【数据结构】顺序表、链表
文章目录
- 一、顺序表
-
- 接口实现
- 题目
- 二、链表
-
- 接口实现
-
- 1.单链表
- 2.带哨兵位的双向链表
- 题目
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
由两种实现方式:静态顺序表(数组)和动态顺序表(动态开辟)。
由于数组的大小的固定的,容易浪费空间,所以动态顺序表是更加优异的选择。
接口实现
SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include SeqList.c
#include "SeqList.h"
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ((ps->capacity == 0) ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity);
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(SLDataType) * 2);
if (tmp==NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
ps->a = tmp;
}
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
//assert(ps);
//SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//ps->a[ps->size] = x;
//ps->size++;
SLInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
//assert(ps);
//assert(ps->size > 0);
//ps->a[ps->size - 1] = 0;
//ps->size--;
SLErase(ps, ps->size - 1);
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
//assert(ps);
//SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//int i = 0;
//for (i = ps->size - 1; i >= 0; i--)
//{
// ps->a[i+1] = ps->a[i];
//}
//ps->a[0] = x;
//ps->size++;
SLInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
//assert(ps);
//assert(ps->size > 0);
//int i = 0;
//for (i = 1; i < ps->size; i++)
//{
// ps->a[i - 1] = ps->a[i];
//}
//ps->size--;
SLErase(ps, 0);
}
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int i = ps->size - 1;
for (i = ps->size - 1; i >= pos; i--)
{
ps->a[i + 1] = ps->a[i];
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos < ps->size);
int i = pos+1;
for (i = pos+1; i < ps->size; i++)
{
ps->a[i - 1] = ps->a[i];
}
ps->size--;
}
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->a)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
}
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x, int begin)
{
assert(ps);
int i = 0;
for (i = begin; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
题目
1.移除元素
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并 原地 修改输入数组。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
int right=0;
int left=0;
for(right=0;right<numsSize;right++)
{
if(nums[right]!=val)
{
nums[left]=nums[right];
left++;
}
}
return left;
}
2. 删除有序数组中的重复项
给你一个 升序排列 的数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。元素的 相对顺序 应该保持 一致 。
由于在某些语言中不能改变数组的长度,所以必须将结果放在数组nums的第一部分。更规范地说,如果在删除重复项之后有 k 个元素,那么 nums 的前 k 个元素应该保存最终结果。
将最终结果插入 nums 的前 k 个位置后返回 k 。
不要使用额外的空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){
int fast=0;
int slow=0;
while(fast<numsSize)
{
if(nums[fast]==nums[slow])
{
fast++;
}
else
{
slow++;
nums[slow]=nums[fast];
fast++;
}
}
return slow+1;
}
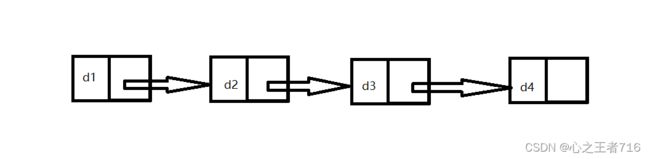
二、链表
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。
接口实现
1.单链表
Slist.h
#pragma once
#include Slist.c
#include "Slist.h"
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)
{
SListNode* newnode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
SListNode* CreateSList(int n)
{
SListNode* phead = NULL, * ptail = NULL;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(i);
if (phead == NULL)
{
phead = ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
ptail->next = newnode;
ptail = newnode;
}
}
return phead;
}
void SListPrint(SListNode* plist)
{
SListNode* cur = plist;
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL");
}
void SListPushBack(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
*pplist = newnode;
}
else
{
SListNode* tail = *pplist;
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
void SListPopBack(SListNode** pplist)
{
assert(*pplist);
if ((*pplist)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pplist);
*pplist = NULL;
}
else
{
SListNode* prev = NULL;
SListNode* tail = *pplist;
while (tail->next)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
void SListPushFront(SListNode** pplist, SLTDateType x)
{
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = *pplist;
*pplist = newnode;
}
void SListPopFront(SListNode** pplist)
{
assert(*pplist);
SListNode* next = *pplist;
free(*pplist);
*pplist = next;
}
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* plist, SLTDateType x)
{
assert(plist);
SListNode* cur = plist;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在pos后插入数据
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{
assert(pos);
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
SListNode* next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
newnode->next = next;
}
//在pos之前插入值
void SListInsert(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{
assert(pos);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
SListNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
SListNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
SListNode* nextnode = pos->next;
pos->next = nextnode->next;
free(nextnode);
}
}
//删除pos位置的值
void SListErase(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(*pphead);
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SListPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
SListNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
}
void SListDestroy(SListNode** pplist)
{
SListNode* cur = *pplist;
while (cur)
{
SListNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*pplist = NULL;
}
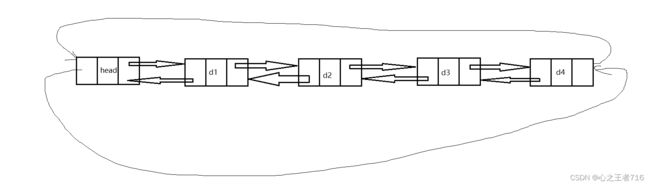
2.带哨兵位的双向链表
List.h
#pragma once
#include List.c
#include "List.h"
LTNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)
{
LTNode* node = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
node->data = x;
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
return node;
}
LTNode* LTInit()
{
LTNode* phead = BuyListNode(-1);
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
void LTPrint(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void LTPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
/*LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* prev = phead->prev;
phead->prev = newnode;
newnode->next = phead;
newnode->prev = prev;
prev->next = newnode;*/
LTInsert(phead, x);
}
void LTPopBack(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
/*LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
phead->prev = tail->prev;
tail->prev->next = phead;
free(tail);*/
LTErase(phead->prev);
}
void LTPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
/*LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* head = phead->next;
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = head;
head->prev = newnode;*/
LTInsert(phead->next, x);
}
void LTPopFront(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next != phead);
/*LTNode* first = phead->next;
LTNode* second = first->next;
phead->next = second;
second->prev = phead;
free(first);*/
LTErase(phead->next);
}
LTNode* LTFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//在pos之前插入
void LTInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
LTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* prev = pos->prev;
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = prev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;
}
//删除pos位置的值
void LTErase(LTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
LTNode* prev = pos->prev;
LTNode* next = pos->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
free(pos);
}
bool LTEmpty(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
return phead->next == phead;
}
size_t LTSize(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
size_t size = 0;
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
void LTDestroy(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
LTNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
}
题目
这里直接给一道比较综合的题
复制带随机指针的链表
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
给出我的思路:
- 首选在每个节点后面都插入一个复制节点,储存的值和前面的节点相同
- 复制节点中random指向的节点是源节点的random节点的next
- 重新弄一个链表,把上面的复制节点不断的尾插到新链表
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* cur=head;
//复制节点
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node* next=cur->next;
copy->val=cur->val;
cur->next=copy;
copy->next=next;
cur=next;
}
cur=head;
//复制random
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random=NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random=cur->random->next;
}
cur=cur->next->next;
}
struct Node* copyhead=NULL,*copytail=NULL;
cur=head;
//复制节点单独拿出来
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
struct Node* next=copy->next;
cur->next=next;
if(copyhead==NULL)
{
copyhead=copytail=copy;
}
else
{
copytail->next=copy;
copytail=copytail->next;
}
cur=next;
}
return copyhead;
}