源码编译安装、rsync命令、远程同步实现、inotify+rsync实时同步
Top
NSD SERVICES DAY03
- 不积跬步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海
- 环境准备
- 源码编译安装
- 数据同步
- 本地同步
- 远程同步(rsync+ssh)
- 实时数据同步
- 书写shell脚本(了解)
- 数据库服务基础(数据库系统)
- 部署MariaDB 数据库系统
- MariaDB基本使用
- 恢复数据到数据库中
- 表格操作
- 为数据库系统管理员设置密码
- 案例:编译安装软件包
- 案例:rsync基本用法
- 案例:rsync+SSH同步
- 案例:使用inotifywait工具
- 案例:搭建mariadb数据库系统
- 案例:使用数据库查询
1 不积跬步,无以至千里;不积小流,无以成江海
2 环境准备
所有虚拟机设置SELinux运行模式
- [root@server ~]# getenforce
- Enforcing
- [root@server ~]# setenforce 0 #当前设置
- [root@server ~]# getenforce
- Permissive
- [root@server ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config
- SELINUX=permissive
所有虚拟机设置防火墙(停止防火墙服务)
- [root@server ~]# yum -y remove firewalld
- [root@server ~]# rpm -q firewalld
3 源码编译安装
RPM软件包:rpm -ivh 或者 yum -y install
源码包----编译:开发工具gcc与make----》可以执行的程序-----》运行安装
•主要优点(可定制性强)
–获得软件的最新版,及时修复bug
–软件功能可按需选择/定制,有更多软件可供选择
–源码包适用各种平台
–……
步骤1:安装开发工具gcc与make,释放源代码至指定目录
步骤2:tar解包,释放源代码至指定目录
步骤3:./configure 配置,指定安装目录/功能模块等选项
步骤4:make 编译,生成可执行的二进制程序文件
步骤5:make install 安装,将编译好的文件复制到安装目录
真机tools.tar.gz 传递数据到虚拟机
真机为Linux:
]# ls /linux-soft/s1
]# scp /linux-soft/s1/tools.tar.gz [email protected]:/root
真机为windows:windterm进行上传tools.tar.gz
虚拟机A
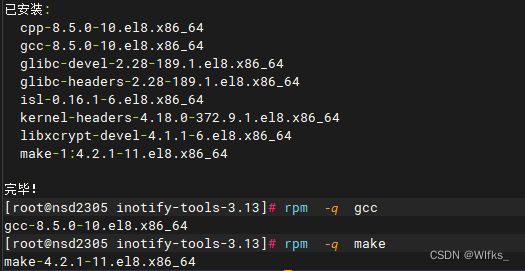
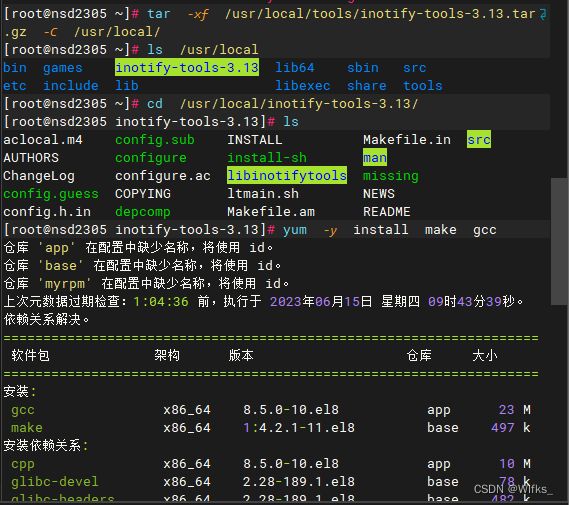
1.安装开发工具
- [root@server ~]# yum -y install gcc make
- [root@server ~]# rpm -q gcc
- [root@server ~]# rpm -q make
- [root@server ~]#
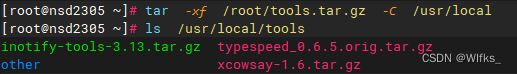
2.进行解压缩
- [root@server ~]# tar -xf /root/tools.tar.gz -C /usr/local
- [root@server ~]# ls /usr/local/tools
- inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz
3.进行tar解包
- [root@server ~]# tar -xf /usr/local/tools/inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz -C /usr/local/
- [root@server ~]# ls /usr/local/
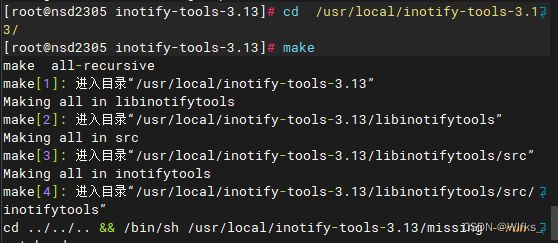
- [root@server ~]# cd /usr/local/inotify-tools-3.13/
- [root@server ~]# ls
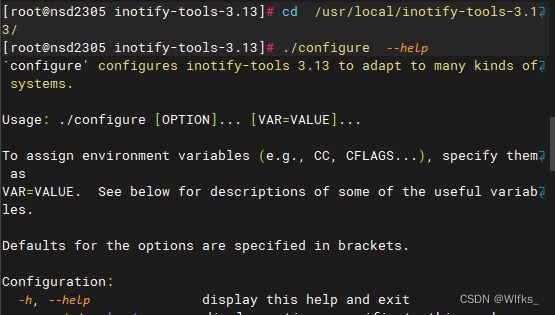
4.运行configure脚本
作用1:检测当前系统是否安装gcc
作用2:指定安装位置与功能
作用3:生成Makefile文件(制作程序的大纲,做菜的菜谱)
- [root@server ~]# cd /usr/local/inotify-tools-3.13/
- [root@server ~]# ./configure --help #查看帮助信息,大概浏览一下
- [root@server ~]# ./configure --prefix=/opt/myrpm #指定安装位置,此步骤不产生相应的目录
常见的报错信息:gcc开发工具没有安装
checking for gcc... no
checking for cc... no
checking for cl.exe... no
configure: error: no acceptable C compiler found in $PATH
See `config.log' for more details.
