springboot与rabbitmq的整合【演示5种基本交换机】
前言:
作者简介:我是笑霸final,一名热爱技术的在校学生。
个人主页:个人主页1 || 笑霸final的主页2
系列专栏:后端专栏
如果文章知识点有错误的地方,请指正!和大家一起学习,一起进步
如果感觉博主的文章还不错的话,点赞 + 关注 + 收藏
话不多说 直接开干
目录
- 一 导入maven坐标与配置
- 二、直连交换机direct exchange
-
- 2.1配置类QueueConfig
- 2.2消息提供者
- 2.2消息消费者
- 2.3测试类
- 三、默认交换机default exchange
-
- 3.1配置类和消息提供者
- 3.2消息消费者
- 3.3测试结果
- 四、扇型交换机fanout exchange
-
- 4.1配置类
- 4.2消息提供者
- 4.3消息消费者
- 4.4测试类
- 五、主题交换机topic exchanges
-
- 5.1配置类
- 5.2消息提供者
- 5.3消息消费者
- 5.4测试
- 六、头交换机 headers exchange
-
- 6.1配置类
- 6.2创建消息提供者
- 6.3消息消费者
- 6、4测试结果
一 导入maven坐标与配置
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqpartifactId>
dependency>
基础配置文件
spring:
rabbitmq:
username: 你的用户名
password: 你的密码
host: rabbitmq安装的主机的 ip地址
port: 5672 #端口号
二、直连交换机direct exchange
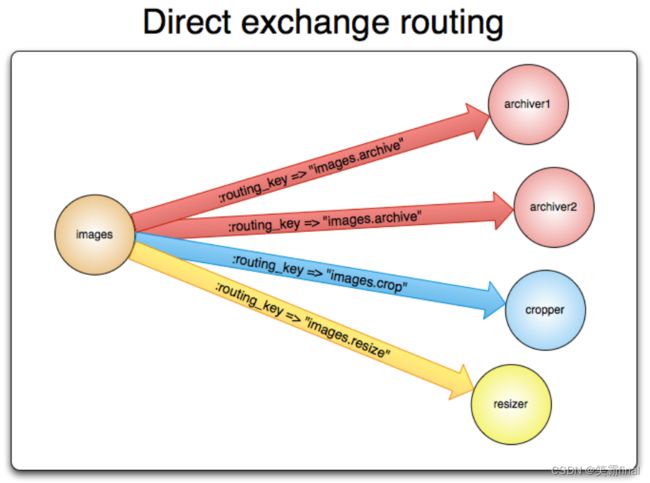
直连型交换机(direct exchange)是根据消息携带的路由键(routing key)将消息投递给对应队列的。
- 将一个队列 绑定到 某个交换机上,同时赋予该绑定一个路由键(routing key)
- 当一个携带着路由键为
routingKey01的消息被发送给直连交换机时,交换机会把它路由给绑定值同样为routingKey01的队列。
直连交换机经常用来循环分发任务给多个工作者(workers)。当这样做的时候,我们需要明白一点,在AMQP 0-9-1中,消息的负载均衡是发生在消费者(consumer)之间的,而不是队列(queue)之间。
2.1配置类QueueConfig
@Configuration
public class QueueConfig {
/**
* 创建一个队列 队列名为direct1
* */
@Bean
public Queue queue01(){
return new Queue("direct1",true);//true表示持久化
}
/**
* 创建一个直连交换机 名为directExchange
* */
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("directExchange");
}
/**
* 在让队列和直连交换机绑定在一起
* */
@Bean
public Binding binding(){
Binding binding= BindingBuilder
.bind(queue01())
.to(directExchange()).with("routingKey01");
return binding;
}
}
2.2消息提供者
@Component
public class MqProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sent_test(Object o){
//convertAndSend(交换机的名字,交换机中路由键名称,参数)
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(
"directExchange",//交换机名字
"routingKey01",//路由key
o);
}
}
2.2消息消费者
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MqConsumer {
/**
* 接收消息
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = {"direct1"})
public void receivedD(Message message, Channel channel)throws Exception{
String msg=new String(message.getBody());
log.info("当前时间:{},消费者1收到消息:{}",new Date().toString(),msg);
}
}
我写了两个消费者内容一致
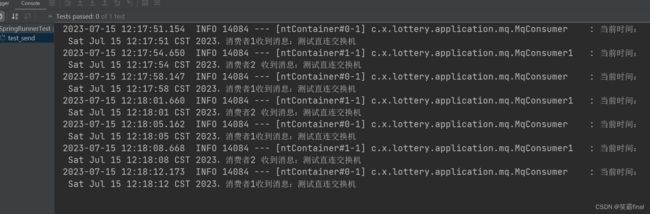
2.3测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class SpringRunnerTest {
@Resource
private MqProducer mqProducer;//注入消息提供者
@Test
public void test_send() throws InterruptedException {
// 循环发送消息
while (true) {
mqProducer.sent_test("你好,我是Lottery 001");
Thread.sleep(3500);
}
}
}
三、默认交换机default exchange
默认交换机(default exchange)实际上是一个由消息代理预先声明好的没有名字(名字为空字符串)的直连交换机(direct exchange)。它有一个特殊的属性使得它对于简单应用特别有用处:那就是每个新建队列(queue)都会自动绑定到默认交换机上,绑定的路由键(routing key)名称与队列名称相同。
3.1配置类和消息提供者
/**
*配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class QueueConfig {
//只需要创建一个队列
//每个`新建队列`(queue)都会`自动`绑定到`默认交换机`上,
