AHB协议理解
从小父亲就教育我,做一个对社会有用的人!
目录
Chapter1 AHB Block Diagram
Ginput signal
lnput signals
Output Signal
Chapter3 Transfers
AHB接口Overview
Chapter6 Data Buses
HWDATA
HRDATA
Chapter1 Introduction
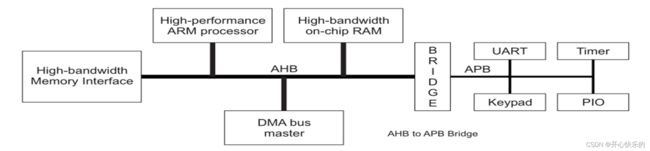
AHB Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows only the main address and data buses and typical data routing. Not all signals are shown.
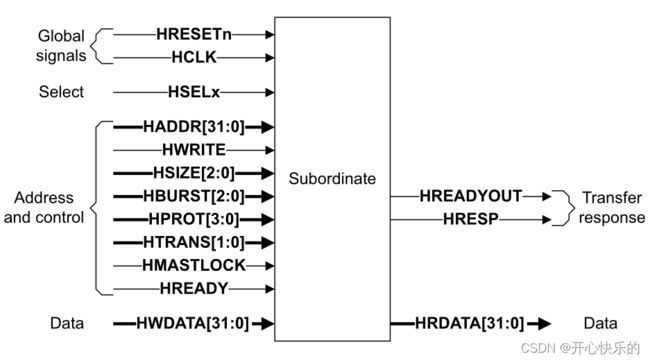
Figure 1-3 Subordinate interface
Global Singal
lnput signals
Output Signal
Chapter3 Transfers
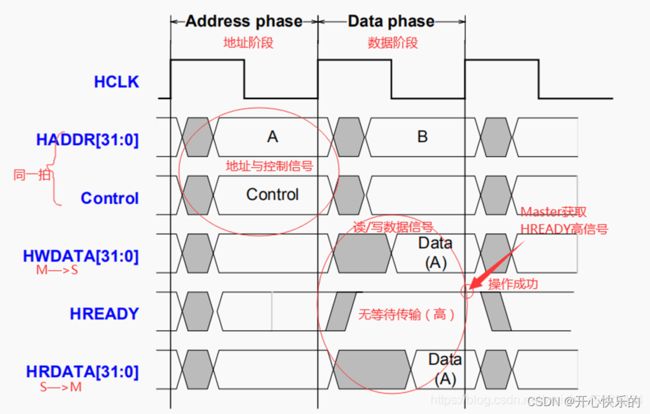
- Address phase One address and control cycle.
- Data phase One or more cycles for the data.
- HWRITE is HIGH, it indicates a write transfer and the Manager broadcasts data on the write data bus, HWDATA.
- HWRITE is LOW, a read transfer is performed, and the Subordinate must generate the data on the read data bus, HRDATA.
Figure Transfer with no wait state
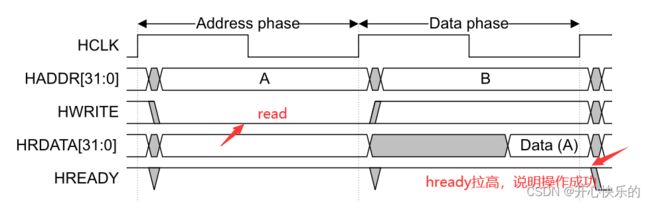
Figure 3-1 Read transfer
Figure 3-2 Write transfer
Figure AHB transfer with wait
原因:从机未必处于就绪状态
等待时的读写:
写:要保持写的状态直至传输完成
读:只有当Hready为高时,slave才会获取有效值
Figure 3-3 Read transfer with two wait states
Figure 3-4 Write transfer with one wait state
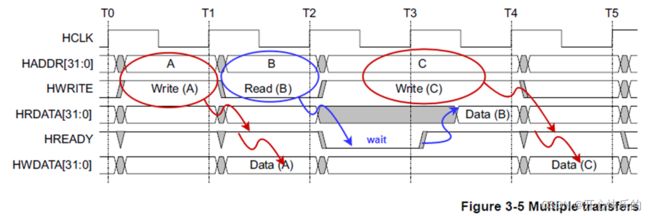
Figure 3-5 Multiple transfers
Table 3-1 Transfer type encoding
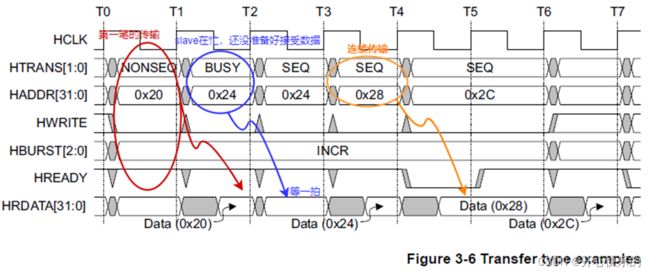
Figure 3-6 shows the use of the NONSEQ, BUSY , and SEQ transfer types.
