JS-27 前端数据请求方式;HTTP协议的解析;JavaScript XHR、Fetch的数据请求与响应函数;前端文件上传XHR、Fetch
目录
- 1_前端数据请求方式
-
- 1.1_前后端分离的优势
- 1.2_网页的渲染过程 – 服务器端渲染
- 1.3_网页的渲染过程 – 前后端分离
- 2_HTTP协议的解析
-
- 2.1_HTTP概念
- 2.2_网页中资源的获取
- 2.3_HTTP的组成
- 2.4_HTTP的版本
- 2.5_HTTP的请求方式
- 2.6_HTTP Request Header
- 2.7_HTTP Response响应状态码
- 3_XHR
-
- 3.1_AJAX发送请求
- 3.2_XMLHttpRequest的state(状态)
- 3.3_XMLHttpRequest其他事件监听
- 3.4_响应数据和响应类型
- 3.5_HTTP响应的状态status
- 3.6_GET/POST请求传递参数
- 3.7_ajax网络请求封装
- 3.8_延迟时间timeout和取消请求
- 4_Fetch
-
- 4.1_Fetch和Fetch API
- 4.2_Fetch数据的响应(Response)
- 4.3_Fetch网络请求的演练
- 4.4_Fetch POST请求
- 5_前端文件上传
-
- 5.1_XMLHttpRequest文件上传
- 5.2_Fetch文件上传
- 5.2_Fetch文件上传
1_前端数据请求方式
1.1_前后端分离的优势
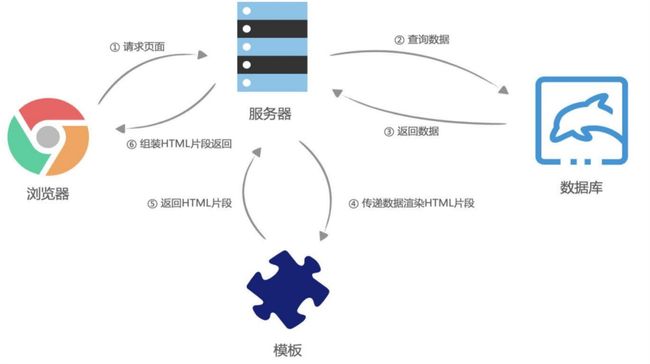
早期的网页都是通过后端渲染来完成的,即服务器端渲染(SSR,server side render): 客户端发出请求 -> 服务端接收请求并返回相应HTML文档 -> 页面刷新,客户端加载新的HTML文档;
服务器端渲染的缺点:
- 当用户点击页面中的某个按钮向服务器发送请求时,页面本质上只是一些数据发生了变化,而此时服务器却要将重绘的整个页面再返回给浏览器加载,这显然有悖于程序员的“DRY( Don‘t repeat yourself )”原则;
- 而且明明只是一些数据的变化却迫使服务器要返回整个HTML文档,这本身也会给网络带宽带来不必要的开销。
AJAX是“Asynchronous JavaScript And XML”的缩写(异步的JavaScript和XML),是一种实现 无页面刷新 获取服务器数据的技术。
AJAX最吸引人的就是它的“异步”特性,它可以在不重新刷新页面的情况下与服务器通信,交换数据,或更新页面。
AJAX最主要的两个特点:
- 在不重新加载页面的情况下发送请求给服务器;
- 接受并使用从服务器发来的数据。
1.2_网页的渲染过程 – 服务器端渲染
1.3_网页的渲染过程 – 前后端分离
2_HTTP协议的解析
2.1_HTTP概念
维基百科的解释:
- 超文本传输协议(英语:HyperText Transfer Protocol,缩写:HTTP)是一种用于分布式、协作式和超媒体信息系统的应用层协议;
- HTTP是万维网的数据通信的基础,设计HTTP最初的目的是为了提供一种发布和接收HTML页面的方法;
- 通过HTTP或者HTTPS协议请求的资源由统一资源标识符(Uniform Resource Identifiers,URI)来标识;
HTTP是一个客户端(用户)和服务端(网站)之间请求和响应的标准。
- 通过使用网页浏览器、网络爬虫或者其它的工具,客户端发起一个HTTP请求到服务器上指定端口(默认端口为80);称这个客户端为用户代理程序(user agent);
- 响应的服务器上存储着一些资源,比如HTML文件和图像。称这个响应服务器为源服务器(origin server);
2.2_网页中资源的获取
网页中的资源通常是被放在Web资源服务器中,由浏览器自动发送HTTP请求来获取、解析、展示的。
页面中很多数据是动态展示的: 比如页面中的数据展示、搜索数据、表单验证等等,也是通过在JavaScript中发送HTTP请求获取的;
2.3_HTTP的组成
一次HTTP请求主要包括:请求(Request)和响应(Response
2.4_HTTP的版本
HTTP/0.9
- 发布于1991年;
- 只支持GET请求方法获取文本数据,当时主要是为了获取HTML页面内容;
HTTP/1.0
- 发布于1996年;
- 支持POST、HEAD等请求方法,支持请求头、响应头等,支持更多种数据类型(不再局限于文本数据) ;
- 但是浏览器的每次请求都需要与服务器建立一个TCP连接,请求处理完成后立即断开TCP连接,每次建立连接增加了性能损耗;
HTTP/1.1(目前使用最广泛的版本)
- 发布于1997年;
- 增加了PUT、DELETE等请求方法;
- 采用持久连接(Connection: keep-alive),多个请求可以共用同一个TCP连接;
2015年,HTTP/2.0
2018年,HTTP/3.0
2.5_HTTP的请求方式
在RFC中定义了一组请求方式,来表示要对给定资源执行的操作:
-
GET:GET 方法请求一个指定资源的表示形式,使用 GET 的请求应该只被用于获取数据。
-
HEAD:HEAD 方法请求一个与 GET 请求的响应相同的响应,但没有响应体。
- 比如在准备下载一个文件前,先获取文件的大小,再决定是否进行下载;
-
POST:POST 方法用于将实体提交到指定的资源。
-
PUT:PUT 方法用请求有效载荷(payload)替换目标资源的所有当前表示;
-
DELETE:DELETE 方法删除指定的资源;
-
PATCH:PATCH 方法用于对资源应部分修改;
-
CONNECT:CONNECT 方法建立一个到目标资源标识的服务器的隧道,通常用在代理服务器,网页开发很少用到。
-
TRACE:TRACE 方法沿着到目标资源的路径执行一个消息环回测试。
在开发中使用最多的是GET、POST请求
2.6_HTTP Request Header
在request对象的header中也包含很多有用的信息,客户端会默认传递过来一些信息。例如下图
