左神算法中级提升(3)
目录
【案例1】
【题目描述】【2018阿里巴巴面试题】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【案例2】
【题目描述】
【思路解析1】
【思路解析2】
【代码实现】
【案例3】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【案例4】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【案例5】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【案例6】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【案例7】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
【代码实现】
【案例1】
【题目描述】【2018阿里巴巴面试题】
【思路解析】
对每个位置,它都有一个至少需要移动多少轮,能使这个地方局部平分,这所有位置中的最大轮数就是我们需要返回的。
(1) 如果数组求和不能被数组.length整除,直接返回-1
说明 a和b可正可负,正代表需要扔出衣服,负代表需要接收衣服
i位置的左侧部分a,右侧部分b
(2)【1】如果a和b均为负,因为一次只能移动一件,所以需要|a+b|轮。
【2】如果a和b均为正,需要max{|a|,|b|}轮
【3】如果a和b不同号,需要max{|a|,|b|}轮
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex1
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/11 7:49
*/
public class Ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {100,0,0,0};
System.out.println(getMin(arr));
}
public static int getMin(int[] arr){
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
if (sum % arr.length != 0){
return -1;
}
int n = sum / arr.length;
int rightSum = sum;
int leftSum = 0;
int leftSize = 0;
int rightSize = arr.length - 1;
int min = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
rightSum -= arr[i];
int left = Math.abs(leftSum - (n * leftSize));
int right = Math.abs(rightSum - (rightSize * n));
if (rightSum - (rightSize * n) < 0 && leftSum - (n * leftSize) < 0){
min = Math.max(left + right, min);
}else {
min = Math.max(Math.max(left, right), min);
}
leftSum += arr[i];
leftSize ++;
rightSize --;
}
return min;
}
}
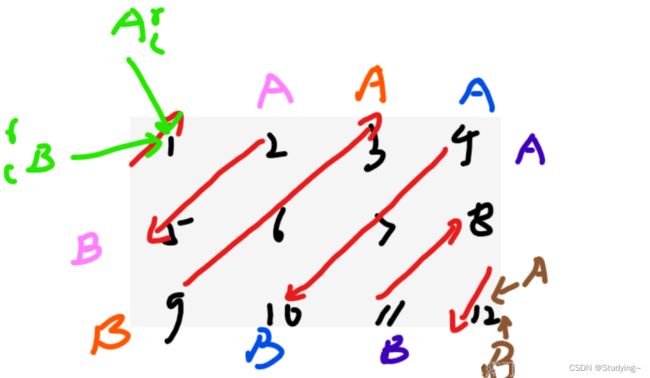
【案例2】
【题目描述】
【思路解析1】
循环打印,再触碰边界时考虑如何转弯即可。此方法容易想到(就是模仿打印顺序的实现),但不容易实现。
【思路解析2】
使用宏观调度的思路,让A和B初始为矩阵的左上角,然后如果A和B指向同一个就直接打印,否则就打印斜线,每次B往下移动,如果不能再往下了,就往右移动,每次A往右移动,如果不能再往右了就往下移动。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex2
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/11 11:44
*/
public class Ex2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {{0, 1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6, 7}, {8, 9, 10, 11}};
print2(arr);
}
public static void print(int[][] arr) {
int N = arr.length;
int M = arr[0].length;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0; // k == 0 打印顺序向右上遍历, k == 1 打印顺序向左下遍历
while (true) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
if (i == N - 1 && j == M - 1) {
break;
}
if (k == 0) {
i--;
j++;
} else {
i++;
j--;
}
if (i < 0 || i > N - 1 || j < 0 || j > M - 1) {
if (k == 0) { // 当左上和右下顺序遍历越界时,调整方向
k = 1;
i++;
if (j == M && i != N) {
j--;
i++;
}
} else {
k = 0;
j++;
if (i == N && j != M) {
i--;
j++;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void print2(int[][] arr) {
int ar = 0;
int ac = 0;
int br = 0;
int bc = 0;
boolean from = false;
int endR = arr.length - 1;
int endC = arr[0].length - 1;
while (ar != endR + 1) {
printM(arr, ar, ac, br, bc, from);
ar = ac == endC ? ar + 1 : ar;
ac = ac == endC ? ac : ac + 1;
bc = br == endR ? bc + 1 : bc;
br = br == endR ? br : br + 1;
from = !from;
}
}
public static void printM(int[][] arr, int ar, int ac, int br, int bc, boolean from) {
if (from) {
while (ar <= br) {
System.out.print(arr[ar++][ac--] + " ");
}
} else {
while (ar <= br) {
System.out.print(arr[br--][bc++] + " ");
}
}
}
}
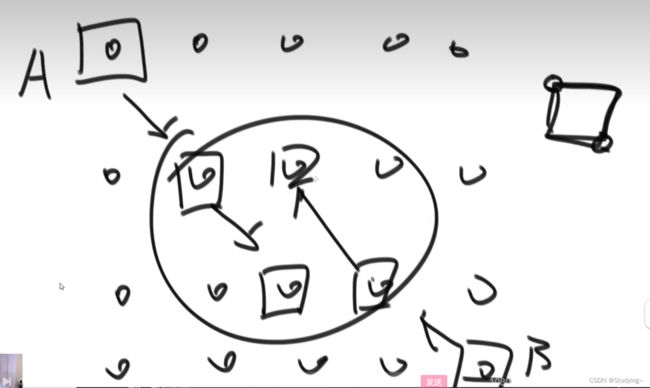
【案例3】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
螺旋打印的思路很好写,但是实现比较复杂,我们怎么使用宏观调度的方法是一个难题。