5.进行make编译,变成可以执行的程序(放在内存中)
- [root@server ~]# cd /usr/local/inotify-tools-3.13/
- [root@server inotify-tools-3.13]# make
6.进行make install安装
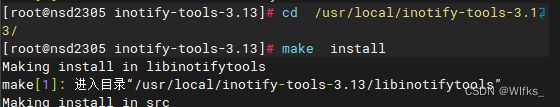
- [root@server ~]# cd /usr/local/inotify-tools-3.13/
- [root@server inotify-tools-3.13]# make install
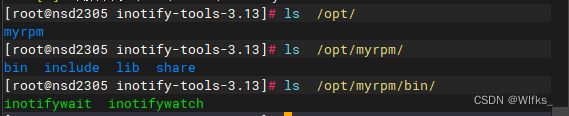
- [root@server inotify-tools-3.13]# ls /opt/
- [root@server inotify-tools-3.13]# ls /opt/myrpm/
- [root@server inotify-tools-3.13]# ls /opt/myrpm/bin/
不指定位置 源码包会装到以下这个文件夹:
做错从来:
删-解包
4 数据同步
• 命令用法
rsync [选项...] 源目录 目标目录(rsync /路径/源目标/ /路径/目标)
• rsync操作选项
-n:测试同步过程,不做实际修改
--delete:删除目标文件夹内多余的文档
-a:归档模式,相当于-rlptgoD (如下图解释)基本属性不变
-v:显示详细操作信息 (常用-av)
-X:保持acl策略不变
5 本地同步
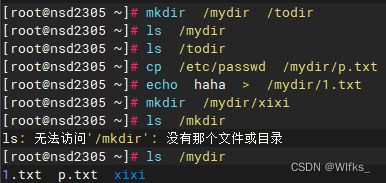
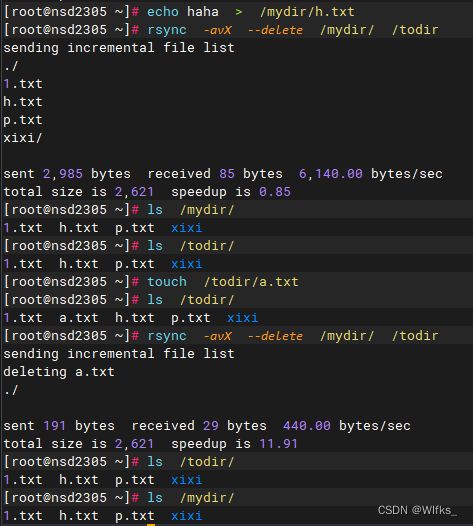
- [root@server ~]# mkdir /mydir /todir
- [root@server ~]# echo haha > /mydir/h.txt
- [root@server ~]# rsync -avX --delete /mydir/ /todir #同步目录的内容
- [root@server ~]# ls /mydir/
- [root@server ~]# ls /todir/
- [root@server ~]# touch /todir/a.txt
- [root@server ~]# ls /todir/
- [root@server ~]# rsync -avX --delete /mydir/ /todir
- [root@server ~]# ls /todir/
- [root@server ~]# ls /mydir/
6 远程同步(rsync+ssh)
• 与远程的 SSH目录保持同步
下行:rsync [...] user@host:远程目录 本地目录
上行:rsync [...] 本地目录 user@host:远程目录
虚拟机A的/mydir目录的内容与虚拟机B的/mnt进行同步
虚拟机A:
- [root@server ~]# rsync -avX --delete /mydir/ [email protected]:/mnt
- ……..connecting (yes/no)? yes
- [email protected]'s password: #输入密码
虚拟机B:
- [root@server ~]# ls /mnt
7 实时数据同步
虚拟机A的/mydir/目录的内容与虚拟机B的/mnt进行同步
实现ssh无密码验证(公钥与私钥)
虚拟机A
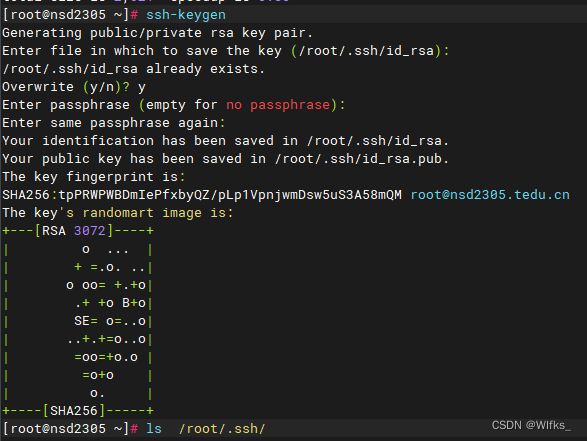
1.虚拟机A生成公钥与私钥
- [root@server ~]# ssh-keygen #一路回车
- [root@server ~]# ls /root/.ssh/
- id_rsa(私钥) id_rsa.pub(公钥) known_hosts(记录曾经远程管理过的机器)
2.虚拟机A将公钥传递给虚拟机B
- [root@server ~]# ssh-copy-id [email protected]
- [root@server ~]# rsync -avX --delete /mydir/ [email protected]:/mnt
监控目录内容变化工具
• 基本用法
inotifywait [选项] 目标文件夹
• 常用命令选项
-m,持续监控(捕获一个事件后不退出)
-r,递归监控、包括子目录及文件
-q,减少屏幕输出信息
-e,指定监视的 modify、move、create、delete、attrib 等事件类别
- inotifywait 监控目录内容变化
- rsync -avX --delete /mydir/ [email protected]:/mnt
监控加同步:
8 书写shell脚本(了解)
