lwip-2.1.3自带的httpd网页服务器使用教程(四)POST类型表单的解析和文件上传
上一篇:lwip-2.1.3自带的httpd网页服务器使用教程(三)使用CGI获取URL参数(GET类型表单)
在阅读本篇内容之前,请修改httpd.c文件,修复lwip自带httpd服务器里面关于post的一个bug:
bug #64458: When tcp_err() is invoked, tcp_pcb is freed but httpd_post_finished() is not called by httpd.c
复现方法:上传一个大文件,在文件还没上传完的时候,按下浏览器的停止按钮。
现象:lwip不会调用httpd_post_finished()函数,导致内存泄露。
修复方法:将下面的代码添加到http_state_eof函数末尾。
/* bug #64458: When tcp_err() is invoked, tcp_pcb is freed but httpd_post_finished() is not called by httpd.c */
/* Workaround: Copy the following code to the end of "static void http_state_eof(struct http_state *hs)" */
#if LWIP_HTTPD_SUPPORT_POST
if ((hs->post_content_len_left != 0)
#if LWIP_HTTPD_POST_MANUAL_WND
|| ((hs->no_auto_wnd != 0) && (hs->unrecved_bytes != 0))
#endif /* LWIP_HTTPD_POST_MANUAL_WND */
) {
/* make sure the post code knows that the connection is closed */
http_uri_buf[0] = 0;
httpd_post_finished(hs, http_uri_buf, LWIP_HTTPD_URI_BUF_LEN);
}
#endif /* LWIP_HTTPD_SUPPORT_POST*/
HTML表单的分类
HTML表单有两种提交方式:GET方式和POST方式。
表单提交方式由
我们先来看一下文件上传表单提交后的http header内容。
HTTP/1.1
Accept: */*
Referer: http://stm32f103ze/form_test.html
Accept-Language: zh-cn
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 5.1; Trident/4.0; InfoPath.3; .NET4.0C; .NET4.0E; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 1.1.4322)
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------7e729f1bf0a7a
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Host: stm32f103ze
Content-Length: 39415
Connection: Keep-Alive
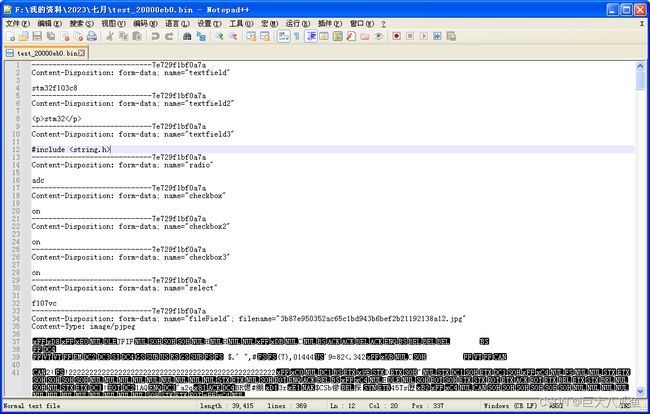
Cache-Control: no-cache其中Content-Type以multipart/form-data开头,后面还有一个boundary字符串,叫做分界符字符串。这个分界符字符串非常重要,分界符字符串是表单内容中各个控件内容的分界符。
Content-Length是整个表单内容(包括文件内容)的总长度。lwip调用httpd_post_begin函数时传入的content_len参数就等于http header中Content-Length属性的数值。
我们再来看一下表单内容的格式。
可以看到,每个表单控件都是用分界符字符串隔开的。
对于普通表单控件(如文本框、单选框、复选框、下拉菜单框等等),name字符串是控件名,后面是控件内容的原文。控件内容是没有进行urlencode编码的,这和普通表单内容的格式很不一样。
对于文件框控件,还多了一个filename字符串,里面存的是文件框选择的文件名。Content-Type是文件的类型,比如image/pjpeg是jpg图片文件(这个数据是浏览器提供的)。后面就是文件的原始二进制内容了。
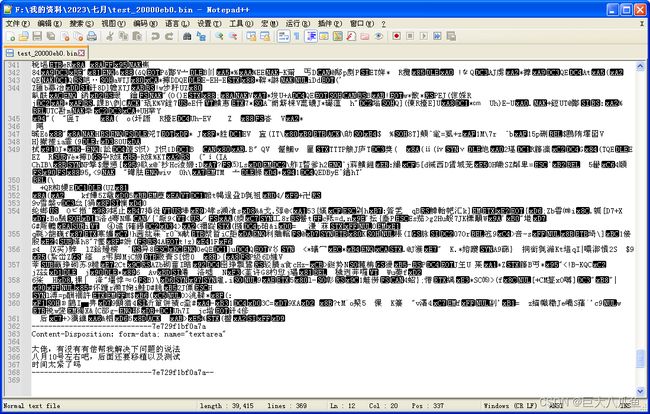
整个表单内容最后是以分界符字符再加两个'-'字符结束的。
由于文件上传表单的内容一般都很大,STM32内存是放不下的,我们可以先把整个表单内容用FatFs写入到SD卡或SPI Flash的一个临时文件上,后面再来慢慢读取并解析,分离出其中的表单控件内容,还有文件内容。临时文件名为test_XXXXXXXX.bin,其中XXXXXXXX是connection指针(连接标识对象)指向的内存地址。
如果没有外接存储设备,也可以在STM32的内部Flash里面划分一块固定的区域,用来存放表单内容。如STM32F407VG单片机有1MB的Flash,前面的扇区0~5可以用来存放程序,把扇区6~11划分为表单内容的临时存放区域,flash地址为0x08040000-0x080fffff,大小为768KB。这样做的好处是不再需要FatFs了,直接用0x08040000地址就可以访问flash存储空间,但是需要使用大容量flash的stm32型号,而且最大能上传的文件的大小也只有几百KB。一般来说,这样的大小用来实现网页在线上传hex文件升级stm32程序,完全足够了。
下一篇:lwip-2.1.3自带的httpd网页服务器使用教程(五)使用COOKIE实现用户登录