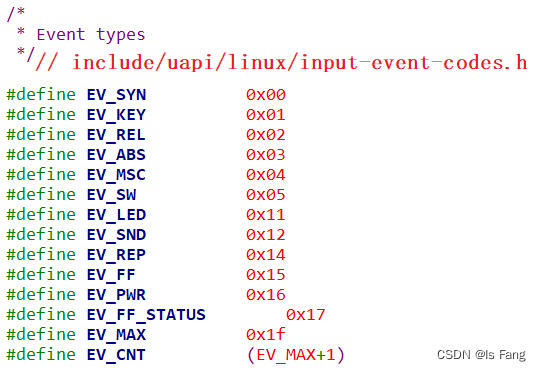
输入系统框架及应用访问输入设备的4种方式
文章目录
- 输入系统框架及调试
-
- 框架概述
- APP 得到事件数据的格式
-
- timeval
- ① type:表示哪类事件
- ② code:表示该类事件下的哪一个事件
- ③ value:表示事件值
- ④ 事件之间的界线
- 查看输入设备信息
-
- 内核中怎么表示一个输入设备?
- 确定输入设备信息
- 设备信息含义
- 获取设备部分信息的应用程序
-
- 获取设备信息函数
- 完整案例代码
- APP 访问硬件的 4 种方式:
-
- 查询方式
- 休眠- 唤醒方式
-
- 查询与休眠-唤醒方式的案例
- POLL/SELECT 方式
-
- POLL 方式案例
- SELECT 方式案例
- 异步通知方式
-
- 异步通知方式案例
- 电阻屏和电容屏
-
- 电容屏
- 使用tslib库的应用程序
输入系统框架及调试
框架概述
假设用户程序直接访问/dev/input/event0 设备节点,或者使用 tslib访问设备节点,数据的流程如下:
- ① APP 发起读操作,
若无数据则休眠; - ② 用户操作设备,硬件上产生中断;
- ③ 输入系统驱动层对应的驱动程序处理中断:
- 读取到数据,转换为标准的输入事件,向核心层汇报。
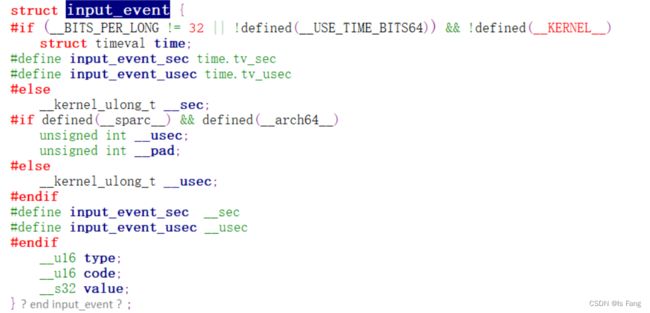
- 所谓输入事件就是一个“struct input_event”结构体。
- ④ 核心层
可以决定把输入事件转发给上面哪个 handler来处理:- 核心层将数据转化为统一的格式,发送给事件层
- 从 handler 的名字来看,它就是用来处输入操作的。有多种 handler,比 如:evdev_handler、kbd_handler、joydev_handler 等等。
最常用的是 evdev_handler:它只是把 input_event 结构体保存在内核buffer 等,APP 来读取时就原原本本地返回。它支持多个 APP 同时访问输入设备,每个 APP 都可以获得同一份输入事件。当 APP 正在等待数据时,evdev_handler 会把它唤醒,这样 APP 就可以返回数据。
- ⑤ APP 对输入事件的处理:APP 获 得 数 据 的 方 法 有 2 种 : 直 接 访 问 设 备 节 点 ( 比 如/dev/input/event0,1,2,…),或者通过 tslib、libinput 这类库来间接访问设备节点。这些库简化了对数据的处理。
APP 得到事件数据的格式
核心层会将事件的数据转化为统一的格式,发送给事件层,上报的数据含义中三项重要内容:

timeval
每个输入事件 input_event 中都含有发生时间:timeval 表示的是“自系统启动以来过了多少时间”,它是一个结构体,含有“tv_sec、tv_usec”两项(即秒、微秒)。
输入事件 input_event 中更重要的是:type(哪类事件)、code(哪个事件)、value(事件值)
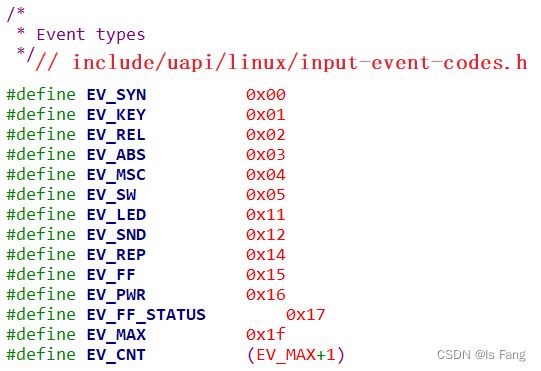
① type:表示哪类事件
比如 EV_KEY 表示按键类、EV_REL 表示相对位移(比如鼠标),EV_ABS 表示绝对位置(比如触摸屏),EV_SYN表示同步事件(硬件已经上报完所有事件)。
② code:表示该类事件下的哪一个事件
比如对于 EV_KEY(按键)类事件,它表示键盘。键盘上有很多按键,比如数字键 1、2、3,字母键 A、B、C 里等。

对于触摸屏,它提供的是绝对位置信息,有 X 方向、Y 方向,还有压力值。

③ value:表示事件值
对于按键,它的 value 可以是 0(表示按键被按下)、1(表示按键被松开)、2(表示长按);
对于触摸屏,它的 value 就是坐标值、压力值。
④ 事件之间的界线
APP 怎么知道它已经读到了完整的数据?
- 驱动程序上报完一系列的数据后,会上报一个“
同步事件”,表示数据上报完毕。APP 读到“同步事件”时,就知道已经读完了当前的数据。同步事件也是一个 input_event 结构体,它的 type、code、value 三项都是 0。,例如触摸屏数据
执行:hexdump /dev/input/event0,输出如下:

查看输入设备信息
内核中怎么表示一个输入设备?
使用 input_dev 结构体来表示输入设备

最关键是evbit数据,表示支持哪类事件,相对应的,下面会有该类事件下的某个事件位,所有的数据都是以位作为单位(位图)
确定输入设备信息
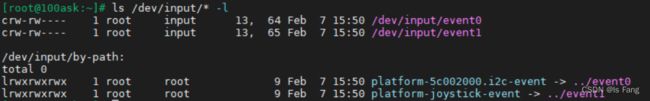
输入设备的设备节点名为/dev/input/eventX(也可能是/dev/eventX,X表示 0、1、2 等数字)。查看设备节点,可以执行以下命令:ls /dev/input/* -l或ls /dev/event* -l
查看设备节点对应什么硬件,输入指令:cat /proc/bus/input/devices
设备信息含义
- ① I:id of the device(设备 ID)
该参数由结构体 struct input_id 来进行描述,驱动程序中会定义这样的结构体:

- ② N:name of the device
设备名称 - ③ P:physical path to the device in the system hierarchy
系统层次结构中设备的物理路径。 - ④ S:sysfs path
位于 sys 文件系统的路径 - ⑤ U:unique identification code for the device(if device has it)
设备的唯一标识码 - ⑥ H:list of input handles associated with the device.
与设备关联的输入句柄列表。 - ⑦ B:bitmaps(位图)
PROP:device properties and quirks( 设备属性)
EV:types of events supported by the device( 设备支持的事件类型)
KEY:keys/buttons this device has( 此设备具有的键/ 按钮)
MSC:miscellaneous events supported by the device( 设备支持的其他事件)
LED:leds present on the device( 设备上的指示灯)
例子:
图中“B: EV=b”用来表示该设备支持哪类输入事件。b 的二进制是 1011,bit0、1、3 为 1,表示该设备支持 0、1、3 这三类事件,即 EV_SYN、EV_KEY、EV_ABS。“B: ABS=2658000 3”表示该设备支持 EV_ABS 这一类事件中的哪一些事件。这是 2 个 32 位的数字:0x2658000、0x3,高位在前低位在后,组成一个 64 位的数字:“0x2658000,00000003”,数值为 1 的位有:0、1、47、48、50、53、54,即:0、1、0x2f、0x30、0x32、0x35、0x36,对应以下这些宏:

获取设备部分信息的应用程序
获取设备信息函数
通过 ioctl 获取设备信息,ioctl 的参数如下:
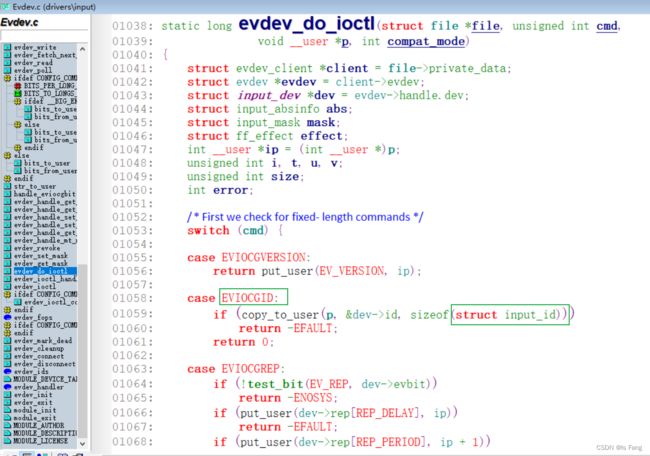
#include 用户态的获取设备信息的函数是ioctl,而内核驱动中对应的获取设备信息的函数是evdev_do_ioctl函数,其中参数request对应cmd
参考evdev.c文件的evdev_do_ioctl函数可知,获取设备的id信息要接收请求cmd为:EVIOCGID, 该宏定义表示id的信息保存在结构体:struct input_id中
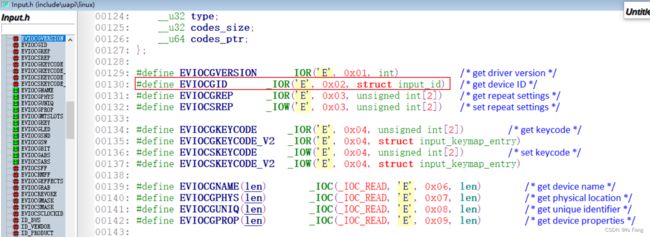

cmd宏定义的头文件在:input.h,通过引入编译工具链include文件夹内的input.h可以使用该宏定义
比如要读取输入设备的 evbit 时,ioctl 的 request 要写为“EVIOCGBIT(0,size)”这个宏定义,len 的大小可以由你决定:你想读多少字节就设置为多少。这个宏的定义如下:
![]()
有些驱动程序对 request 的格式有要求,它的格式如下:

比如 dir 为_IOC_READ(即 2)时,表示 APP 要读数据;例如:
![]()
为_IOC_WRITE(即 4)时,表示 APP 要写数据。size 表示这个 ioctl 能传输数据的最大字节数。type、nr 的含义由具体的驱动程序决定。
完整案例代码
#include \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
err = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &id);
if (err == 0)
{
printf("bustype = 0x%x\n", id.bustype );
printf("vendor = 0x%x\n", id.vendor );
printf("product = 0x%x\n", id.product );
printf("version = 0x%x\n", id.version );
}
len = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(0, sizeof(evbit)), &evbit);
if (len > 0 && len <= sizeof(evbit))
{
printf("support ev type: ");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
byte = ((unsigned char *)evbit)[i];
for (bit = 0; bit < 8; bit++)
{
if (byte & (1<<bit)) {
printf("%s ", ev_names[i*8 + bit]);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
APP 访问硬件的 4 种方式:
查询方式
休眠-唤醒
poll 方式
异步通知
这 4 种方法没有优劣之分,在不同的场合使用不同的方法。
查询方式
APP 调用 open 函数时,传入“O_NONBLOCK”表示“非阻塞”。
APP 调用 read 函数读取数据时,如果驱动程序中有数据,那么 APP 的read 函数会返回数据,否则也会立刻返回错误。
休眠- 唤醒方式
APP 调用 open 函数时,不要传入“O_NONBLOCK”。表示阻塞
APP 调用 read 函数读取数据时,如果驱动程序中有数据,那么 APP 的read 函数会返回数据;否则 APP 就会在内核态休眠,当有数据时驱动程序会把APP 唤醒,read 函数恢复执行并返回数据给 APP。
查询与休眠-唤醒方式的案例
查看evdev.c文件,用户态调用读取事件的函数,最终会调用内核态的evdev_read函数,最终会将数据存储在input_event结构体中