带控制信号的多笔传输时序
Figure 3-6 Transfer type examples
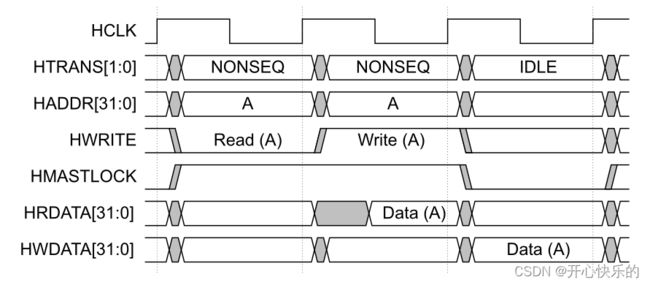
Figure 3-7 Locked transfer
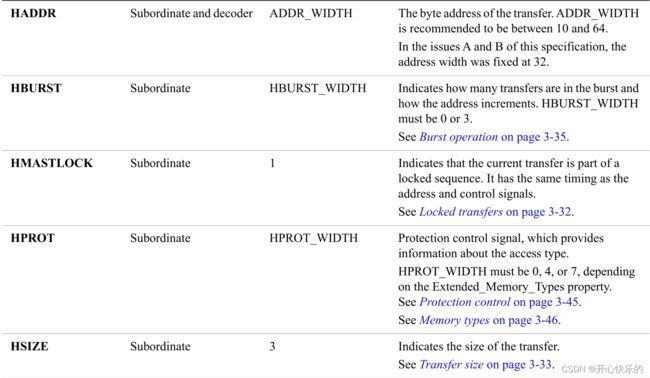
Table 3-2 Transfer size encoding
Table 3-4 Burst signal encoding
Figure 3-8 shows a write transfer using a four-beat wrapping burst, with a wait state added for the first transfer.
Figure 3-8 Four-beat wrapping burst
AHB接口Overview
MASTER
SLAVE
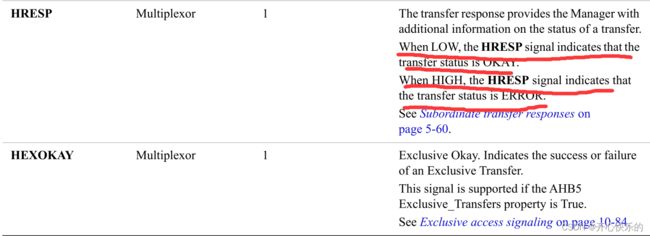
Figure 5-1 ERROR response
Chapter6 Data Buses
HWDATA
The Manager drives the write data bus during write transfers. If the transfer is extended, then the Manager must hold the data valid until the transfer completes, as indicated by HREADY HIGH. See Clock on page 7-72 for details on holding signals valid across multiple cycles.
For transfers that are narrower than the width of the bus, for example a 16-bit transfer on a 32-bit bus, the Manager only has to drive the appropriate byte lanes. The Subordinate selects the write data from the correct byte lanes. See Endianness on page 6-65 for details of the byte lanes that are active for a little-endian and big-endian system.
HRDATA
The appropriate Subordinate drives the read data bus during read transfers. If the Subordinate extends the read transfer by holding HREADY LOW, then the Subordinate only has to provide valid data in the final cycle of the transfer, as indicated by HREADY HIGH.
For transfers that are narrower than the width of the bus, the Subordinate is only required to provide valid data on the active byte lanes. The Manager selects the data from the correct byte lanes.
A Subordinate only has to provide valid data when a transfer completes with an OKAY response. ERROR responses do not require valid read data.