脚本:可以运行一个文件,实现某种功能
中文:新建用户zhangsan shell: useradd zhangsan
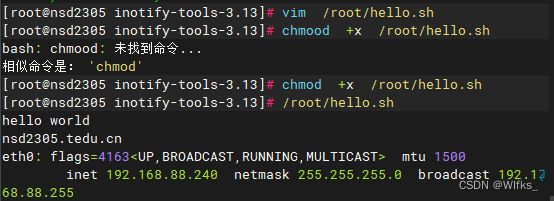
- [root@server /]# vim /root/hello.sh
- echo hello world
- hostname
- id root
- ifconfig | head -2
- [root@server /]# chmod +x /root/hello.sh #所有人赋予执行权限
- [root@server /]# /root/hello.sh #绝对路径执行脚本
重复性:循环解决
for 循环:有一定次数
格式:
while 循环:不定次数或者无限次数
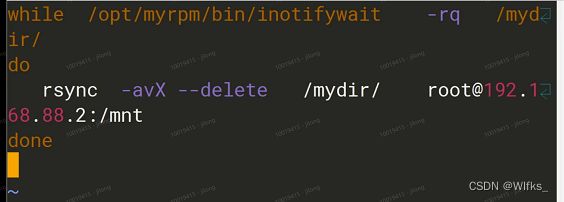
- [root@server /]# vim /etc/rsync.sh #命名名字可任意修改
- while /opt/myrpm/bin/inotifywait -rqq /mydir/ #两个q不要屏幕输出
- do
- rsync -aX --delete /mydir/ [email protected]:/mnt
- done
- [root@server /]# chmod +x /etc/rsync.sh #赋予执行权限
- [root@server /]# /etc/rsync.sh & #放入后台运行脚本程序
- [root@server /]# jobs -l #-l选项 显 示进程的pid
- [1] + 17707 运行中 /etc/rsync.sh &
- [root@server /]# kill 17707 #停止脚本,可以杀死进
9 数据库服务基础(数据库系统)
数据库:存放数据的仓库
在数据库系统中,有很多的数据库,在每一个库中有很多的表格
• 常见的关系型 数据库管理系统
微软的 SQL Server
IBM的 DB2
甲骨文的 Oracle、MySQL
社区开源版 MariaDB
……
- database :数据库
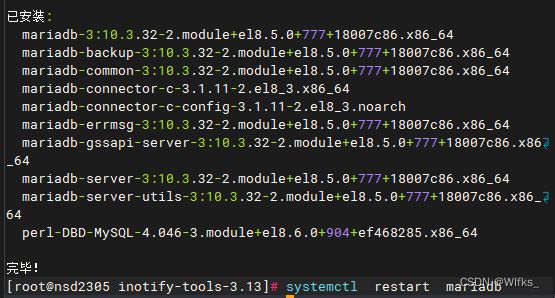
10 部署MariaDB 数据库系统
- [root@server /]# yum -y install mariadb-server
- [root@server /]# systemctl restart mariadb
11 MariaDB基本使用
1. Linux系统的管理指令不能使用
2. 所有的数据库系统指令都必须以 ; 结尾
3. 数据库系统的指令大部分不支持tab补全
- [root@server /]# mysql #进入数据库系统
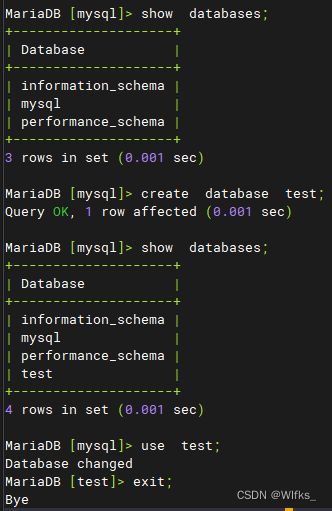
- > create database nsd01; #创建nsd01数据库
- > show databases; #查看所有数据库
- > drop database nsd01; #删除数据库nsd01
- > show databases; #查看所有数据库
- > exit;
- Bye
- [root@server ~]#
- [root@server /]# mysql #进入数据库系统
- > use mysql; #切换到mysql数据库
- > show tables; #查看当前库中所有表格
- > show databases; #查看所有数据库
- > use test; #切换到test数据库
- > exit;
12 恢复数据到数据库中
真机传递数据到虚拟机
真机为Linux:
- ]# ls /linux-soft/1
- ]# scp /linux-soft/1/users.sql [email protected]:/root
真机为windows利用windterm软件
2.恢复数据到数据库
- [root@server /]# mysql #进入数据库系统
- > create database test; #创建test数据库
- > show databases; #查看所有数据库
- > exit;
- Bye
- [root@server ~]#
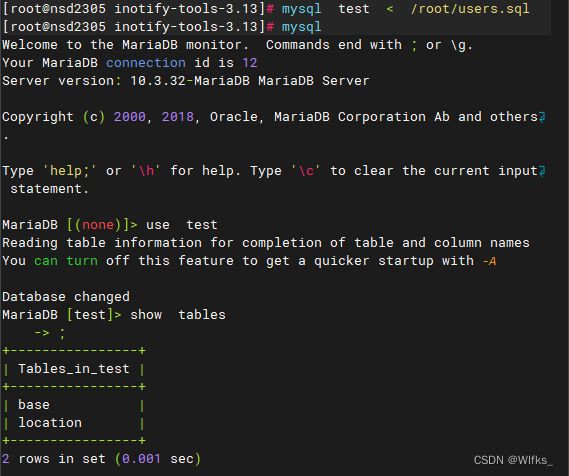
- [root@server ~]# mysql test < /root/users.sql
- [root@server ~]# mysql #进入数据库系统
- MariaDB [(none)]> use test; #切换到数据库test
- MariaDB [test]> show tables; #查看当前库有哪些表格
- +-------------------+
- | Tables_in_test |