content-type是这次请求携带的数据的类型:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded:表示数据被编码成以 ‘&’ 分隔的键 - 值对,同时以 ‘=’ 分隔键和值
- application/json:表示是一个json类型;
- text/plain:表示是文本类型;
- application/xml:表示是xml类型;
- multipart/form-data:表示是上传文件;
content-length:文件的大小长度
keep-alive:
- http是基于TCP协议的,但是通常在进行一次请求和响应结束后会立刻中断;
- 在http1.0中,如果想要继续保持连接:
- 浏览器需要在请求头中添加 connection: keep-alive;
- 服务器需要在响应头中添加 connection:keey-alive;
- 当客户端再次放请求时,就会使用同一个连接,直接一方中断连接;
- 在http1.1中,所有连接默认是 connection: keep-alive的;
- 不同的Web服务器会有不同的保持 keep-alive的时间;
- Node中默认是5s中;
accept-encoding:告知服务器,客户端支持的文件压缩格式,比如js文件可以使用gzip编码,对应 .gz文件;
accept:告知服务器,客户端可接受文件的格式类型;
user-agent:客户端相关的信息;
响应的header中包括一些服务器给客户端的信息
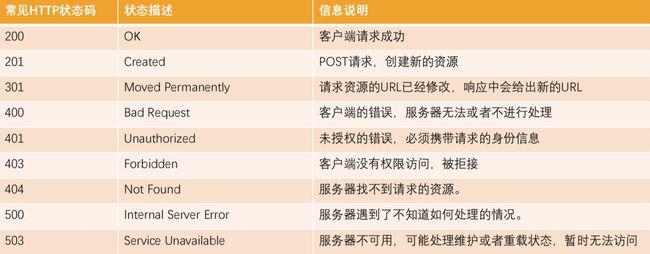
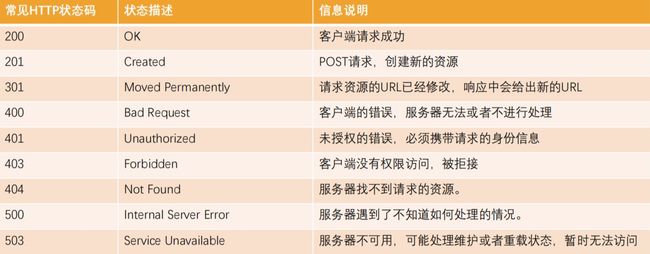
2.7_HTTP Response响应状态码
Http状态码(Http Status Code)是用来表示Http响应状态的数字代码:
- Http状态码非常多,可以根据不同的情况,给客户端返回不同的状态码;
- MDN响应码解析地址:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/web/http/status
安装谷歌浏览器插件:FeHelper,帮助更好地查看数据
3_XHR
3.1_AJAX发送请求
AJAX 是异步的 JavaScript 和 XML(Asynchronous JavaScript And XML),它可以使用 JSON,XML,HTML 和 text 文本等格式发送和接收数据;
如何完成AJAX请求呢?
- 第一步:创建网络请求的AJAX对象(使用XMLHttpRequest)
- 第二步:监听XMLHttpRequest对象状态的变化,或者监听onload事件(请求完成时触发);
- 第三步:配置网络请求(通过open方法);
- 第四步:发送send网络请求;
// 1.创建XMLHttpRequest对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2.监听状态的改变(宏任务)
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
// console.log(xhr.response)
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return
// 将字符串转成JSON对象(js对象)
const resJSON = JSON.parse(xhr.response)
const banners = resJSON.data.banner.list
console.log(banners)
}
// 3.配置请求open
// method: 请求的方式(get/post/delete/put/patch...)
// url: 请求的地址
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata")
// 4.发送请求(浏览器帮助发送对应请求)
xhr.send()
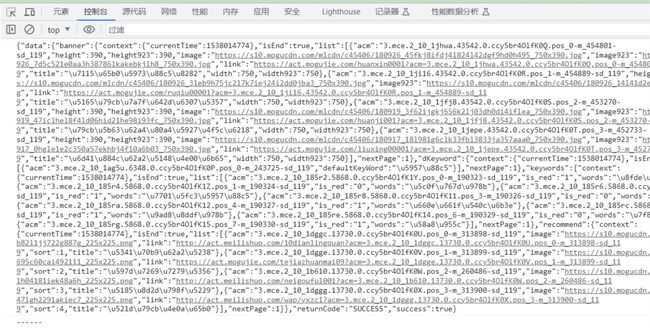
执行结果
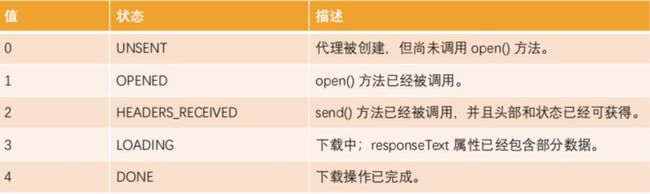
3.2_XMLHttpRequest的state(状态)
在一次网络请求中状态发生了很多次变化,对于一次请求来说包括如下的状态:
// 1.创建XMLHttpRequest对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2.监听状态的改变(宏任务)
// 监听四种状态
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
// 1.如果状态不是DONE状态, 直接返回
if (xhr.readyState !== XMLHttpRequest.DONE) return
// 2.确定拿到了数据
console.log(xhr.response)
}
// 3.配置请求open
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata")
// 4.发送请求(浏览器帮助发送对应请求)
xhr.send()
这个状态并非是HTTP的相应状态,而是记录的XMLHttpRequest对象的状态变化, http响应状态通过status获取;
发送同步请求:将open的第三个参数设置为false
// 1.创建XMLHttpRequest对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 3.配置请求open
// async: false
// 实际开发中要使用异步请求, 异步请求不会阻塞js代码继续执行
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata", false)
// 4.发送请求(浏览器帮助发送对应请求)
xhr.send()
// 5.同步必须等到有结果后, 才会继续执行
console.log(xhr.response)
console.log("------")