//绑定的`路由键(routing //key)名称`与`队列名称` 相同
@Bean
public Queue queue02(){
return new Queue("def");
}
}
/**
*消息提供者
*/
@Component
public class MqProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void def_sent_test(Object obj){
//convertAndSend(交换机的名字,交换机中路由键名称,参数)
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(
//没有名字(名字为空字符串)
"",
"def",
obj);//消息内容
}
}
默认交换机名字是
空字符串。每个新建队列(queue)都会自动绑定到默认交换机上,绑定的路由键(routing key)名称与队列名称相同。
3.2消息消费者
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MqConsumer {
/**
* 接收消息
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = {"def"})
public void receivedD02(Message message, Channel channel)throws Exception{
String msg=new String(message.getBody());
log.info("当前时间:{},消费者收到消息:{}",new Date().toString(),msg);
}
}
3.3测试结果
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class SpringRunnerTest {
@Resource
private MqProducer mqProducer;//注入消息提供者
@Test
public void test_send02() throws InterruptedException {
// 循环发送消息
while (true) {
mqProducer.def_sent_test("测试默认交换机");
Thread.sleep(3500);
}
}
}
四、扇型交换机fanout exchange
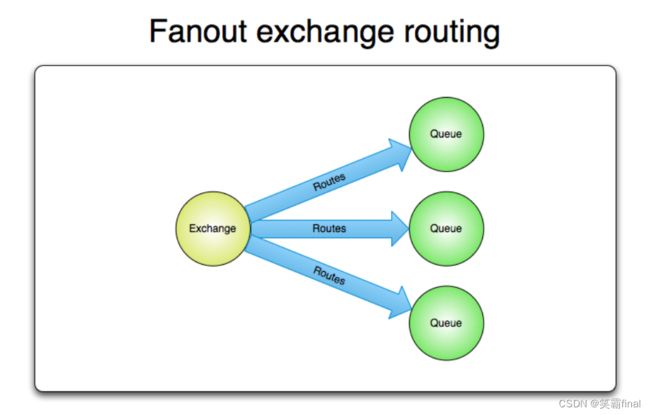
扇型交换机(fanout exchange)将消息路由给绑定到它身上的所有队列,而不理会绑定的路由键。如果N个队列绑定到某个扇型交换机上,当有消息发送给此扇型交换机时,交换机会将消息的拷贝分别发送给这所有的N个队列。扇型用来交换机处理消息的广播路由(broadcast routing)
这个交换机上的路由键将失效
4.1配置类
@Configuration
public class QueueConfig {
/**
* 创建多个队列
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue queue03_1(){
return new Queue("fanout03_1");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue03_2(){
return new Queue("fanout03_2");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue03_3(){
return new Queue("fanout03_3");
}
/**
* 创建一个扇形交换机
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");
}
/**
* 队列和扇形交换机绑定
*/
@Bean
public Binding binding_3_1(){
Binding binding= BindingBuilder
.bind(queue03_1())
.to(fanoutExchange());
return binding;
}
@Bean
public Binding binding_3_2(){
Binding binding= BindingBuilder
.bind(queue03_2())
.to(fanoutExchange());
return binding;
}
@Bean
public Binding binding_3_3(){
Binding binding= BindingBuilder
.bind(queue03_3())
.to(fanoutExchange());
return binding;
}
}
4.2消息提供者
@Component
public class MqProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 扇形交换机
*/
public void fanout_sent_test(Object o){
//convertAndSend(交换机的名字,交换机中路由键名称,参数)
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(
"fanoutExchange",
"",//扇形交换机也没有路由建
o);
}
}
注意:扇形交换机也
没有路由key也用空字符串
4.3消息消费者
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MqConsumer {
@RabbitListener(queues = {"fanout03_1"})
public void receivedD03_1(Message message, Channel channel)throws Exception{
String msg=new String(message.getBody());
log.info("绑定队列一 当前时间:{},消费者收到消息:{}",new Date().toString(),msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = {"fanout03_2"})