- +-------------------+
- | base |
- | location |
- +-------------------+
13 表格操作
–增(insert) 删(delete) 改(update) 查(select)
- –表字段、表记录
- 编号 姓名 住址
- 1 Dc 东村
- 2 Tc 西村
查(select)
格式: select 表字段,表字段,…… from 库名.表名;
- [root@server /]# mysql
- > use test;
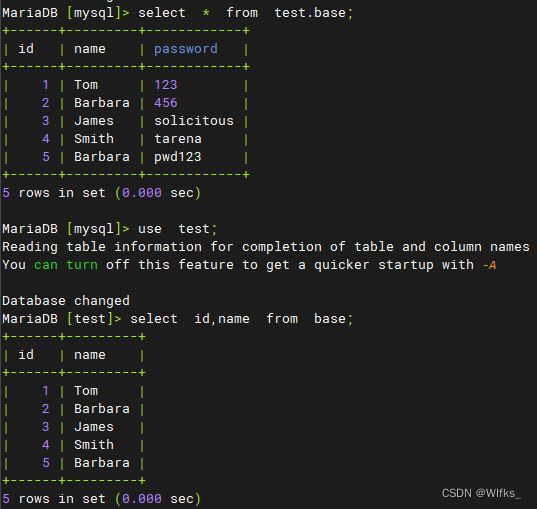
- > select * from base; #查看base所有表字段内容
- > select * from location; #查看location所有表字段内容
- > select name,password from base;
- > use mysql;
- > select * from test.base;
- > use test;
- > select id,name from base;
- [root@server /]# mysql
- > use test; #切换到test库
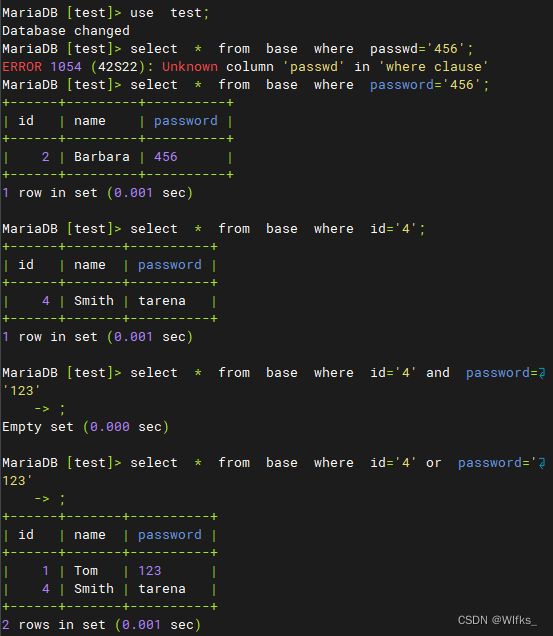
- 查询密码为456的记录
- > select * from base where password='456';
- 查看id编号为4的记录
- > select * from base where id='4';
- 查询id编号为4并且密码为123的记录
- > select * from base where id='4' and password='123';
- 查询id编号为4或者密码为123的记录
- > select * from base where id='4' or password='123';
增(insert)
格式:insert 表名 values (‘值’,‘值’,‘值’);
- MariaDB [test]> insert base values('10','dc','789');
- MariaDB [test]> insert base values('11','tcc','369');
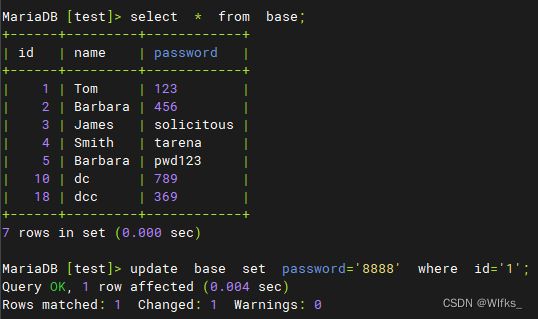
- MariaDB [test]> select * from base ;
改(update)
格式:
update 表名 set 表字段=‘新值’ where 表字段=’值’;
- > select * from base ;
- > update base set password='8888' where id='1';
- > select * from base ;
- > update base set password='9999' where id='2';
- > select * from base ;
删(delete)
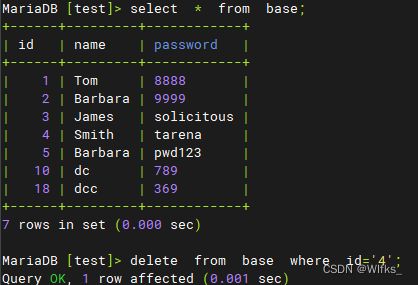
- > use test;
- > delete from base where id='4' ;
- > select * from base ;
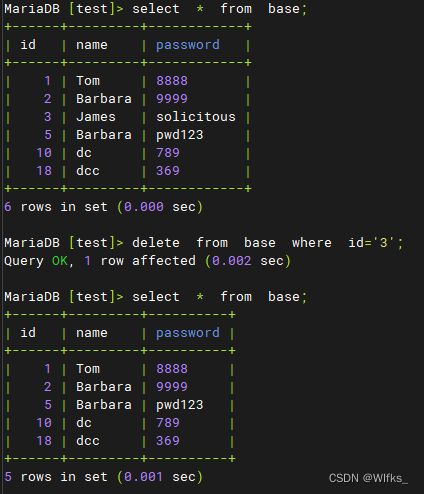
- > delete from base where id='3' ;
- > select * from base ;
14 为数据库系统管理员设置密码
mysqladmin [-u用户名] [-p[旧密码]] password '新密码'
数据库系统管理员:对于数据库系统有最高权限,名字为root,能够登陆数据系统的用户信息,由mysql库中user表进行储存
Linux系统管理员: 对于Linux系统有最高权限,名字为root,能够登陆Linux系统的用户信息,/etc/passwd进行储存
- [root@server /]# mysqladmin -u root password '456'
- [root@server /]# mysql -u root -p #交互式进行登录
- Enter password:
- [root@server /]# mysql -u root -p456 #非交互式进行登录
- 已知旧密码修改新密码
- [root@server ~]# mysqladmin -u root -p456 password '123'
- [root@server ~]# mysql -u root -p123
15 案例:编译安装软件包
15.1 问题
本例要求掌握常规源代码应用的安装过程,通过编译的方式安装inotify-tools 软件工具,完成下列任务:
- 释放 inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz 源码包
- 配置 ./configure
- 编译 make、安装 make install
- 测试inotifywait监控工具的用法及用途
15.2 方案
对于标准源码发布的C/C++软件包,编译安装一般包括以下过程:
- 解包:使用tar命令,将下载的源代码释放至指定目录
- 配置:执行源码目录内的 ./configure 脚本,指定安装目录/功能模块等选项
- 编译:在源码目录下执行 make 操作,根据配置清单Makefile生成可执行的二进制程序文件
- 安装:在源码目录下执行make install 操作,将编译好的程序及相关文件复制到安装目录
15.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:确认已配置好编译环境
- [root@svr7 ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make
- .. ..
- [root@svr7 ~]# gcc --version
- gcc (GCC) 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-4)
- Copyright (C) 2015 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
- This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
- warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
步骤二:编译安装inotify-tools软件包
1)解包inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz文件
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz
- inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz
- [root@svr7 ~]# tar xf inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
2)配置 ./configure,安装目录默认(/usr/local/*/)
- [root@svr7 ~]# cd /usr/src/inotify-tools-3.13/ //进入源码目录
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# ./configure //配置操作
- checking for a BSD-compatible install... /usr/bin/install -c
- checking whether build environment is sane... yes
- checking for gawk... gawk
- .. ..
- configure: creating ./config.status
- config.status: creating Makefile
- .. ..
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# ls Makefile //检查配置结果
- Makefile
3)编译 make
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# make
- .. ..
- Making all in src
- make[2]: Entering directory `/usr/src/inotify-tools-3.13/src'
- make[3]: Entering directory `/usr/src/inotify-tools-3.13'
- make[3]: Leaving directory `/usr/src/inotify-tools-3.13'
- .. ..
4)安装 make install
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# make install
- .. ..
- /usr/bin/install -c .libs/inotifywait /usr/local/bin/inotifywait
- /bin/sh ../libtool --mode=install /usr/bin/install -c 'inotifywatch' '/usr/local/bin/inotifywatch'
- .. ..