3.3_XMLHttpRequest其他事件监听
除了onreadystatechange还有其他的事件可以监听
- loadstart:请求开始。
- progress: 一个响应数据包到达,此时整个 response body 都在 response 中。
- abort:调用 xhr.abort() 取消了请求。
- error:发生连接错误,例如,域错误。不会发生诸如 404 这类的 HTTP 错误。
- load:请求成功完成。
- timeout:由于请求超时而取消了该请求(仅发生在设置了 timeout 的情况下)。
- loadend:在 load,error,timeout 或 abort 之后触发。
也可以使用load来获取数据
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// onload监听数据加载完成
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log("onload")
}
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata")
xhr.send()
3.4_响应数据和响应类型
发送了请求后,需要获取对应的结果:response属性
- XMLHttpRequest response 属性返回响应的正文内容;
- 返回的类型取决于responseType的属性设置;
通过responseType可以设置获取数据的类型, 如果将 responseType 的值设置为空字符串,则会使用 text 作为默认值。
xhr.responseType = "json"
和responseText、responseXML的区别:
- 早期通常服务器返回的数据是普通的文本和XML,所以通常会通过responseText、 responseXML来获取响应结果;
- 之后将它们转化成JavaScript对象形式;
- 目前服务器基本返回的都是json数据,直接设置为json即可;
// 1.创建XHR对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2.onload监听数据加载完成
xhr.onload = function() {
// const resJSON = JSON.parse(xhr.response)
console.log(xhr.response)
// console.log(xhr.responseText)
// console.log(xhr.responseXML)
}
// 3.告知xhr获取到的数据的类型
xhr.responseType = "json"
// xhr.responseType = "xml"
// 4.配置网络请求
// 4.1.json类型的接口
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata")
// 4.2.json类型的接口
// xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/01_basic/hello_json")
// 4.3.text类型的接口
// xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/01_basic/hello_text")
// 4.4.xml类型的接口
// xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/01_basic/hello_xml")
// 5.发送网络请求
xhr.send()
3.5_HTTP响应的状态status
XMLHttpRequest的state是用于记录xhr对象本身的状态变化,并非针对于HTTP的网络请求状态。
如果希望获取HTTP响应的网络状态,创建好XHR对象后就可通过status和statusText来获取:
// 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2.监听结果
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log(xhr.status, xhr.statusText)
// 根据http的状态码判断是否请求成功
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
console.log(xhr.response)
} else {
console.log(xhr.status, xhr.statusText)
}
}
//获取状态码
xhr.onerror = function() {
console.log("onerror", xhr.status, xhr.statusText)
}
// 3.设置响应类型
xhr.responseType = "json"
// 4.配置网络请求
// xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:8000/abc/cba/aaa")
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata")
// 5.发送网络请求
xhr.send()
3.6_GET/POST请求传递参数
在开发中,使用最多的是GET和POST请求,在发送请求的过程中,也可以传递给服务器数据。
常见的传递给服务器数据的方式有如下几种:
open网址,是提前写好的
- 方式一:GET请求的query参数
// 创建xhr对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 监听数据响应
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log(xhr.response)
}
// 配置请求
xhr.responseType = "json"
// 1.传递参数方式一: get -> query