public void receivedD03_2(Message message, Channel channel)throws Exception{
String msg=new String(message.getBody());
log.info("绑定队列二 当前时间:{},消费者收到消息:{}",new Date().toString(),msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = {"fanout03_3"})
public void receivedD03_3(Message message, Channel channel)throws Exception{
String msg=new String(message.getBody());
log.info("绑定队列三 当前时间:{},消费者收到消息:{}",new Date().toString(),msg);
}
}
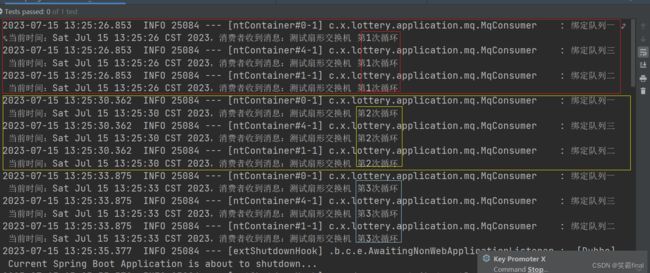
4.4测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class SpringRunnerTest {
@Resource
private MqProducer mqProducer;//注入消息提供者
@Test
public void test_send03() throws InterruptedException {
int a=1;
// 循环发送消息
while (true) {
mqProducer.fanout_sent_test("测试扇形交换机 第"+ a++ +"次循环");
Thread.sleep(3500);
}
}
}
五、主题交换机topic exchanges
主题交换机(topic exchanges)通过对消息的
路由键和队列到交换机的绑定模式之间的匹配,将消息路由给一个或多个队列。主题交换机经常用来实现各种分发/订阅模式及其变种。主题交换机通常用来实现消息的多播路由(multicast routing)。
5.1配置类
@Configuration
public class QueueConfig {
/**
* 创建;两个队列
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue_1(){
return new Queue("topicQueue_1");
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue_2(){
return new Queue("topicQueue_2");
}
/**
* 创建主题交换机
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange TopicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("TopicExchange");
}
/**
* 根据不同的key绑定不同的队列
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingTopicExchange_1(){
Binding binding= BindingBuilder
.bind(topicQueue_1())
.to(TopicExchange()).with("key1");
return binding;
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingTopicExchange_2(){
Binding binding= BindingBuilder
.bind(topicQueue_2())
.to(TopicExchange()).with("key2");
return binding;
}
}
5.2消息提供者
@Component
public class MqProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 主题交换机
*/
public void topic_sent_test(Object o,String key){
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(
"TopicExchange",
key, //后面动态的传递key
o);
}
}
5.3消息消费者
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MqConsumer1 {
/**
* 接收消息
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = {"topicQueue_1"})
public void topicQueue_1(Message message, Channel channel)throws Exception{
String msg=new String(message.getBody());
log.info("队列一 当前时间:{},消费者收到消息:{}",new Date().toString(),msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = {"topicQueue_2"})
public void topicQueue_2(Message message, Channel channel)throws Exception{
String msg=new String(message.getBody());
log.info("队列二 当前时间:{},消费者收到消息:{}",new Date().toString(),msg);
}
}
5.4测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class SpringRunnerTest {
@Resource
private MqProducer mqProducer;//注入消息提供者
@Test
public void test_send04() throws InterruptedException {
// 循环发送消息
