一文详解Linux常用命令
系统常用命令
-
echo [选项] [输出内容] :用来输出内容
-
-n:取消输出后行末的换行符号(即内容输出后不换行)
[root@linuxprobe network-scripts]# echo this is a test this is a test [root@linuxprobe network-scripts]# echo "the root path is $HOME" the root path is /root -
-
ifconfig 用来查看和配置网络设备
-
ctrl+c :强制中断当前程序的执行
-
ctrl+z :将任务中止(暂停的意思),但是此任务并没有结束,他仍然在进程中他只是维持挂起的状态
-
top:命令查看各个进程的cpu使用情况,默认按cpu使用率排序
工作目录切换命令
-
pwd 显示用户当前所处的目录;
-
cd 用户切换工作路径;
-
cd - 返回上一次所处的目录
-
cd .. 进入上级目录
-
cd ~ 回到当前用户的家目录
-
-
ls 显示目录中的文件信息
-
ls -a 查看全部文件(包括隐藏文件)
-
ls -l 查看文件的属性、大小等信息
-
文本编辑命令
-
cat 查看纯文本文件(内容较少的)
-
cat -n 查看文本内容时显示行号
-
-
more 查看纯文本文件(内容较多的,可使用空格键或回车键翻页)
-
head 查看纯文本文档的前N行
[root@linuxprobe ~]# head -20 initial-setup-ks.cfg #version=RHEL7 # X Window System configuration information xconfig --startxonboot # License agreement eula --agreed -
tail 查看纯文本文档的后N行或持续刷新内容
-
tail -n 20 文件名 :查看文档的后20行数据;
[root@linuxprobe ~]# tail -20 initial-setup-ks.cfg # Partition clearing information clearpart --none --initlabel %packages -
tail -f 文件名 :持续刷新一个文件的内容;
[root@linuxprobe ~]# tail -f /var/log/messages Feb 8 20:09:03 linuxprobe dbus[1039]: [system] Successfully activated service 'org.freedesktop.PackageKit' Feb 8 20:10:01 linuxprobe systemd: Starting Session 3 of user root. Feb 8 20:10:01 linuxprobe systemd: Started Session 3 of user root.
-
-
tr 用户替换文本文件中的字符串
[root@linuxprobe ~]# cat anaconda-ks.cfg|tr [a-z] [A-Z] #VERSION=RHEL7 # SYSTEM AUTHORIZATION INFORMATION AUTH --ENABLESHADOW --PASSALGO=SHA512
-
wc 用户统计指定文本中的行数、字数、字节数
-
wc -l 只显示行数
-
wc -w 只显示单词数
-
wc -c 只显示字节数
[root@linuxprobe ~]# wc -l /etc/passwd 38 /etc/passwd
-
-
stat 查看文件的具体存储信息和时间等信息
-
cut [参数] 文本 :用于按列提取文本字符串
[root@linuxprobe ~]# head -n 2 /etc/passwd root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin [root@linuxprobe ~]# cut -d: -f1 /etc/passwd root bin daemon adm -
diff 用于比较多个文本的差异
-
diif -brief 用于确认两个文件是否相同
-
diff -c 详细比较多个文件的差异之处
-
文件目录管理命令
-
touch 创建空白文件或设置文件的时间
-
touch 文件名:创建空白文件
-
touch -a 仅修改读取时间
-
touch -m 仅修改修改时间
-
touch -d 同时修改读取和修改时间
-
-
mkdir 创建空白的目录
-
mkdir -p 递归创建嵌套文件夹
[root@linuxprobe ~]# mkdir -p a/b/c [root@linuxprobe ~]# cd a [root@linuxprobe a]# ls b
-
-
cp [选项] 源文件 目标文件:复制文件或目录
-
cp -p 保留原始文件属性
-
cp -d 文件为链接,则保留链接文件的属性
-
cp -r 递归持续复制,用于目录
-
cp -i 若目标文件存在,则询问是否覆盖
-
cp -a 相当于 -pdr(pdr为上述选项参数)
[root@linuxprobe ~]# cp hello-world.txt first-test.txt [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls a anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Documents Downloads first-test.txt hello-world.txt
-
-
mv [选项] 源文件 [目标路径|目标文件名] :用于剪切文件或将文件重命名
[root@linuxprobe ~]# mv first-test.txt second.txt [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls a anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Documents Downloads hello-world.txt initial-setup-ks.cfg linuxtest Music Pictures Public second.txt -
rm 用于删除文件或目录
-
rm -f 强制删除文件(默认询问是否删除)
-
rm -r 递归持续删除,用于目录
