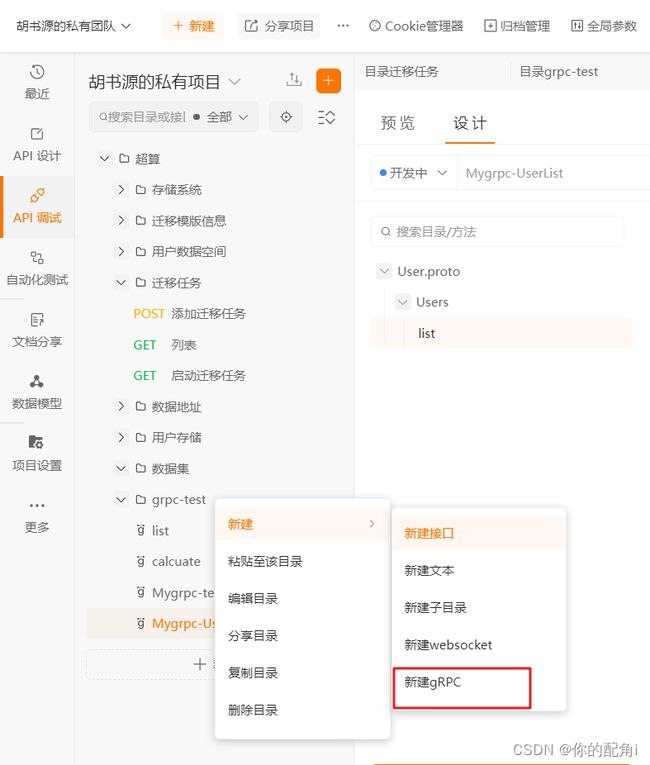
SpringBoot使用GRPC框架(服务端)
概述:
GRPC是什么? 首先我们知道 RPC是远程过程调用。
而GRPC是RPC的一种实现。 那么为什么要用GRPC呢?
因为它支持跨语言的开发,换句话说,大家都用过FeignRPC,尤其在spring cloud中。
然而它只支持java语言,而作为微服务,可能有很多其他的服务不是java开发的。
因此需要满足这个需求,就需要一个跨语言的RPC,所以就会考虑使用GRPC
使用流程(服务端):
流程:
先创建一个普通的Maven项目
导入依赖
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.5.6
com.leadtrans
report
1.6.0
report
Demo project for Spring Boot
11
2020.0.4
2.3.2
1.6.0
0.5.1
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.78
org.lognet
grpc-spring-boot-starter
${grpc-spring-boot-starter.version}
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-dependencies
${spring-cloud.version}
pom
import
kr.motd.maven
os-maven-plugin
${os-maven-plugin.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
repackage
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-surefire-plugin
true
org.xolstice.maven.plugins
protobuf-maven-plugin
${protobuf-maven-plugin.version}
com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.5.1-1:exe:${os.detected.classifier}
grpc-java
io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.11.0:exe:${os.detected.classifier}
${project.build.sourceDirectory}
false
compile
compile-custom
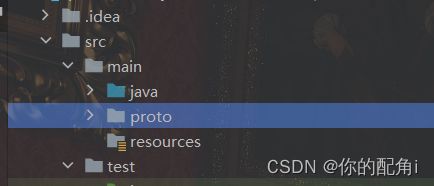
创建proto文件夹:
proto文件夹必须和java文件夹同级
在文件夹下创建proto文件:
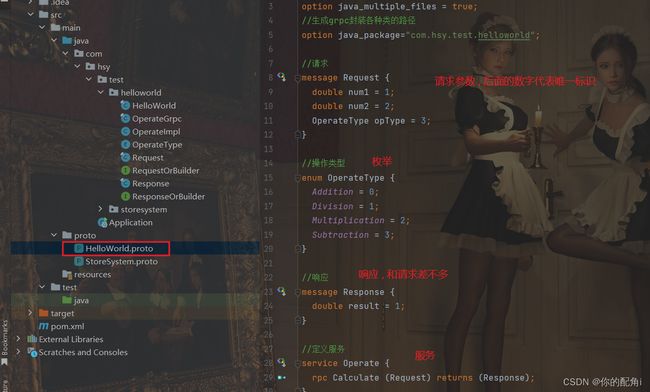
HelloWorld.protp
syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
//生成grpc封装各种类的路径, 必须和SpringBoot启动类同级或更低
option java_package="com.example.test.helloworld";
//请求
message Request {
double num1 = 1;
double num2 = 2;
OperateType opType = 3;
}
//操作类型
enum OperateType {
Addition = 0;
Division = 1;
Multiplication = 2;
Subtraction = 3;
}
//响应
message Response {
double result = 1;
}
//定义服务
service Operate {
rpc Calculate (Request) returns (Response);
}
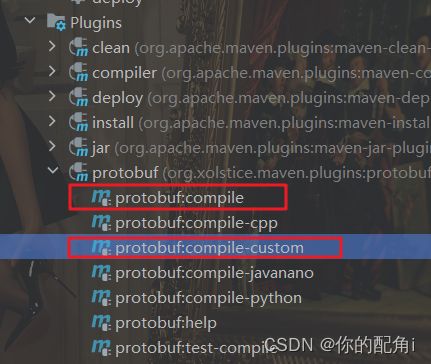
按顺序执行指令
执行完之后会生成如下代码
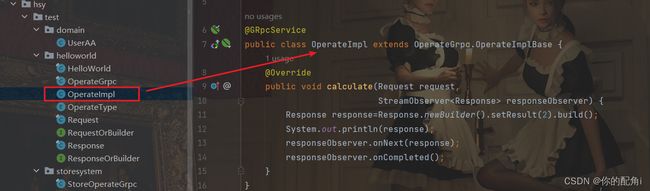