int a=1;
while (true) {
if(a%2 == 0){
mqProducer.topic_sent_test("!!给队列二的消息==第"
+ a++ +"次循环","key2");
}else{
mqProducer.topic_sent_test("!!给队列一的消息==第"
+ a++ +"次循环","key1");
}
Thread.sleep(3500);
}
}
}
使用案例:
- 分发有关于特定地理位置的数据,例如销售点
- 由多个工作者(workers)完成的后台任务,每个工作者负责处理某些特定的任务
- 股票价格更新(以及其他类型的金融数据更新)
- 涉及到分类或者标签的新闻更新(例如,针对特定的运动项目或者队伍)
- 云端的不同种类服务的协调
- 分布式架构/基于系统的软件封装,其中每个构建者仅能处理一个特定的架构或者系统。
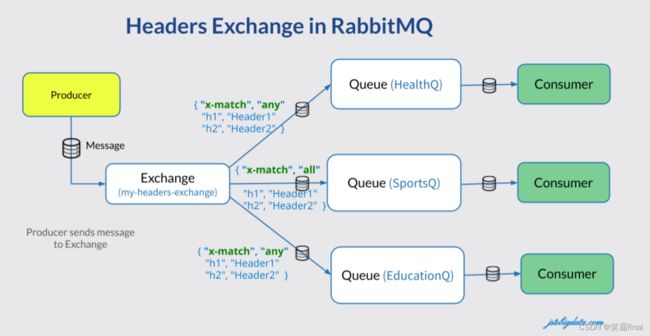
六、头交换机 headers exchange
有时消息的路由操作会涉及到多个属性,此时使用消息头就比用路由键更容易表达,头交换机(headers exchange)就是为此而生的。头交换机使用多个
消息属性来代替路由键建立路由规则。通过判断消息头的值能否与指定的绑定相匹配来确立路由规则。
6.1配置类
@Configuration
public class QueueConfig {
/**
* 创建2个队列
*/
@Bean(name = "headersQ1")
public Queue queue1() {
return new Queue("headersQ1");
}
@Bean(name = "headersQ2")
public Queue queue2() {
return new Queue("headersQ2");
}
/**
* 创建交换机
* @return
*/
@Bean
public HeadersExchange headersExchange() {
return new HeadersExchange("headersExchange");
}
/**
* 绑定交换机和队列
*/
@Bean
public Binding binding1() {
HashMap<String, Object> header = new HashMap<>();
header.put("queue", "queue1");
header.put("bindType", "whereAll");
return BindingBuilder
.bind(queue1())
.to(headersExchange())
.whereAll(header).match();
}
@Bean
public Binding binding2() {
HashMap<String, Object> header = new HashMap<>();
header.put("queue", "queue2");
header.put("bindType", "whereAny");
return BindingBuilder
.bind(queue2())
.to(headersExchange())
.whereAny(header).match();
}
}
6.2创建消息提供者
@Component
public class MqProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 头交换机
* @param msg
*/
public void headers_send(String msg,int a) {
//a用来控制头信息 达到传递给不同的队列效果
MessageProperties messageProperties = new MessageProperties();
if( a % 3 ==0){
messageProperties.setHeader("queue", "queue2");
messageProperties.setHeader("bindType", "whereAny");
}else{
messageProperties.setHeader("queue", "queue1");
messageProperties.setHeader("bindType", "whereAll");
}
Message message = new Message(msg.getBytes(), messageProperties);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("headersExchange", null, message);
}
}
6.3消息消费者
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MqConsumer1 {
/**
* 接收消息
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "headersQ1")
public void receive1(String msg) {
log.info("接收到 headersQ1 发送的消息:" + msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "headersQ2")
public void receive2(String msg) {
log.info("接收到 headersQ2 发送的消息:" + msg);
}
}
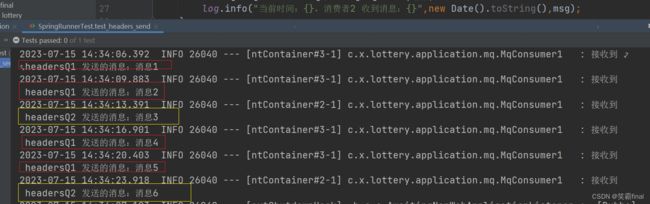
6、4测试结果
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class SpringRunnerTest {
@Resource
private MqProducer mqProducer;//注入消息提供者
@Test
public void test_headers_send() throws InterruptedException {
// 循环发送消息
int a=1;
while (true) {
mqProducer.headers_send("消息"+a,a++);
Thread.sleep(3500);
}
}
}