[root@linuxprobe ~]# rm second.txt rm: remove regular empty file ‘second.txt’? n [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls a anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Documents Downloads hello-world.txt initial-setup-ks.cfg linuxtest Music Pictures Public second.txt Templates Videos [root@linuxprobe ~]# rm -f second.txt [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls a anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Documents Downloads hello-world.txt initial-setup-ks.cfg linuxtest Music Pictures Public Templates Videos -
-
file 用于查看文件类型
[root@linuxprobe ~]# file anaconda-ks.cfg anaconda-ks.cfg: ASCII text [root@linuxprobe ~]# file /dev/sda /dev/sda: block special
打包压缩与搜索命令
-
tar [选项] [文件] :对文件进行打包压缩或解压
-
tar -c 创建压缩文件
-
tar -x 解开压缩文件
-
tar -t 查看压缩包内文件
-
tar -z 用于Gzip压缩或解压
-
tar -j 用于bzip2压缩或解压
-
tar -v 显示压缩或解压的过程
-
tar -f 目标文件名
-
tar -p 保留原始文件的权限和属性
-
tar -P 使用绝对路径来压缩
-
tar -C 指定到解压目录
例:将/etc目录通过gzip格式进行压缩,并命名etc.tar.gz
[root@linuxprobe ~]# tar -czvf etc.tar.gz /etc tar: Removing leading `/' from member names /etc/ /etc/fstab /etc/crypttab /etc/mtab /etc/fonts/ ...... [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls a anaconda-ks.cfg Desktop Documents Downloads etc.tar.gz hello-world.txt将上面打包的压缩文件,解压到指定目录/root/etc中
[root@linuxprobe ~]# tar -czvf etc.tar.gz /etc tar: Removing leading `/' from member names /etc/ /etc/fstab /etc/crypttab /etc/mtab /etc/fonts/ /etc/fonts/conf.d/ ...... -
-
grep [选项] [文件]:用于在文本中执行关键词搜索,并显示匹配结果
-
-b 将可执行文件(binary)当作文本文件(txt)来搜索
-
-c 仅显示找到的行数
-
-i 忽略大小写
-
-n 显示行数
-
-v 反向选择,竟列出没有命中关键词的行
[root@linuxprobe ~]# grep /sbin/nologin /etc/passwd bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
-
-
find [查找路径] 寻找条件 操作 :按照指定条件来查找文件
-
-name 匹配名称
-
-perm 匹配权限
-
-user 匹配所有者
-
-group 匹配所有组
-
-mtime -n +n 匹配修改内容时间(-n指填以内,+n指n天以前)
-
-atime -n +n 匹配访问时间
-
--type b/d/c/p/l/f 匹配文件类型(字母依次表示设备、目录、字符设备、管道、链接文件、文本文件)
-
-prune 忽略某个文件
-
-exec 用于进一步处理搜索结果的命令
[root@linuxprobe ~]# find /etc -name "host*" -print /etc/avahi/hosts /etc/host.conf /etc/hosts /etc/hosts.allow -
重定向命令
概念
标准输入(STDIN,文件描述符为0):
默认从键盘输入,也可以从其他文件或命令中输入
标准输出(STDOUT,文件描述符为1):
默认输出到屏幕,也可以输出到文件
错误输出(STDERR,文件描述符为2):
默认输出到屏幕
重定向命令
-
输入重定向
-
命令 < 文件 :将文件作为命令的标准输入
-
命令 << 分解符 :从标准输入中读入,直到遇见分界符才停止
-
命令 < 文件1 > 文件2 :文件1作为命令的标准输入,并标准输出到文件2
-
-
输出重定向
-
命令 > 文件:标准输出到文件中(清空原文件内容)
-
命令 2 > 文件 :错误输出到文件中(清空原文件内容)
-
命令 >> 文件:标准输出到文件中 (原文件内容后追加)
-
命令 2 >> 文件:错误输出到文件中(原文件后追加)
-
命令 >> 文件 2>&1: 将标准输出与错误输出共同写入文件(追加到原内容后)
-
命令 &>> 文件:作用同e
对于标准输出模式,可以省略文件描述符1不写,而错误输出的文件描述符2是必须要写的。
例:将信息输出到文件
[root@linuxprobe ~]# man bash > hello.txt [root@linuxprobe ~]# cat hello.txt BASH(1) General Commands Manual BASH(1) NAME bash - GNU Bourne-Again SHell[root@linuxprobe ~]# echo "welcome to my world" > hello.txt [root@linuxprobe ~]# cat hello.txt welcome to my world[root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l etc.tar.gz -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8596806 Feb 13 14:50 etc.tar.gz [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l etc.tar.gz > hello.txt [root@linuxprobe ~]# cat hello.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8596806 Feb 13 14:50 etc.tar.gz将错误信息写入到文件