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/get?name=why&age=18&address=广州市")
- 方式二:POST请求 x-www-form-urlencoded 格式
// 2.传递参数方式二: post -> urlencoded
xhr.open("post", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/posturl")
// 发送请求(请求体body)
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
xhr.send("name=why&age=18&address=广州市")
- 方式三:POST请求 FormData 格式
<body>
<form class="info">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="password" name="password">
</form>
<button class="send">发送请求</button>
<script>
const formEl = document.querySelector(".info")
const sendBtn = document.querySelector(".send")
sendBtn.onclick = function() {
// 创建xhr对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 监听数据响应
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log(xhr.response)
}
// 配置请求
xhr.responseType = "json"
// 3.传递参数方式三: post -> formdata
xhr.open("post", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/postform")
// formElement对象转成FormData对象
const formData = new FormData(formEl)
xhr.send(formData)
}
</script>
</body>
- 方式四:POST请求 JSON 格式
// 4.传递参数方式四: post -> json
xhr.open("post", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/postjson")
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/json")
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({name: "why", age: 18, height: 1.88}))
3.7_ajax网络请求封装
// 练习hyajax -> axios
function hyajax({
url,
method = "get",
data = {},
headers = {}, // token
success,
failure
} = {}) {
// 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2.监听数据
xhr.onload = function() {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
success && success(xhr.response)
} else {
failure && failure({ status: xhr.status, message: xhr.statusText })
}
}
// 3.设置类型
xhr.responseType = "json"
// 4.open方法
if (method.toUpperCase() === "GET") {
const queryStrings = []
for (const key in data) {
queryStrings.push(`${key}=${data[key]}`)
}
url = url + "?" + queryStrings.join("&")
xhr.open(method, url)
xhr.send()
} else {
xhr.open(method, url)
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/json")
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(data))
}
return xhr
}
// 调用者
hyajax({
url: "http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/get",
method: "GET",
data: {
name: "why",
age: 18
},
success: function(res) {
console.log("res:", res)//返回一个对象
},
failure: function(err) {
// alert(err.message)
}
})
用promise重构
// 练习hyajax -> axios
function hyajax({
url,
method = "get",
data = {},
timeout = 10000,
headers = {}, // token
} = {}) {
// 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2.创建Promise
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 2.监听数据