#include [noblock]\n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
if (argc == 3 && !strcmp(argv[2], "noblock"))
{
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);//非阻塞,查询方式
}
else
{
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);//阻塞,休眠-唤醒
}
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
err = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &id);
if (err == 0)
{
printf("bustype = 0x%x\n", id.bustype );
printf("vendor = 0x%x\n", id.vendor );
printf("product = 0x%x\n", id.product );
printf("version = 0x%x\n", id.version );
}
len = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(0, sizeof(evbit)), &evbit);
if (len > 0 && len <= sizeof(evbit))
{
printf("support ev type: ");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
byte = ((unsigned char *)evbit)[i];
for (bit = 0; bit < 8; bit++)
{
if (byte & (1<<bit)) {
printf("%s ", ev_names[i*8 + bit]);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
while (1)
{
len = read(fd, &event, sizeof(event));
if (len == sizeof(event))
{
printf("get event: type = 0x%x, code = 0x%x, value = 0x%x\n", event.type, event.code, event.value);
}
else
{
printf("read err %d\n", len);
}
}
return 0;
}
POLL/SELECT 方式
在调用 poll、select 函数时可以传入“超时时间”。在这段时间内,条件合适时(比如有数据可读、有空间可写)就会立刻返回,否则等到“超时时间”结束时返回错误。
用法如下
- APP 先调用 open 函数时。
APP 不是直接调用 read 函数,而是先调用 poll 或 select 函数,这 2 个函数中可以传入“超时时间”。它们的作用是:如果驱动程序中有数据,则立刻返回;否则就休眠。在休眠期间,如果有人操作了硬件,驱动程序获得数据后就会把 APP 唤醒,导致 poll 或 select 立刻返回;如果在“超时时间”内无人操作硬件,则时间到后 poll 或 select 函数也会返回。APP 可以根据函数的返回值判断返回原因:有数据?无数据超时返回?- APP 根据 poll 或 select 的返回值判断有数据之后,就调用 read 函数读取数据时,这时就会立刻获得数据。
- poll/select 函数可以监测多个文件,可以监测多种事件:
| 事件类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
POLLIN |
有数据可读 |
| POLLRDNORM | 等同于 POLLIN |
| POLLRDBAND | Priority band data can be read,有优先级较较高的“band data”可读。Linux 系统中很少使用这个事件 |
| POLLPRI | 高优先级数据可读 |
POLLOUT |
可以写数据 |
| POLLWRNORM | 等同于 POLLOUT |
| POLLWRBAND | Priority data may be written |
| POLLERR | 发生了错误 |
| POLLHUP | 挂起 |
| POLLNVAL | 无效的请求,一般是 fd 未 open |
POLL 方式案例
- *fds表示数组,该数组成员是结构体polldf,成员个数由nfds_t参数决定
#include \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
//选择非阻塞方式打开设备
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
err = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &id);
if (err == 0)
{
printf("bustype = 0x%x\n", id.bustype );
printf("vendor = 0x%x\n", id.vendor );
printf("product = 0x%x\n", id.product );
printf("version = 0x%x\n", id.version );
}
len = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(0, sizeof(evbit)), &evbit);
if (len > 0 && len <= sizeof(evbit))
{
printf("support ev type: ");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
byte = ((unsigned char *)evbit)[i];
for (bit = 0; bit < 8; bit++)
{
if (byte & (1<<bit)) {
printf("%s ", ev_names[i*8 + bit]);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
while (1)
{
fds[0].fd = fd;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
fds[0].revents = 0;//初始值为0
ret = poll(fds, nfds, 5000);
if (ret > 0)//先判断poll返回值是否超时,在判断fds数组中的revents
{
if (fds[0].revents == POLLIN)
{ //当有数据可读时,将读取到的事件信息放在event结构体中
while (read(fd, &event, sizeof(event)) == sizeof(event))
{
printf("get event: type = 0x%x, code = 0x%x, value = 0x%x\n", event.type, event.code, event.value);
}
}
}
else if (ret == 0)
{
printf("time out\n");//超时
}
else
{
printf("poll err\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
SELECT 方式案例
通过man手册可以查询到用户态中select函数的使用规则:

与poll函数不一样的是在文件描述符和超时时间的配置
#include \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
err = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &id);
if (err == 0)
{
printf("bustype = 0x%x\n", id.bustype );
printf("vendor = 0x%x\n", id.vendor );
printf("product = 0x%x\n", id.product );
printf("version = 0x%x\n", id.version );
}
len = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(0, sizeof(evbit)), &evbit);
if (len > 0 && len <= sizeof(evbit))
{
printf("support ev type: ");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
byte = ((unsigned char *)evbit)[i];
for (bit = 0; bit < 8; bit++)
{
if (byte & (1<<bit)) {
printf("%s ", ev_names[i*8 + bit]);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
while (1)
{
/* 设置超时时间 */
tv.tv_sec = 5;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
/* 想监测哪些文件? */
FD_ZERO(&readfds); /* 先全部清零 */
FD_SET(fd, &readfds); /* 想监测fd */
/* 函数原型为:
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,
fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
* 我们为了"read"而监测, 所以只需要提供readfds
*/
nfds = fd + 1; /* nfds 是最大的文件句柄+1, 注意: 不是文件个数, 这与poll不一样 */
//select函数
ret = select(nfds, &readfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
if (ret > 0) /* 有文件可以提供数据了 */
{
/* 再次确认fd有数据 */
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &readfds))
{
while (read(fd, &event, sizeof(event)) == sizeof(event))
{
printf("get event: type = 0x%x, code = 0x%x, value = 0x%x\n", event.type, event.code, event.value);
}
}
}
else if (ret == 0) /* 超时 */
{
printf("time out\n");
}
else /* -1: error */
{
printf("select err\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
异步通知方式
异步通知,就是 APP 可以忙自己的事,当驱动程序用数据时它会主动给 APP 发信号,这会导致 APP 执行信号处理函数。
Linux 系统中也有很多信号,在 Linux 内核源文件 include\uapi\asm-generic\signal.h 中,有很多信号的宏定义:
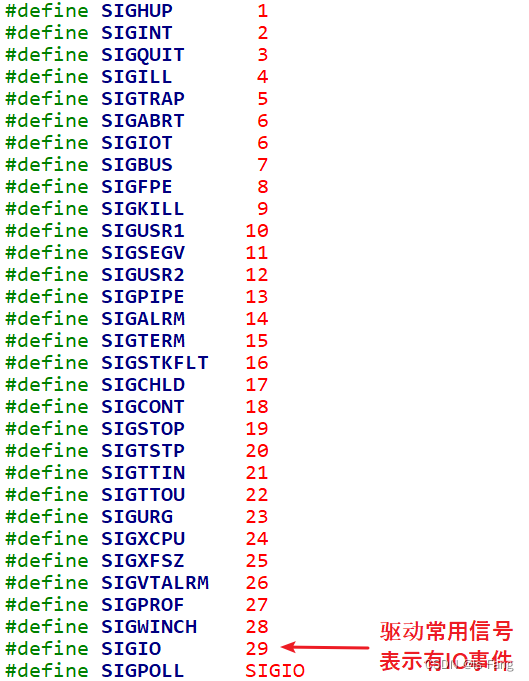
驱动程序通知 APP 时,它会发出“SIGIO”这个信号,表示有“IO 事件”要处理
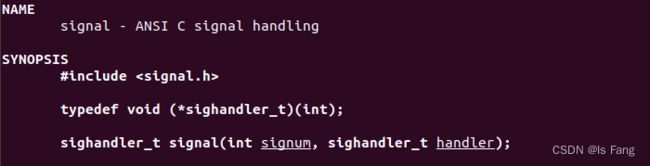
信号处理函数和信号,之间怎么挂钩:APP 注册信号处理函数,可以通过一个 signal 函数来“给某个信号注册处理函数”

