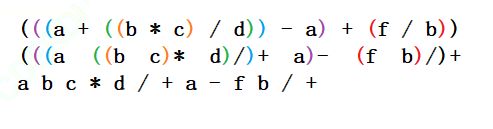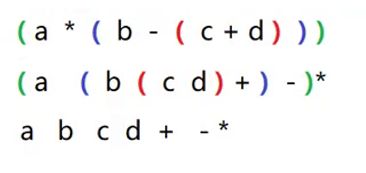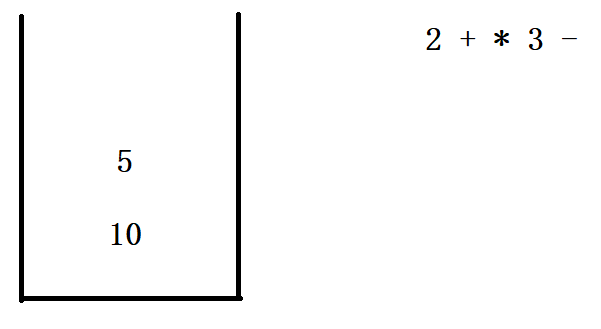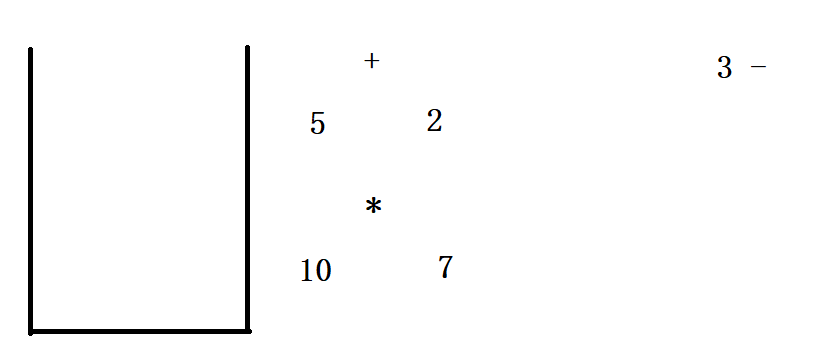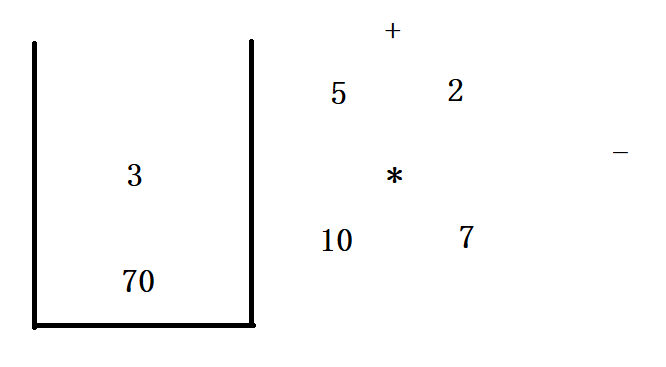栈和队列详解
目录:
- 栈
- 队列
- 双端队列
- 刷题巩固
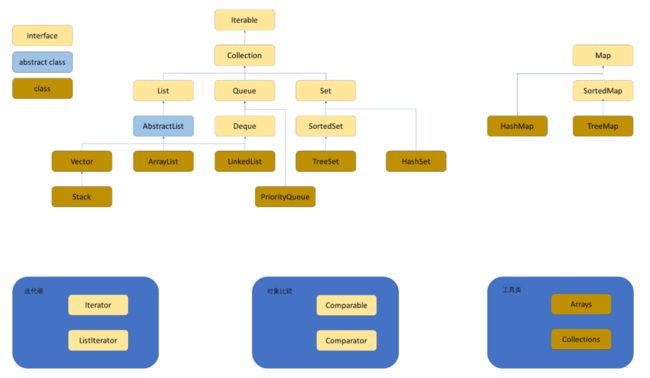
1.栈
概念:
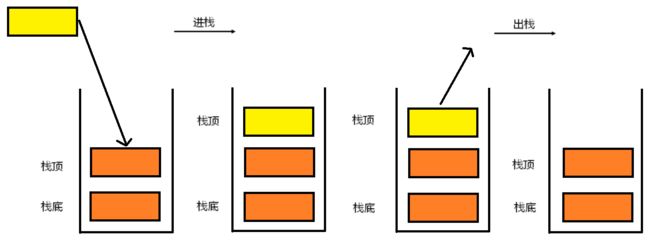
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出的原则.