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l linuxprobe ls: cannot access linuxprobe: No such file or directory [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l linuxprobe 2 > hello.txt ls: cannot access linuxprobe: No such file or directory ls: cannot access 2: No such file or directory [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l linuxprobe 2> hello.txt [root@linuxprobe ~]# cat hello.txt ls: cannot access linuxprobe: No such file or directory -
-
管道命令符
-
命令A | 命令B:将命令A输出的正常数据当作命令B的标准输入
例:搜索被限制登录的用户,并统计文本行数
[root@linuxprobe ~]# grep "/sbin/nologin" /etc/passwd | wc -l 33 -
-
命令行通配符
-
*:代表匹配零个或多个字符
-
?:匹配单个字符
-
[0-9]:匹配0-9之间的单个数字
-
[abc]:匹配a、b、c三个字符中的任意一个字符
[root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l /dev/sda* brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 0 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 2 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda2 [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l /dev/sda? brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 2 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda2 [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l /dev/sda[0-9] brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 2 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda2 [root@linuxprobe ~]# ls -l /dev/sda[135] brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Feb 13 2022 /dev/sda1 -
-
常用的转义字符
-
\ :使反斜杠后面的变量变为单纯的字符串
-
" :转义其中所有的变量为单纯的字符串
-
"" :保留其中的变量属性,不进行转义处理
-
`` :把其中的命令执行后返回结果
[root@linuxprobe ~]# PRICE=5 [root@linuxprobe ~]# echo "Price is $PRICE" Price is 5 [root@linuxprobe ~]# echo "Price is \$$PRICE" Price is $5 [root@linuxprobe ~]# echo `uname -a` Linux linuxprobe.com 3.10.0-123.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Mon May 5 11:16:57 EDT 2014 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux -
-
重要的环境变量
-
HOME :用户的主目录
-
SHELL :用户在使用的shell解释器名称
-
HISTSIZE :输出的历史命令记录条数
-
HISTFILESIZE :保存的历史命令记录条数
-
MAIL :邮件保存地址
-
LANG :系统语言、语系名称
-
RANDOM :生成一个随机数字
-
PS1 :Bash解释器的提示符
-
PATH :定义解释器搜素用户执行命令的路径
-
EDITOR :用户默认的文本编辑器
[root@linuxprobe ~]# echo $HOME /root [root@linuxprobe ~]# su - linuxprobe su: user linuxprobe does not exist [root@linuxprobe ~]# echo $HOME /root [root@linuxprobe ~]# su - snow Last login: Sun Feb 6 19:28:32 CST 2022 on :0 [snow@linuxprobe ~]$ echo $HOME /home/snow -
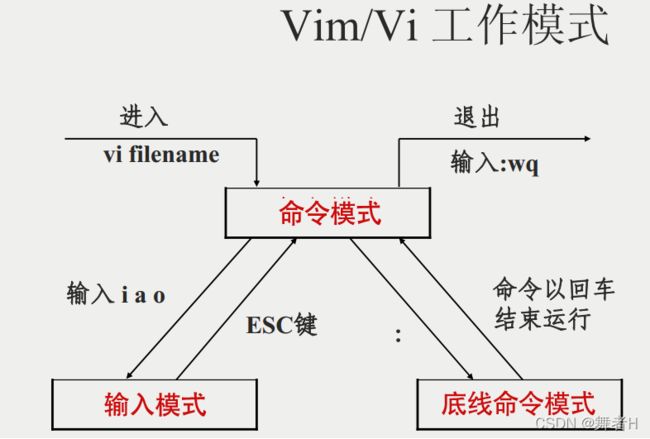
Vim编辑器
Vim操作的三种模式
-
命令模式:控制光标移动,可对文本进行复制、粘贴、删除和查找等
-
输入模式:正常的文本录入
-
末行模式:保存或退出文档,以及设置编辑环境
a/i 分别是在光标后面一位和光标当前位置切换到输入模式;
o 是在光标的下面在创建一个空行
Vim中常用命令
-
命令模式中常用的命令
-
dd 删除光标所在行
-
5dd 删除光标所在处的5行
-
yy 复制光标所在整行
-
5yy 复制从光标开始处的5行
-
n 显示搜索命令定位到的下一个字符串
-
N 显示搜索命令定位到的上一个字符串
-
u 撤销上一步的操作
-
p 将之前删除(dd)或复制(yy)过的数据粘贴到光标后面
-
-
末行模式中常用命令
-
:w 保存
-
:q 退出
-
:q! 强制退出(放弃对文档的修改内容)
-
:wq! 强制保存退出
-
:set nu 显示行号
-
:set nonu 不显示行号
-
:命令 执行改命令
-
:整数 跳到该行
-
?字符串 在文本中从下往上搜索该字符串
-
/字符串 在文本中从上往下搜索该字符串
-
参考文献
- 菜鸟教程
- 《Linux就该这么学》刘遄