xhr.onload = function() {
if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
resolve(xhr.response)
} else {
reject({ status: xhr.status, message: xhr.statusText })
}
}
// 3.设置类型
xhr.responseType = "json"
xhr.timeout = timeout
// 4.open方法
if (method.toUpperCase() === "GET") {
const queryStrings = []
for (const key in data) {
queryStrings.push(`${key}=${data[key]}`)
}
url = url + "?" + queryStrings.join("&")
xhr.open(method, url)
xhr.send()
} else {
xhr.open(method, url)
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/json")
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(data))
}
})
promise.xhr = xhr
return promise
}
3.8_延迟时间timeout和取消请求
<body
> 取消请求button>
<script>
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log(xhr.response)
}
xhr.onabort = function() {
console.log("请求被取消掉了")
}
xhr.responseType = "json"
// 1.超时时间的设置
xhr.ontimeout = function() {
console.log("请求过期: timeout")
}
// timeout: 浏览器达到过期时间还没有获取到对应的结果时, 取消本次请求
// xhr.timeout = 3000
xhr.open("get", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/01_basic/timeout")
xhr.send()
// 2.手动取消结果
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("button")
cancelBtn.onclick = function() {
xhr.abort()
}
script>
body>
4_Fetch
4.1_Fetch和Fetch API
Fetch可以看做是早期的XMLHttpRequest的替代方案,它提供了一种更加现代的处理方案:
- 比如返回值是一个Promise,提供了一种更加优雅的处理结果方式
- 在请求发送成功时,调用resolve回调then;
- 在请求发送失败时,调用reject回调catch;
- 比如不像XMLHttpRequest一样,所有的操作都在一个对象上;
fetch函数的使用:
- input:定义要获取的资源地址,可以是一个URL字符串,也可以使用一个Request对象(实验性特性)类型;
- init:其他初始化参数
- method: 请求使用的方法,如 GET、POST;
- headers: 请求的头信息;
- body: 请求的 body 信息;
4.2_Fetch数据的响应(Response)
Fetch的数据响应主要分为两个阶段
阶段一:当服务器返回了响应(response)
- fetch 返回的 promise 就使用内建的 Response class 对象来对响应头进行解析;
- 在这个阶段,可以通过检查响应头,来检查 HTTP 状态以确定请求是否成功;
- 如果 fetch 无法建立一个 HTTP 请求,例如网络问题,亦或是请求的网址不存在,那么 promise 就会 reject;
- 异常的 HTTP 状态,例如 404 或 500,不会导致出现 error;
在 response 的属性中看到 HTTP 状态:
- status:HTTP 状态码,例如 200;
- ok:布尔值,如果 HTTP 状态码为 200-299,则为 true;
第二阶段,为了获取 response body,需要使用一个其他的方法调用。
- response.text() —— 读取 response,并以文本形式返回 response;
- response.json() —— 将response 解析为 JSON;
4.3_Fetch网络请求的演练
Promise
fetch("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata").then(res => {
// 1.获取到response
const response = res
// 2.获取具体的结果
return response.json()
}).then(res => {
console.log("res:", res)
}).catch(err => {
console.log("err:", err)
})
async、await
async function getData() {
const response = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata")
const res = await response.json()
console.log("res:", res)
}
getData()
4.4_Fetch POST请求
创建一个 POST 请求,或者其他方法的请求,需要使用 fetch 选项:
- method:HTTP 方法,例如 POST,
- body:request body,其中之一:
- 字符串(例如 JSON 编码的),