异步通知方式案例
#include \n" , argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 注册信号处理函数 */
signal(SIGIO, my_sig_handler);
/* 打开驱动程序 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s err\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
err = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &id);
if (err == 0)
{
printf("bustype = 0x%x\n", id.bustype );
printf("vendor = 0x%x\n", id.vendor );
printf("product = 0x%x\n", id.product );
printf("version = 0x%x\n", id.version );
}
len = ioctl(fd, EVIOCGBIT(0, sizeof(evbit)), &evbit);
if (len > 0 && len <= sizeof(evbit))
{
printf("support ev type: ");
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
byte = ((unsigned char *)evbit)[i];
for (bit = 0; bit < 8; bit++)
{
if (byte & (1<<bit)) {
printf("%s ", ev_names[i*8 + bit]);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
/* 把APP的进程号告诉驱动程序 */
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
/* 使能"异步通知" */
//APP 有时候想收到信号,有时候又不想收到信号:应该可以把 APP 的意愿告诉驱动:
//设置 Flag 里面的 FASYNC 位为 1,使能“异步通知”。
flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | FASYNC);
while (1)
{
printf("main loop count = %d\n", count++);
sleep(2);
}
return 0;
}
电阻屏和电容屏
触摸屏分为电阻屏、电容屏。电阻屏结构简单,在以前很流行;电容屏支持多点触摸,现在的手机基本都是使用电容屏。
注意:LCD、触摸屏不是一回事,LCD 是输出设备,触摸屏是输入设备。制作触摸屏时特意把它的尺寸做得跟 LCD 一模一样,并且把触摸屏覆盖在 LCD 上。
电容屏
电容屏中有一个控制芯片,它会周期性产生驱动信号,接收电极接收到信号,并可测量电荷大小。当电容屏被按下时,相当于引入了新的电容,从而影响了接收电极接收到的电荷大小。主控芯片根据电荷大小即可计算出触点位置
怎么通过电荷计算出触点位置?这由控制芯片实现,这类芯片一般是 I2C接口。我们只需要编写程序,通过 I2C 读取芯片寄存器即可得到这些数据。
电容屏可以支持多点触摸(Multi touch),驱动程序上报的数据中会根据TYPE B方法分辨触点:
该类型的触摸屏能分辨是哪一个触点,上报数据时会先上报触点 ID,再上报它的数据。
电容屏的实验数据
假设你的开发板上电容屏对应的设备节点是/dev/input/event0,执行以下命令:hexdump /dev/input/event0,然后用一个手指点击触摸屏,只有一个触摸点,没有上报slot
 为了兼容老程序,它也上报了 ABS_X、ABS_Y 数据,电阻触摸屏就是使用这类型的数据,所以基于电阻屏的程序,也可以用在电容屏上。
为了兼容老程序,它也上报了 ABS_X、ABS_Y 数据,电阻触摸屏就是使用这类型的数据,所以基于电阻屏的程序,也可以用在电容屏上。
使用两个手指点击触摸屏时,会上报slot,对于 ABS_X、ABS_Y 数据,只上报第 1 个触点的数据

使用tslib库的应用程序
第三方库介绍——tslib库