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# find /usr/local/ -name "inotify*"
- /usr/local/bin/inotifywait //确认安装结果
- /usr/local/bin/inotifywatch
- /usr/local/include/inotifytools
- /usr/local/include/inotifytools/inotifytools.h
步骤三:测试inotify-tools软件程序
软件包inotify-tools提供了一个主要程序inotifywait,可以用来监控指定目录或文档的变化,并及时给出通知。
1)开启对/opt目录的事件监控
- [root@svr7 ~]# inotifywait -mrq /opt & //开启监控
- [1] 15568
2)修改/opt/目录内容,观察屏幕输出信息
- [root@svr7 ~]# touch /opt/a.txt //新建文件a.txt
- /opt/ CREATE a.txt
- /opt/ OPEN a.txt
- /opt/ ATTRIB a.txt
- /opt/ CLOSE_WRITE,CLOSE a.txt
- [root@svr7 ~]# mv /opt/a.txt /opt/b.txt //将文件改名
- /opt/ MOVED_FROM a.txt
- /opt/ MOVED_TO b.txt
3)结束inotifywait监控
杀死当前用户的第一个后台任务:
- [root@svr7 ~]# kill -9 %1
- [1]+ Killed inotifywait -mrq /opt
16 案例:rsync基本用法
16.1 问题
本例要求掌握远程同步的基本操作,使用rsync命令完成下列任务:
- 将目录 /boot 同步到目录 /todir 下
- 将目录 /boot 下的文档同步到目录 /todir 下
- 在目录 /boot 下新增文件 a.txt,删除 /todir 下的子目录 grub2,再次同步使 /todir 与 /boot 一致
- 验证 -a、-n、-v、--delete 选项的含义
16.2 方案
本地同步操作:
- rsync [选项...] 本地目录1 本地目录2
- rsync [选项...] 本地目录1/ 本地目录2
rsync同步工具的常用选项:
- -n:测试同步过程,不做实际修改
- --delete:删除目标文件夹内多余的文档
- -a:归档模式,相当于-rlptgoD
- -v:显示详细操作信息
- -z:传输过程中启用压缩/解压
16.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:rsync同步基本操作
1)将目录 /boot 同步到目录 /todir 下
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -l /todir //同步前
- ls: 无法访问/todir: 没有那个文件或目录
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -a /boot /todir //将目录1作为目录2的子目录
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -l /todir //检查同步结果
- 总用量 4
- dr-xr-xr-x. 4 root root 4096 11月 30 18:50 boot
2)将目录 /boot 下的文档同步到目录 /todir 下
- [root@svr7 ~]# rm -rf /todir //清理掉目录2
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -a /boot/ /todir //将目录1下的文档同步到目录2下
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -l /todir //检查同步结果
- 总用量 126708
- -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 126426 10月 30 2015 config-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64
- drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 11月 30 18:50 extlinux
- drwx------. 6 root root 104 12月 9 09:58 grub2
- .. ..
3)同步效果测试
在目录/boot下新增文件a.txt,删除/todir下的子目录 grub2:
- [root@svr7 ~]# touch /boot/a.txt
- [root@svr7 ~]# rm -rf /todir/grub2/
现在目录/boot和/todir目录下的内容已经不一致了:
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -ld /boot/a.txt /todir/a.txt
- ls: 无法访问/todir/a.txt: 没有那个文件或目录
- -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 11 21:09 /boot/a.txt
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -ld /boot/grub2 /todir/grub2
- ls: 无法访问/todir/grub2: 没有那个文件或目录
- drwx------. 6 root root 104 12月 9 09:58 /boot/grub2
再次同步使/todir与/boot一致:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -a /boot/ /todir/
确认同步结果:
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -ld /boot/a.txt /todir/a.txt
- -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 11 21:09 /boot/a.txt
- -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 11 21:09 /todir/a.txt
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -ld /boot/grub2 /todir/grub2
- drwx------. 6 root root 104 12月 9 09:58 /boot/grub2
- drwx------. 6 root root 104 12月 9 09:58 /todir/grub2
步骤二:验证 -a、-v、-n、--delete 选项的含义
1)验证-a选项
当目录1包含文件夹时,若缺少-a或-r选项则文件夹会被忽略:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync /home /testa
- skipping directory home
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -ld /testa
- ls: 无法访问/testa: 没有那个文件或目录
添加-a后才会执行同步:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -a /home/ /testa
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -ld /testa
- drwxr-xr-x. 4 root root 31 1月 6 17:33 /testa
类似的情况,当目录1中的数据出现权限、归属、修改时间等变化时,若文件内容不变默认不会同步,若希望目录2也同步这些变化,也需要-a选项。
2)验证-v选项
创建测试目录及文档:
- [root@svr7 ~]# mkdir /fdir
- [root@svr7 ~]# touch /fdir/1.txt
添加-v选项时,可以看到操作细节信息,比如第一次同步时:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -av /fdir/ /tdir
- sending incremental file list
- created directory /tdir
- ./
- 1.txt //传输文档列表
- sent 82 bytes received 34 bytes 232.00 bytes/sec
- total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
在目录/fdir/添加文件2.txt,再次跟踪同步信息:
- [root@svr7 ~]# touch /fdir/2.txt
- sending incremental file list
- ./
- 2.txt //传输文档列表
- sent 100 bytes received 34 bytes 268.00 bytes/sec
- total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
确认目录1和目录2的内容已经一致:
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls /fdir/ /tdir/
- /fdir/:
- 1.txt 2.txt
- /tdir/:
- 1.txt 2.txt
再次跟踪同步信息,已经无需传输文件:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -av /fdir/ /tdir
