Redis实现skipList(跳表) 代码有详解
Redis实现skipList(跳表)
项目介绍
非关系型数据库redis,以及levedb,rockdb其核心存储引擎的数据结构就是跳表。
本项目就是基于跳表实现的轻量级键值型存储引擎,使用C++实现。插入数据、删除数据、查询数据、数据展示、数据落盘、文件加载数据,以及数据库大小显示。
函数提供接口
int insert_element(K,V); (插入数据)
void display_list(); (展示跳表中数据)
bool search_element(K); (搜索数据)
void delete_element(K); (删除数据)
void dump_file(); (读取数据)
void load_file(); (存放数据)
int size(); (元素数量)
跳表原理解释
什么是跳表
单链表是是一种各性能比较优秀的动态数据结构,可以支持快速的插入、删除、查找操作。
即便在有序的单链表中,插入、删除操作仍然时间复杂度为O(N),那么有没有更好的优化方法呢?
跳表是在单链表的基础上进行对数据结构的优化,将插入、删除、查找时间复杂度都控制在O(log N)。我们这主要解释跳表原理和怎么讲单链表的插入、删除操作时间复杂度降低到O(log N)
我们可以按照元素的个数(n)分成好多层,每一层都有对应元素的索引。例如第一层就是原始单链表,第一层索引个数就是n,然而到了第二层,每个元素都有50%的几率上升到第二层。(解释:咱们要求插入、删除操作都控制在O(log N),每个元素都是随机,这个时间复杂度是O(1),如果隔一元素上升一层的话,要加判定条件,就需要时间复杂度为O(N))
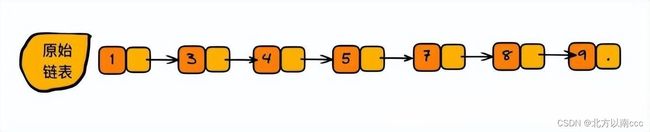
下列是按照最优操作建的图
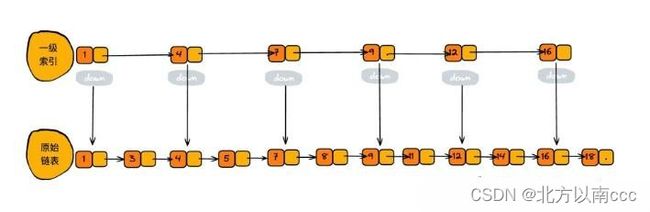
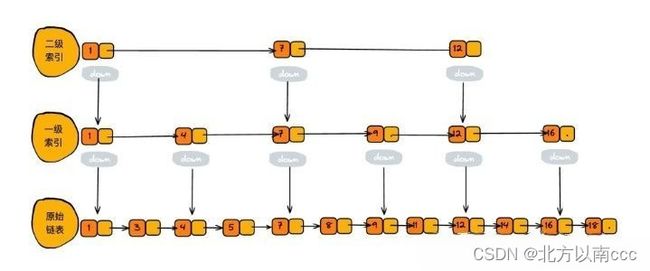
查找元素时,就是从顶层索引开始,对于每一层,大于当前索引对应的值,小于下层对应的值,开始执行下一层的操作。
当查找元素8时,按照二级索引,找到区间[ 7-12 ],执行下一层,执行[ 7-9 ]区间。继续执行下一层,找到元素8,只需要四次操作!
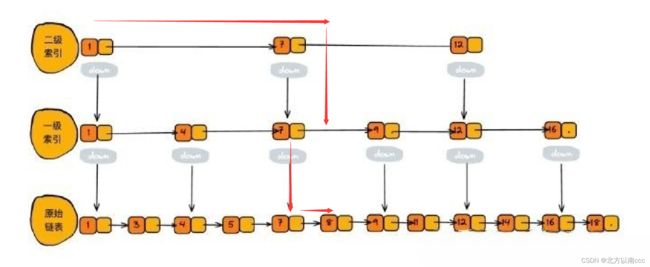
但是现在发现如果按照单链表查找的8话也只需要5次操作,根本没有表示出跳表的强大魅力!!!
那接下来咱们试试更多元素的查找
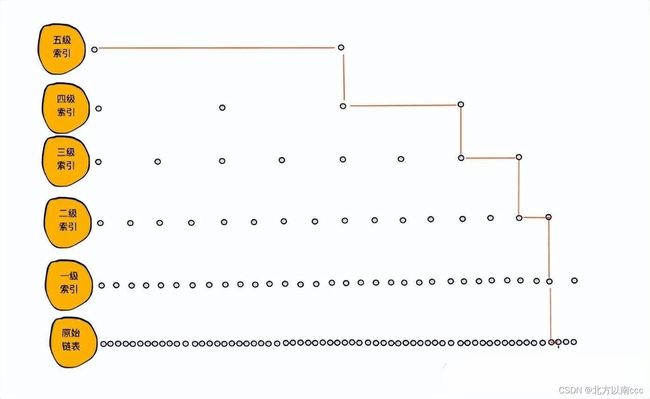 原始链表有64个元素,查找第60个元素,如果按照单链表查找需要60次操作,如果跳表操作的话就可以6次操作即可查找出来第60个元素,符合时间复杂度O(log N)。
原始链表有64个元素,查找第60个元素,如果按照单链表查找需要60次操作,如果跳表操作的话就可以6次操作即可查找出来第60个元素,符合时间复杂度O(log N)。
这次是不是就可以体现跳表的强大能力啦!!!
分析跳表插入、删除、查找时间复杂度
插入、删除、查找在跳表中都是按照索引的方式查找,可以说三种方式几乎一样。以查找为例:
单链表元素个数为16,按照每元素50%的几率上升一层
0级(原始链表)索引数量 : 16
1级索引数量:8
2级索引数量:4
3级索引数量:2
基本可以确定索引数量按照层数以log次方递减。
分析跳表的空间复杂度
跳表的时间复杂度为O(log N),空间复杂度是拿空间换时间的操作,索引个数随着层数减半,成等比数列,空间复杂度为O(N)。
跳表索引更新
从上面插入元素8的过程中发现,我们插入8时没有更新索引,会出现 2 个索引结点之间数据非常多的情况,若频繁的插入数据,但不更新索引,最终会退化成单链表的数据结构,会导致查找数据效率变低。
跳表作为一个动态的数据结构,需要动态的维护索引与原始链表中的大小。若原始链表插入的结点变多了,那么相应的索引结点也需要增加,避免查找、删除、插入的性能下降。
其实是通过一个随机函数,来决定将这个结点插入到哪几级索引中,比如随机函数生成了值rand,那就将这个结点添加到第一级到第rand级这rand级索引中。
代码源码
skipList.h包括函数的源码及详解
#includemain函数负责函数的调用测数据测试。
//所有函数的解释与用法都在skiplist.h中,main主函数主要用于测试各种函数是否可行
#include 下载源码地址
Github下载地址(国际网站)
Gitee下载地址 (国内网站)
参考资料
https://github.com/youngyangyang04/Skiplist-CPP
https://juejin.cn/post/7149101822756519949