- FormData 对象,以 multipart/form-data 形式发送数据,
// 2.post请求并且有参数
async function getData() {
//字符串JSON
// const response = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/postjson", {
// method: "post",
// // headers: {
// // "Content-type": "application/json"
// // },
// body: JSON.stringify({
// name: "why",
// age: 18
// })
// })
//FromData对象
const formData = new FormData()
formData.append("name", "why")
formData.append("age", 18)
const response = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/postform", {
method: "post",
body: formData
})
// 获取response状态
console.log(response.ok, response.status, response.statusText)
const res = await response.json()
console.log("res:", res)
}
getData()
5_前端文件上传
文件上传是开发中经常遇到的需求,比如头像上传、照片等。 要想真正理解文件上传,必须了解服务器如何处理上传的文件信息
5.1_XMLHttpRequest文件上传
<body>
<input class="file" type="file">
<button class="upload">上传文件</button>
<script>
// xhr/fetch
const uploadBtn = document.querySelector(".upload")
uploadBtn.onclick = function() {
// 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 2.监听结果
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log(xhr.response)
}
xhr.onprogress = function(event) {
console.log(event)
}
xhr.responseType = "json"
xhr.open("post", "http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/upload")
// 表单
const fileEl = document.querySelector(".file")
const file = fileEl.files[0]
const formData = new FormData()
formData.append("avatar", file)
xhr.send(formData)
}
</script>
</body>
5.2_Fetch文件上传
Fetch也支持文件上传,但是Fetch没办法监听进度。
<body>
<input class="file" type="file">
<button class="upload">上传文件</button>
<script>
// xhr/fetch
const uploadBtn = document.querySelector(".upload")
uploadBtn.onclick = async function() {
// 表单
const fileEl = document.querySelector(".file")
const file = fileEl.files[0]
const formData = new FormData()
formData.append("avatar", file)
// 发送fetch请求
const response = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/upload", {
method: "post",
body: formData
})
const res = await response.json()
console.log("res:", res)
}
</script>
</body>
le)
xhr.send(formData)
}
5.2_Fetch文件上传
Fetch也支持文件上传,但是Fetch没办法监听进度。
<body>
<input class="file" type="file">
<button class="upload">上传文件</button>
<script>
// xhr/fetch
const uploadBtn = document.querySelector(".upload")
uploadBtn.onclick = async function() {
// 表单
const fileEl = document.querySelector(".file")
const file = fileEl.files[0]
const formData = new FormData()
formData.append("avatar", file)
// 发送fetch请求
const response = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:1888/02_param/upload", {
method: "post",
body: formData
})
const res = await response.json()
console.log("res:", res)
}
</script>
</body>