- sending incremental file list
- sent 58 bytes received 12 bytes 140.00 bytes/sec
- total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
3)验证-n选项
将-n、-v选项合用,可以模拟同步过程,显示需要做哪些操作(但并不真的同步)。
在目录/fdir下新建文件3.txt,测试同步操作:
- [root@svr7 ~]# touch /fdir/3.txt
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -avn /fdir/ /tdir/
- sending incremental file list
- ./
- 3.txt //提示同步时会传输哪些文件
- sent 78 bytes received 18 bytes 192.00 bytes/sec
- total size is 0 speedup is 0.00 (DRY RUN)
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -l /tdir/3.txt //但实际并未真的同步
- ls: 无法访问/tdir/3.txt: 没有那个文件或目录
去掉-n选项才会真正同步:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -av /fdir/ /tdir/
- sending incremental file list
- ./
- 3.txt
- sent 114 bytes received 34 bytes 296.00 bytes/sec
- total size is 0 speedup is 0.00
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls -l /tdir/3.txt
- -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 11 21:46 /tdir/3.txt
4)验证--delete选项
rsync同步操作默认只是将目录1的数据同步到目录2,但如果目录2存在多余的文件却并不会去除,除非添加—delete选项。
在目录/fdir、/tdir已经完成同步后,删除/tdir/2.txt文件,再次同步:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rm -rf /fdir/2.txt
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -a /fdir/ /tdir/
检查发现目标文件夹/tdir下的2.txt文件还在:
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls /fdir/ /tdir/
- /fdir/:
- 1.txt 3.txt
- /tdir/:
- 1.txt 2.txt 3.txt
这种情况下添加--delete选项再次执行同步,两个目录的内容就一致了:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rsync -a --delete /fdir/ /tdir/
- [root@svr7 ~]# ls /fdir/ /tdir/
- /fdir/:
- 1.txt 3.txt
- /tdir/:
- 1.txt 3.txt
17 案例:rsync+SSH同步
17.1 问题
本例要求掌握rsync与远程SSH资源的同步操作,使用rsync命令访问远程主机svr7,完成下列任务:
- 查看远程主机的 / 目录下有哪些子目录
- 从远程主机下载 /etc/passwd 文件到当前目录
- 将远程主机的 /boot/ 目录同步为本地的 /fromssh
- 将本机的 /etc 目录同步到远程主机的 /opt/下
17.2 方案
列出 SSH 服务端资源
- rsync user@host:远程目录/
rsync+SSH远程同步操作:
- rsync [...] user@host:远程目录 本地目录
- rsync [...] 本地目录 user@host:远程目录
17.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:列出远程主机的SSH资源
查看远程主机svr7的/目录下有哪些子目录:
- [root@pc207 ~]# rsync [email protected]:/
- [email protected]'s password: //验证对方的密码
- dr-xr-xr-x 4096 2016/12/15 10:39:34 .
- lrwxrwxrwx 7 2016/12/07 09:21:50 bin
- lrwxrwxrwx 7 2016/12/07 09:21:50 lib
- lrwxrwxrwx 9 2016/12/07 09:21:50 lib64
- lrwxrwxrwx 8 2016/12/07 09:21:50 sbin
- dr-xr-xr-x 4096 2016/12/07 11:25:29 boot
- drwxr-xr-x 6 2016/12/07 09:21:14 data
- drwxr-xr-x 3200 2016/12/15 10:46:15 dev
- drwxr-xr-x 8192 2016/12/20 17:01:02 etc
步骤二:rsync+SSH同步操作
1)从远程主机svr7下载/etc/passwd文件到当前目录
- [root@pc207 ~]# rsync [email protected]:/etc/passwd ./
- [email protected]'s password: //验证对方的密码
- [root@pc207 ~]# cat passwd //检查同步结果
- root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
- bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
- daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
- adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
- lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
- .. ..
2)将远程主机svr7的/boot/目录同步为本地的/fromssh
- [root@pc207 ~]# rsync -a [email protected]:/boot/ /fromssh
- [email protected]'s password: //验证对方的密码
- [root@pc207 ~]# ls /fromssh/ //检查同步结果
- config-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64
- extlinux
- grub2
- initramfs-0-rescue-a19921505cc7e19d20dfcd5cea7d8aa2.img
- initramfs-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64.img
- initramfs-3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64kdump.img
- .. ..
3)将本机的/etc目录同步到远程主机svr7的/opt/下
确认目录大小:
- [root@pc207 ~]# du -sh /etc
- 35M /etc
上行同步到远程主机svr7上:
- [root@pc207 ~]# rsync -a /etc [email protected]:/opt/
- [email protected]'s password:
在远程主机上检查同步结果:
- [root@svr7 ~]# du -sh /opt/etc
- 35M /opt/etc
18 案例:使用inotifywait工具
18.1 问题
本例要求安装inotify-tools工具,并针对文件夹 /opt 启用 inotifywait 监控,完成下列任务:
- 当此目录下出现新建、修改、更改权限、删除文件等事件时能给出提示
- 验证上述监控事件的效果
18.2 方案
inotifywait监控操作:
- inotifywait [选项] 目标文件夹
inotifywait常用命令选项:
- -m,持续监控(捕获一个事件后不退出)
- -r,递归监控、包括子目录及文件
- -q,减少屏幕输出信息
- -e,指定监视的 modify、move、create、delete、attrib 等事件类别
18.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:安装inotify-tools软件包
1)解包
- [root@svr7 ~]# tar xf inotify-tools-3.13.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
2)配置
- [root@svr7 ~]# cd /usr/src/inotify-tools-3.13/
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# ./configure
3)编译
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# make
4)安装
- [root@svr7 inotify-tools-3.13]# make
5)检查安装结果(inotifywait程序可用)
- [root@svr7 ~]# inotifywait --help
- inotifywait 3.13
- Wait for a particular event on a file or set of files.
