候,回答的那可谓是坑坑洼洼,前前后后,补补贴贴。。。
总而言之就是不行,再次看一下源码发掘一下。。。
在Spring Boot还没有广泛到家家在用的时候,我们都还在书写繁琐的配置,什么web.xml、spring.xml、bean.xml等等。虽然现在很少,可以说几乎没有企业在去使用Spring的老一套,而会去使用Spring Boot约定大于配置来进行快速开发,但是,Spring的也要去学习,去挖掘,毕竟是我们Java程序员的基础呀。
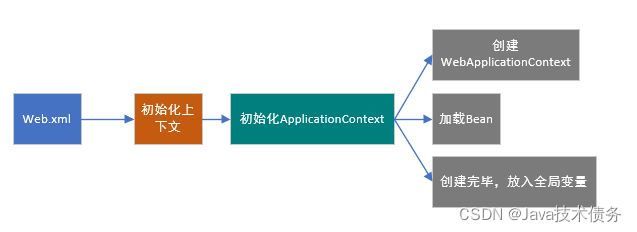
spring的启动是建筑在servlet容器之上的,所有web工程的初始位置就是web.xml,它配置了servlet的上下文(context)和监听器(Listener)
web.xml
<!--上下文监听器,用于监听servlet的启动过程-->
<listener>
<description>ServletContextListener</description>
<!--这里是自定义监听器,个性化定制项目启动提示-->
<listener-class>com.trace.app.framework.listeners.ApplicationListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--dispatcherServlet的配置,这个servlet主要用于前端控制,这是springMVC的基础-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>service_dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/services/service_dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!--spring资源上下文定义,在指定地址找到spring的xml配置文件-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/application_context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--spring的上下文监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--Session监听器,Session作为公共资源存在上下文资源当中,这里也是自定义监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>
com.trace.app.framework.listeners.MySessionListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
Spring启动过程
spring的上下文监听器
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/application_context.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
listener-class>
listener>
spring的启动其实就是IOC容器的启动过程,通过上述的第一段配置 ContextLoaderListener这个上下文监听器,ContextLoaderListener是一个实现了ServletContextListener接口的监听器,他的父类是 ContextLoader,在启动项目时会触发contextInitialized上下文初始化方法。
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
调用了父类ContextLoader的initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());方法,很显然,这是对ApplicationContext的初始化方法,也就是到这里正是进入了springIOC的初始化。
接下来看一下initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext())的工作:
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
总结:
- 创建WebApplicationContext。
- 加载对应的spring配置文件中的Bean。
- 将WebApplicationContext放入ServletContext(Java Web的全局变量)中。
接下来,来到了configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法
作用:
就是用来加载spring配置文件中的Bean实例的。这个方法于封装ApplicationContext数据并且初始化所有相关Bean对象。它会从web.xml中读取名为 contextConfigLocation的配置,这就是spring xml数据源设置,然后放到ApplicationContext中,最后调用传说中的refresh方法执行所有Java对象的创建。
总结
-
首先对于一个web应用,需要部署到web容器中,web容器提供了一个全局的上下文环境,ServletContext,SpringIOC的宿主环境。
-
其次,在web容器启动时,触发容器初始化,web.xml中提供的有ContextLoaderListener监听器会监听这个事件,初始化方法contextInitialized被调用,初始化spring上下文
WebApplicationContext接口,实现类时XmlWebApplicationContext即SpringIOC容器,对应的Bean定义是有context-param标签定义指定,然后存储到ServletContext中,方便获取。 -
ContextLoaderListener监听初始化完成后,开始初始化web.xml中配置的Servlet,指DisapatchServlet前端控制器,用来匹配,转发,处理每个Servlet请求,DisaptchServlet初始化时会创建自己的IOC上下文,用来持有Spring MVC的相关bean。
首先会从之前初始化存储在ServletContext中的上下文左右parent上下文,再初始化自己的上下文,大概的工作就是初始化处理器映射、视图解析等。这个servlet自己持有的上下文默认实现类也是xmlWebApplicationContext。然后存储到ServletContext。每个Servlet拥有自己的上下文,也会共享parent的上下文。
下期讲解refresh()做了什么,以及Spring Boot的启动原理,敬请观看,谢谢。。。
下期讲解refresh()做了什么,以及Spring Boot的启动原理,敬请观看,谢谢。。。
下期讲解refresh()做了什么,以及Spring Boot的启动原理,敬请观看,谢谢。。。
![]()
JVM内存泄漏和内存溢出的原因
JVM常用监控工具解释以及使用
Redis 常见面试题(一)
ClickHouse之MaterializeMySQL引擎(十)
三种实现分布式锁的实现与区别
线程池的理解以及使用
号外!号外!
最近面试BAT,整理一份面试资料,覆盖了Java核心技术、JVM、Java并发、SSM、微服务、数据库、数据结构等等。想获取吗?如果你想提升自己,并且想和优秀的人一起进步,感兴趣的朋友,可以在扫码关注下方公众号。资料在公众号里静静的躺着呢。。。

- 喜欢就收藏
- 认同就点赞
- 支持就关注
- 疑问就评论
一键四连,你的offer也四连
————————————————
本文作者:Java技术债务
原文链接:https://www.cuizb.top/myblog/article/1643358761
版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY 3.0 CN协议进行许可。转载请署名作者且注明文章出处。