使用A和B确定两个边界,这两个边界确定一个长方形,然后我们只用螺旋打印长方形上的点,然后打印完后,边界A往右下移动,边界B往左上移动,然后再次打印这个长方形上的点。要求B不能越过A。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex3
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/11 12:19
*/
public class Ex3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {{0, 1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6, 7}, {8, 9, 10, 11}};
print(arr);
}
public static void print(int[][] map) {
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = map.length - 1;
int d = map[0].length - 1;
while (a <= c && b <= d) {
process(map, a++, b++, c--, d--);
}
}
public static void process(int[][] map, int a, int b, int c, int d) {
if (a == c) { // A 和 B 同行
for (int i = b; i <= d; i++) {
System.out.print(map[a][i] + " ");
}
} else if (b == d) { // A 和 B 同列
for (int i = a; i <= c; i++) {
System.out.print(map[i][b] + " ");
}
} else { // 常规矩形的情况
int curR = a; // 当前行
int curC = b; // 当前列
for (curC = b; curC < d; curC++) {
System.out.print(map[a][curC] + " ");
}
for (curR = a; curR < c; curR++) {
System.out.print(map[curR][d] + " ");
}
for (curC = d; curC > b; curC--) {
System.out.print(map[c][curC] + " ");
}
for (curR = c; curR > a; curR--) {
System.out.print(map[curR][b] + " ");
}
}
}
}
【案例4】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
因为给定的矩阵是正方形,然后实现矩阵就可以分成多层正方形,矩阵中每个位置的数顺时针转动90度,它只会在它的那层正方形上转动。所以我们只用实现每层正方形转动完成即可。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex4
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/11 13:07
*/
public class Ex4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] matrix = {{0,1,2,3},{4,5,6,7},{8,9,10,11},{12,13,14,15}};
rotate(matrix);
}
public static void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = matrix.length - 1;
int d = matrix.length - 1;
while (a <= c) {
rotateEdge(matrix, a++, b++, c--, d--);
}
printMatrix(matrix); // 旋转完成后打印矩阵
}
public static void rotateEdge(int[][] matrix, int a, int b, int c, int d) {
for (int i = 0; i < d - b; i++) { // 将正方形分组旋转
int tmp = matrix[a][b + i];
matrix[a][b + i] = matrix[c - i][b];
matrix[c - i][b] = matrix[c][d - i];
matrix[c][d - i] = matrix[a + i][d];
matrix[a + i][d] = tmp;
}
}
public static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) { // 打印矩阵
int n = matrix.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
【案例5】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
(1)如果n是质数,则只调用操作2,就是它的最好结果
(2)如果n不是质数,假设是某一些质数相乘。n = x*y*z*r*q;
先只使用操作2来达到x,后面对于y、z、r、q都是先第一步使用操作1,剩余( i-2)步使用操作2,这里的i是泛指。
【代码实现】
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex5
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/11 15:12
*/
public class Ex5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static int[] sumAndCount(int n) {
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
while (n % i == 0) {
count++;
sum += i;
n /= i;
}
}
return new int[] {sum, count};
}
public static int gewWays(int n){
if (n < 2){
return 0;
}
if (isPrime(n)){
return n-1;
}
return sumAndCount(n)[0] - sumAndCount(n)[1];
}
public static boolean isPrime(int n){
if (n < 2){
return false;
}
if (n == 2){
return true;
}
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++) {
if (n % i == 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
【案例6】
【题目描述】
【思路解析】
先对数组arr进行词频统计,然后规定小根堆的大小为k个,当大小未达到k个,就直接加入;否则,与堆顶比较,大的值进入小根堆。
【代码实现】
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex6
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/11 15:37
*/