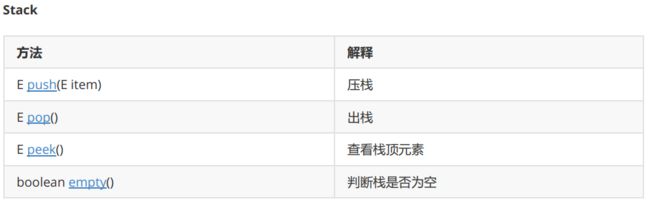
- 压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶
- 出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶
实现
- 1. 利用顺序表实现,即使用尾插 + 尾删的方式实现
- 2. 利用链表实现,则头尾皆可
使用顺序表实现栈:
public class MyStack {
// 简单起见,我们就不考虑扩容问题了
private int[] array = new int[100];
private int size = 0;
public void push(int val) {
array[size++] = val;
}
public int pop() {
return array[--size];
}
public int peek() {
return array[size - 1];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
使用链表实现栈
头插法 入栈:时间复杂度:O(1),出栈是从头出(删): O(1)
尾插法 入栈:时间复杂度:O(N), 出栈是从尾巴(删)O(N)
package test1;
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
class MyLinkedList {
public Node head;
public void createList() {
Node node1 = new Node(12);
Node node2 = new Node(3);
Node node3 = new Node(5);
Node node4 = new Node(2);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
this.head = node1;
}
public void show() {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public int size() {
Node cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
public boolean contains(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
public void addLast(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
public Node searchNode(int index) {
Node cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while (count != index) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("下标不合法!");
return;
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
Node cur = searchNode(index);
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
public Node searchPrevNode(int data) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == data) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
//删除第一次出现val的节点
public void remove(int val) {
if (this.head == null) {
return;
}
if (this.head.val == val) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
Node cur = searchPrevNode(val);
if (cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的节点!");
return;
}
Node del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
//删除所有值是val的节点
public void removeAllKey(int val) {
if (this.head == null) {
return;
}
Node pre = this.head;
Node cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (this.head.val == val) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
}
//删除所有节点
public void clear() {
while (this.head != null) {
Node curNext = this.head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = curNext;
}
}
}
public class MyStack {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