- Usage: inotifywait [ options ] file1 [ file2 ] [ file3 ] [ ... ]
- Options:
- -h|--help Show this help text.
- .. ..
步骤二:测试inotifywait监控
1)开启监控任务,置入后台
- [root@svr7 ~]# inotifywait -mrq -e create,modify,move,attrib,delete /opt &
- [1] 55564
2)测试/opt/目录下的新建、修改、改名、更改权限、删除文件等事件的响应消息
观察新建文件时的监控信息:
- [root@svr7 ~]# touch /opt/a.txt
- /opt/ CREATE a.txt
- /opt/ ATTRIB a.txt
观察修改文件内容时的监控信息:
- [root@svr7 ~]# echo Hello > /opt/a.txt
- [root@svr7 ~]# /opt/ MODIFY a.txt
- /opt/ MODIFY a.txt
观察将文件改名时的监控信息:
- [root@svr7 ~]# mv /opt/a.txt /opt/b.txt
- /opt/ MOVED_FROM a.txt
- /opt/ MOVED_TO b.txt
观察修改文件权限时的监控信息:
- [root@svr7 ~]# chmod 600 /opt/b.txt
- /opt/ ATTRIB b.txt
观察删除文件时的监控信息:
- [root@svr7 ~]# rm -rf /opt/b.txt
- /opt/ DELETE b.txt
3)停止监控任务
- [root@svr7 ~]# kill -9 %1
- [1]+ 已杀死 inotifywait -mr -e create,modify,move,attrib,delete /opt
19 案例:搭建mariadb数据库系统
19.1 问题
本例要求在虚拟机server0上安装 MariaDB 数据库系统:
- 安装 mariadb-server、mariadb 软件包
- 启动 mariadb 服务
然后在客户端访问此数据库服务:
- 执行 SHOW DATABASES; 指令列出有哪些库
- 退出 mysql 交互界面
19.2 方案
数据库表及相关软件的基本知识:
- 数据(记录):用来表示一个事物(实体)的一些信息(属性)的文字/图片文件等,例如字符串“:tedu.cn”
- 数据表:存放很多条数据记录的容器,例如学员联系信息表、学员月考成绩表
- 数据表的每一行:存放一条记录
- 数据表的每一列/字段:很多个事物的同一个属性
- 数据库:存放很多个相互关联的表格的容器,例如NSD1609学员档案库
- 数据库管理系统(DBMS):用来管理(创建库/添加/查询/删除/授权等)数据库信息的软件平台
MariaDB服务端:软件包mariadb-server、系统服务mariadb
MariaDB客户端:软件包mariadb、管理工具mysql
MariaDB服务端配置文件:/etc/my.cnf
mysql命令的简单用法:
- mysql [-u用户名] [-p[密码]]
19.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:搭建MariaDB数据库服务器
1)安装软件包mariadb-server、mariadb
- [root@server0 ~]# yum -y install mariadb-server
- .. ..
2)启动系统服务mariadb,并设置开机自启
- [root@server0 ~]# systemctl restart mariadb
- [root@server0 ~]# systemctl enable mariadb
- ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service'
步骤二:访问本机的MariaDB数据库系统
1)以用户root连接本机的mariadb(或mysqld)数据库服务
- [root@server0 ~]# mysql -uroot
- Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
- Your MariaDB connection id is 3
- Server version: 5.5.35-MariaDB MariaDB Server
- Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle, Monty Program Ab and others.
- Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
- MariaDB [(none)]>
2)查看当前数据库系统内有哪些库
- MariaDB [(none)]> SHOW DATABASES;
- +--------------------+
- | Database |
- +--------------------+
- | information_schema |
- | mysql |
- | performance_schema |
- | test |
- +--------------------+
- 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3)退出操作环境
- MariaDB [(none)]> QUIT
- Bye
- [root@server0 ~]#
20 案例:使用数据库查询
20.1 问题
本例要求配置MariaDB数据库,完成以下任务:
- 在系统server0上使用数据库Contacts,通过SQL查询回答下列问题:密码是solicitous的人的名字?
20.2 方案
表记录增删改查:
- insert into [库名.]表名 values(值1,值2,值3);
- delete from [库名.]表名 where ...;
- update [库名.]表名 set 字段名=字段值 where ....;
- select 字段列表 from [库名.]表名 where 字段名1=值 and|or 字段名2=值;
统计查询结果的数量:
- select count(*) from [库名.]表名 where .. ..;
20.3 步骤
实现此案例需要按照如下步骤进行。
步骤一:按条件查询表记录
1)按单个条件查询
找出密码是solicitous的人的名字?
- MariaDB [(none)]> SELECT name FROM Contacts.base WHERE Password='solicitous';
- +-------+
- | name |
- +-------+
- | James |
- +-------+
- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)