public class Ex6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] strings = {"abc", "abc","abc","as","as","bck","bck","bck"};
topK(strings,2);
}
public static void topK(String[] str, int k) {
if (k == 0) {
return;
}
// 词频统计
HashMap strs = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (strs.containsKey(str[i])) {
strs.put(str[i], strs.get(str[i]) + 1);
} else {
strs.put(str[i], 1);
}
}
// 构建小根堆
PriorityQueue strs1 = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Str o1, Str o2) {
return o1.count - o2.count;
}
});
// 将词频统计后的数据,加入小根堆
for (String s : strs.keySet()) {
Str str1 = new Str(s, strs.get(s));
if (strs1.size() == k) {
if (str1.count > strs1.peek().count) {
strs1.poll();
strs1.add(str1);
}
} else {
strs1.add(str1);
}
}
// 将小根堆的数据打印出来
while (!strs1.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(strs1.poll().s);
}
}
public static class Str {
public String s;
public int count = 0;
public Str(String s, int count) {
this.s = s;
this.count = count;
}
}
}
【案例7】
【题目描述】
假设用户让我们实现某个结构,这个结构可以随时接收一个字符串,也可以随时打印当前出现次数最多的前k个字符串。
【思路解析】
这道题和上题类似,但是需要动态更新,所以需要一个结构来存放它在小根堆的位置来实现动态更新。
【代码实现】
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @ProjectName: study3
* @FileName: Ex7
* @author:HWJ
* @Data: 2023/7/11 16:16
*/
public class Ex7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static class Str {
public String s;
public int count = 0;
public Str(String s, int count) {
this.s = s;
this.count = count;
}
}
public static class topK{
public HashMap strIndex;
public HashMap strMap;
int heapSize;
Str[] strs;
public topK(int K){
this.heapSize = 0;
this.strs = new Str[K]; // 大小为k的小根堆
this.strMap = new HashMap<>(); // 词频统计的表结构
this.strIndex = new HashMap<>(); // 此数据在堆中的位置结构
}
public void add(String s){
int preIndex = -1;
Str cur;
if (!strMap.containsKey(s)){ // 如果这个字符串的信息没有出现过
cur = new Str(s, 1); // 新建
strMap.put(s, cur);
strIndex.put(cur, -1); // 位置信息为-1
}else { // 如果有,直接取出它的信息,然后词频++
cur = strMap.get(s);
cur.count++;
preIndex = strIndex.get(cur);
}
if (preIndex == -1){// 如果位置信息为-1,说明他们不在小根堆中
if (heapSize == strs.length){ // 如果小根堆已经满了
if (cur.count > strs[0].count){ // 大于堆顶就让它替换堆顶,并且修改他们的位置信息,然后调整为小根堆
strIndex.put(strs[0], -1);
strIndex.put(cur, 0);
strs[0] = cur;
heapify(strs, 0, heapSize);
}
}else { // 没满直接加入,修改位置信息,然后修改为小根堆
strIndex.put(cur, heapSize);
strs[heapSize] = cur;
heapInsert(strs, heapSize++);
}
}else {
// 如果它在小根堆中,更新小根堆
heapify(strs, preIndex, heapSize);
}
}
public void printTop(){
System.out.println("TopK: ");
for (int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++) {
if(strs[i] == null){
break;
}
System.out.println("String: " + strs[i].s);
System.out.println("Count: " + strs[i].count);
}
}
public void heapify(Str[] strs, int index, int heapSize){ // 往下整理
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < heapSize){
int smallest = left + 1 < heapSize && strs[left].count > strs[left + 1].count ? left + 1: left;
if (strs[index].count > strs[smallest].count){
swap(strs, index, smallest);
index = smallest;
left = 2 * index + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public void heapInsert(Str[] strs, int index){ // 往上整理
int father = (index - 1) / 2;
while (strs[index].count < strs[father].count){
swap(strs, index, father);
index = father;
father = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
public void swap(Str[] strs, int i, int j){
Str tmp = strs[i];
strs[i] = strs[j];
strs[j] = tmp;
strIndex.put(strs[i], j);
strIndex.put(strs[j], i);
}
}
}