实现接口接收请求:
代码:
package com.hsy.test.helloworld;
import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver;
import org.lognet.springboot.grpc.GRpcService;
@GRpcService
public class OperateImpl extends OperateGrpc.OperateImplBase {
@Override
public void calculate(Request request,
StreamObserver responseObserver) {
Response response=Response.newBuilder().setResult(2).build();
System.out.println(response);
responseObserver.onNext(response);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
}
注意事项:
proto文件解释:
grpc返回集合数据:
在 gRPC 中,可以使用消息类型(Message)来表示集合。通常使用 Protocol Buffers 来定义 gRPC 中的消息类型。
假设定义了一个 User 消息类型:
proto文件:
syntax = "proto3";
message User {
int32 id = 1;
string name = 2;
string email = 3;
}
如果要返回一个包含多个 User 对象的集合,可以定义一个消息类型,将多个 User 对象放在一个列表中。修改 UserList.proto 文件,添加一个新的消息类型 UserList:
message UserList {
repeated User users = 1;
}
在上面的定义中,使用了`repeated` 字段类型,表示该字段可以包含重复的值,也就是一个集合。
完整proto文件:
syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
//生成grpc封装各种类的路径, 必须和SpringBoot启动类同级或更低
option java_package="com.hsy.test.user";
//对象的属性
message User {
int32 id = 1;
string name = 2;
string email = 3;
}
//定义集合数据
message UserList {
repeated User users = 1;
}
//请求
message UserRequest {
string type = 1;
}
//响应
message UserResponse {
UserList result = 1;
}
//定义服务
service Users {
rpc list (UserRequest) returns (UserResponse);
}
响应接口实现:
@GRpcService
public class UserOperateImpl extends UsersGrpc.UsersImplBase {
@Override
public void list(UserRequest request, StreamObserver responseObserver) {
//根据名称获取参数
String type = request.getType();
//创建一个几个准备测试数据
ArrayList users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new UserAA(1, "zhangs", "[email protected]"));
users.add(new UserAA(2, "lisi", "[email protected]"));
users.add(new UserAA(3, "wangwu", "[email protected]"));
//使用UserList的构建器创建一个新的 UserList.Builder对象