public void push(int val) {
myLinkedList.addFirst(val);
}
public int pop() {
int val = myLinkedList.head.val;
myLinkedList.remove(myLinkedList.head.val);
return val;
}
public int peek() {
return myLinkedList.head.val;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return myLinkedList.size() == 0;
}
public int size() {
return myLinkedList.size();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.peek());
}
}
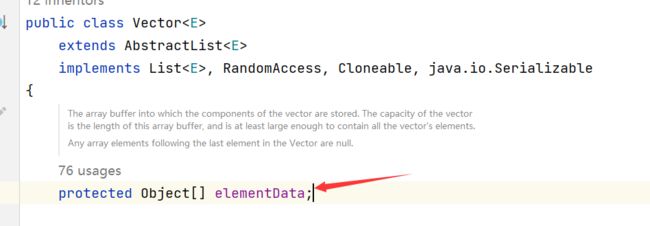
栈的底层是一个数组
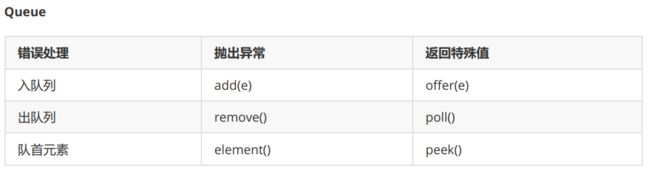
2.队列
概念:
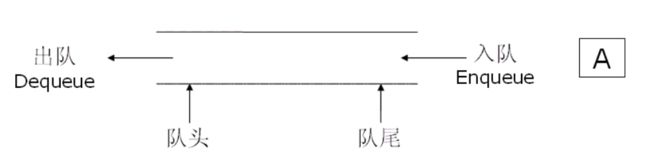
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出
- 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
- 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
实现:
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
使用链表实现队列:
package test1;
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public Node(int val, Node next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class MyQueue {
private Node head = null;
private Node tail = null;
private int size = 0;
public void offer(int val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
if (tail == null) {
head = node;
} else {
tail.next = node;
}
tail = node;
size++;
}
public int poll() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
Node oldHead = head;
head = head.next;
if (head == null) {
tail = null;
}
size--;
return oldHead.val;
}
public int peek() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
}
return head.val;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
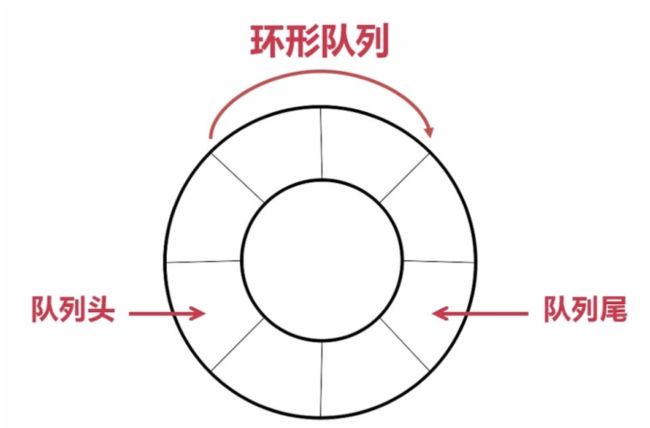
循环队列
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型时可以就会使用循环队列。环形队列通常使用数组实现。
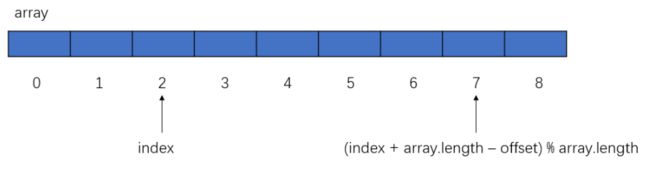
数组下标循环的小技巧:
1. 下标最后再往后(offset 小于 array.length): index = (index + offset) % array.length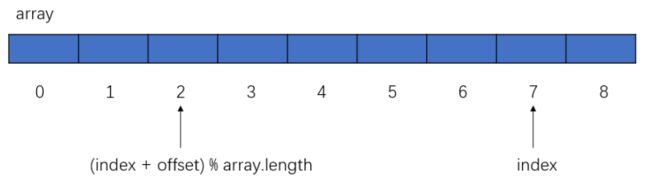
注意:offset是偏移量(往后走几步)的意思。
2. 下标最前再往前(offset 小于 array.length): index = (index + array.length - offset) % array.length
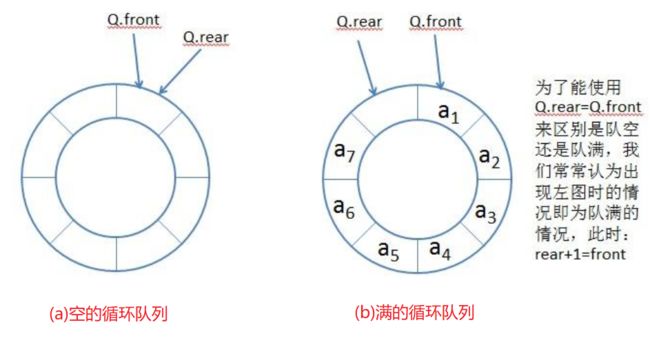
如何区分空与满?
- 通过添加 size 属性记录
- 保留一个位置
栈和队列经典习题
1.已知一个栈的入栈序列是mnxyz,则不可能出现的出栈顺序是?
- A.mnxyz
- B.xnyzm
- C.nymxz
- D.nmyzx
核心思路:(入栈的同时也可以出栈,此题选C.)
2.将中缀表达式转为后缀表达式,输入a + b* c / d - a + f / b 输出 a b c * d / + a - f b / +
从左往右先乘除后加减,加括号把每个括号里面对应的运算符都移到对应的括号后边去除掉所有的括号,结果就是后缀表达式。
3.有一个中缀表达式为a * ( b - ( c + d ) ),它的后缀表达式可以是什么?
- A.abcd+-*
- B.abc+d-*
- C.ab-cd+*
- D.abd+c-*
思路:
从左往右先乘除后加减,加括号把每个括号里面对应的运算符都移到对应的括号后边去除掉所有的括号,结果就是后缀表达式。
4.什么是前中后缀表达式?
