《视觉SLAM十四讲》手写高斯牛顿—笔记记录
《视觉SLAM十四讲》手写高斯牛顿—笔记记录
我们的最终目的:使用高斯牛顿法,拟合参数abc
我们的实际小目标:求解增量方程得到ΔX(有了Δx就可以不停的迭代Eabc使得拟合Rabc啦)
三个步骤:
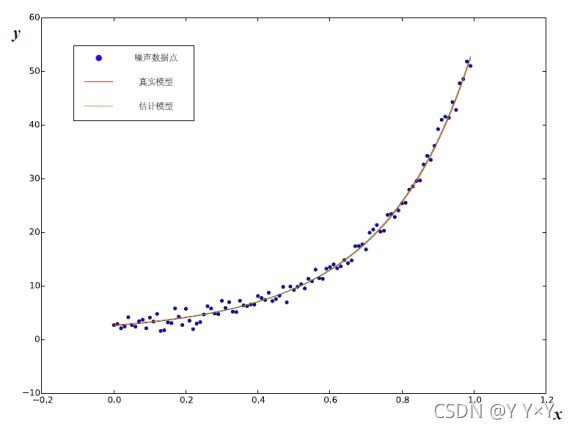
1、先根据模型生成x,y的真值,并在真值中添加高斯分布的噪声
2、使用高斯牛顿法进行迭代
3、求解高斯牛顿法的增量方程
首先定义真实的a,b,c参数值为ar,br,cr
这三个也是我们要拟合的最终目标,最终的拟合结果跟这三个值越接近越好
double ar = 1.0, br = 2.0, cr = 1.0;
然后定义初始的估计参数值ae,be,ce
这三个就是用于迭代的,最后效果最好是ae,be,ce迭代到与ar,br,cr一样。
double ae = 2.0, be = -1.0, ce = 5.0;
然后我们假设有100个数据点,设置噪声值sigma
第一步,根据模型生成X,Y的真值,并添加高斯分布的噪声
vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 数据
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
double x = i / 100.0;
x_data.push_back(x);
y_data.push_back(exp(ar * x * x + br * x + cr) + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma));
}
第二步,使用高斯牛顿法进行迭代
迭代次数设为100次
定义误差:
double error = yi - exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce);
然后分别对每个误差项对a,b,c进行求导,然后生成雅可比矩阵
Vector3d J; // 雅可比矩阵
J[0] = -xi * xi * exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/da
J[1] = -xi * exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/db
J[2] = -exp(ae * xi * xi + be * xi + ce); // de/dc
然后求解海塞矩阵H和偏移量b
H += inv_sigma * inv_sigma * J * J.transpose();
b += -inv_sigma * inv_sigma * error * J;
第三步,求解高斯牛顿法的增量方程(相当于梯度下降的Δx,就是向前迈一小步~)
这里的关键语句是Vector3d dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);
涉及一个eigen库中的LDLT分解,其中L为一下三角形单位矩阵(即主对角线元素皆为1),D为一对角矩阵(只在主对角线上有元素,其余皆为零),L^T为L的转置矩阵。
// 求解线性方程 Hx=b
Vector3d dx = H.ldlt().solve(b);
if (isnan(dx[0])) {
cout << "result is nan!" << endl;
break;
}
if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) {
cout << "cost: " << cost << ">= last cost: " << lastCost << ", break." << endl;
break;
}
ae += dx[0];
be += dx[1];
ce += dx[2];
lastCost = cost; //更新损失
完整代码如下:
#include 最终结果:
/home/yjc/SLAM_Study/ch6/cmake-build-debug/gaussNewton
total cost: 3.19575e+06, update: 0.0455771 0.078164 -0.985329 estimated params: 2.04558,-0.921836,4.01467
total cost: 376785, update: 0.065762 0.224972 -0.962521 estimated params: 2.11134,-0.696864,3.05215
total cost: 35673.6, update: -0.0670241 0.617616 -0.907497 estimated params: 2.04432,-0.0792484,2.14465
total cost: 2195.01, update: -0.522767 1.19192 -0.756452 estimated params: 1.52155,1.11267,1.3882
total cost: 174.853, update: -0.537502 0.909933 -0.386395 estimated params: 0.984045,2.0226,1.00181
total cost: 102.78, update: -0.0919666 0.147331 -0.0573675 estimated params: 0.892079,2.16994,0.944438
total cost: 101.937, update: -0.00117081 0.00196749 -0.00081055 estimated params: 0.890908,2.1719,0.943628
total cost: 101.937, update: 3.4312e-06 -4.28555e-06 1.08348e-06 estimated params: 0.890912,2.1719,0.943629
total cost: 101.937, update: -2.01204e-08 2.68928e-08 -7.86602e-09 estimated params: 0.890912,2.1719,0.943629
cost: 101.937>= last cost: 101.937, break.
solve time cost = 0.000237057 seconds.
estimated abc = 0.890912, 2.1719, 0.943629
进程已结束,退出代码为 0