UserList.Builder userList = UserList.newBuilder();
//list.forEach(c ->{...}); 遍历 list 列表,对每个元素执行 lambda 表达式中的代码块。
users.forEach(
c -> {
//创建一个新的 StoreSystemBean.Builder 对象,并设置其属性值,然后将其添加到 resList 中。
User.Builder bean = User.newBuilder()
.setId(c.getId())
.setName(c.getName())
.setEmail(c.getEmail());
userList.addUsers(bean);
}
);
//使用 StoreResponse 的构建器创建一个新的响应对象,并将其设置为包含 resList 的结果
UserResponse response = UserResponse.newBuilder().setResult(userList).build();
//将响应对象返回给客户端。
responseObserver.onNext(response);
//通知客户端,该调用已完成。
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
} 实现类与proto文件的对应关系
设置grpc服务的端口号:
方式一:
在 gRPC 中,服务端和客户端通过网络进行通信,服务端必须公开端口来侦听客户端请求。在 gRPC 中为侦听客户端请求,通常可以通过以下方式来设置端口号:
1. 在 gRPC Server 启动时,指定端口号。 在 Java 中,启动 gRPC Server 时可以使用 ServerBuilder 组件指定端口号和其他配置。例如:
在SpringBoot启动类中的main方法中添加如下代码
Server server = ServerBuilder.forPort(8088)
.addService(new MyServiceImpl())
.build();
server.start();方式二:
使用 gRPC Server 上提供的绑定 API。 gRPC Server 提供了一个绑定 API,允许您在指定的 IP 和端口绑定服务。例如:
在SpringBoot启动类中的main方法中添加如下代码
Server server = ServerBuilder.forAddress(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080))
.addService(new MyServiceImpl())
.build();
server.start();
在上述示例中,通过绑定地址 'localhost' 和端口 '8080',可以将 gRPC 服务绑定到本地主机上的该端口上。
方式三:
在升级到gRPC v1.34及之后的版本中,还可以使用使用Bootstrap和SystemProperty配置端口的方式如下:
在SpringBoot启动类中的main方法 中添加如下代码
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(EpollSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast(new GrpcClientInitializer());
}
});
System.setProperty("grpc.port", "8080");
ChannelFuture f = b.connect("localhost", Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("grpc.port"))); 在这种方式中,我们将grpc.port属性设置为端口号,而后使用Bootstrap配置客户端。
无论使用哪种方式来设置端口号,都需要确保端口号未被其他应用程序占用,并且需要部署到能够访问其所在网络的位置。
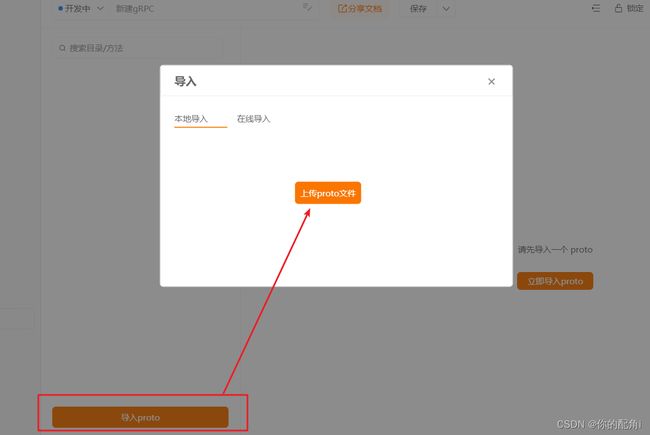
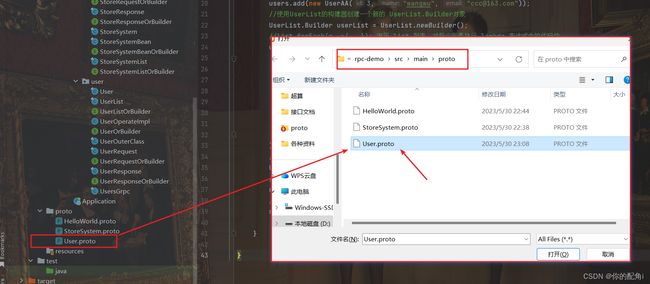
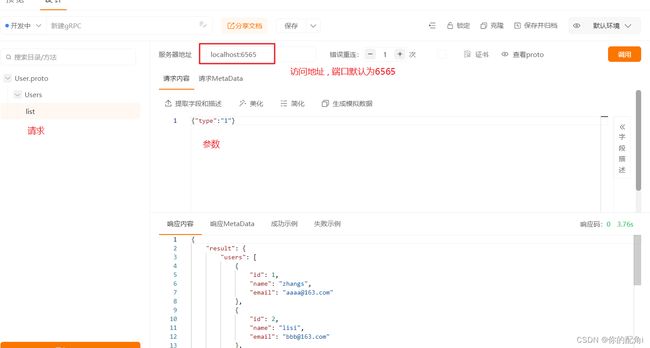
测试方式:
按图走