前缀表达式 - * 10 + 5 2 3 把运算符移动到括号左边
中缀表达式:10 * (5 + 2) - 3 平时你看到的表达式就是中缀表达式
后缀表达式 10 5 2 + * 3 - 把运算符移到括号右边
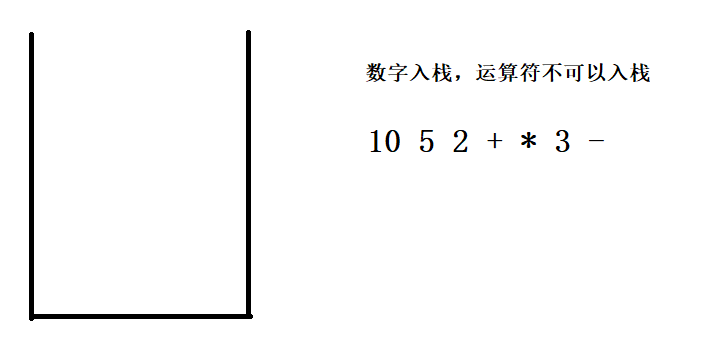
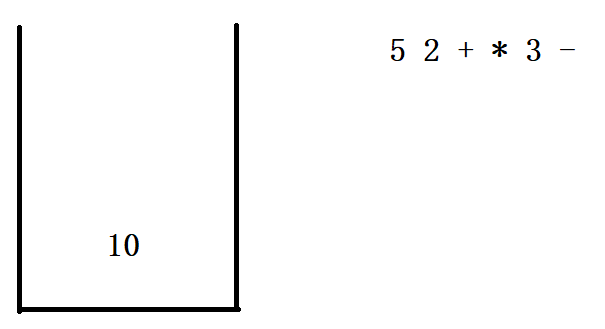
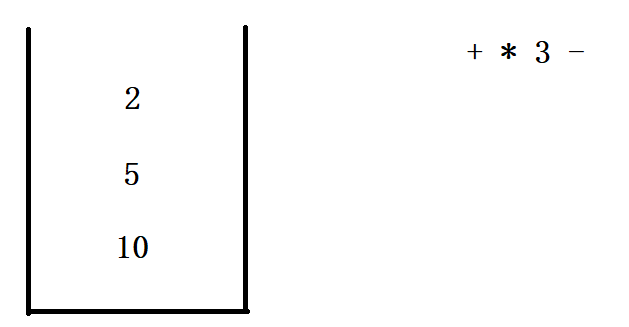
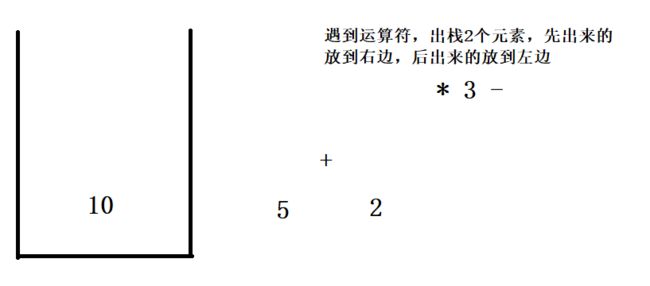
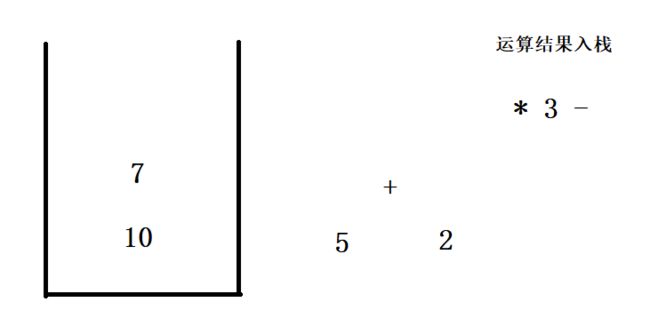
5.后缀表达式如何利用栈进行运算?
例如 10 5 2 + * 3 - 换成中缀表达式运算结果是10 * 7 - 3 = 67
画个图看一下运算原理
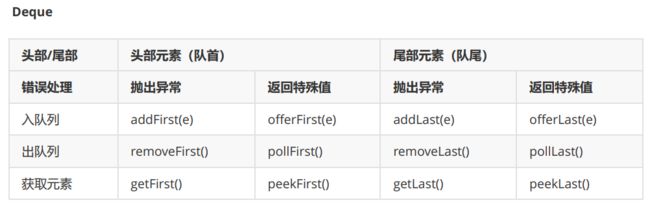
3. 双端队列
概念:
双端队列(deque)是指允许两端都可以进行入队和出队操作的队列,deque 是 “double ended queue” 的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和入队,也可以从队尾出队和入队。
java 中的栈和队列:
4.刷题巩固
20. 有效的括号
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n = s.length();
if(n % 2 == 1){
return false;
}
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(')','(');
map.put('}','{');
map.put(']','[');
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i 225. 用队列实现栈
class MyStack {
Queue queue;
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
int n = queue.size();
queue.offer(x);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
public int pop() {
return queue.poll();
}
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
} 232. 用栈实现队列
class MyQueue {
private Deque in;
private Deque out;
public MyQueue() {
in = new ArrayDeque();
out = new ArrayDeque();
}
public void push(int x) {
in.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (out.isEmpty()) {
in2out();
}
return out.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (out.isEmpty()) {
in2out();
}
return out.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();
}
public void in2out() {
while (!in.isEmpty()) {
out.push(in.pop());
}
}
} 155. 最小栈
class MinStack {
Deque stack;
Deque minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new LinkedList<>();
minStack = new LinkedList<>();
minStack.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
minStack.push(Math.min(minStack.peek(), val));
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return minStack.peek();
}
} 622. 设计循环队列