Set集合类详解(附加思维导图)
目录
一、Set集合思维导图
二、set集合类常用方法
2.1、HashSet集合常用方法
2.2、TreeSet集合的使用
三、HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet的使用场景
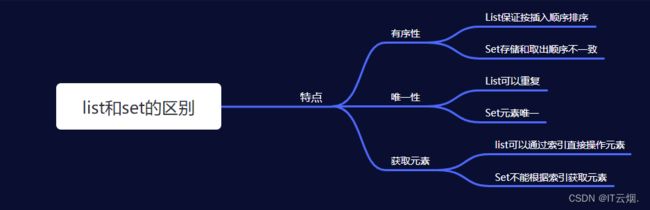
四、list和set集合的区别
一、Set集合思维导图
二、set集合类常用方法
2.1、HashSet集合常用方法
①:add(Object o):向Set集合中添加元素,不允许添加重复数据。
②:size():返回Set集合中的元素个数
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet(); //调用HashSet无参构造方法——>创建HashMap对象并给map全局变量。
set.add("你好");
set.add("世界");
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println(set.size());
}
} 注意:不会按照保存的顺序存储数据(顺序不定),遍历时不能保证下次结果和上次相同。且向HashSet集合中添加元素,HashSet add方法实质是map全局变量调用了put方法,将数据存到了key,因为HashMap的 key不允许,所以HashSet添加的元素也不允许重复。
③.remove(Object o): 删除Set集合中的obj对象,删除成功返回true,否则返回false。
④.isEmpty():如果Set不包含元素,则返回 true。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add("你好");
set.add("世界");
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());
System.out.println(set.remove("世界"));
System.out.println(set);
}
} ⑤.clear(): 移除此Set中的所有元素。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add("你好");
set.add("世界");
System.out.println(set);
set.clear();
System.out.println(set);
}
} ⑥.iterator():返回在此Set中的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add("你好");
set.add("世界");
Iterator ite =set.iterator();
while(ite.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(ite.next());
}
} ⑦.contains(Object o):判断集合中是否包含obj元素。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add("你好");
set.add("世界");
System.out.println(set.contains("你好"));
}
} ⑧:加强for循环遍历Set集合:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add("你好");
set.add("世界");
for (String name : set) { //使用foreach进行遍历。
System.out.println(name);
}
}
} 2.2、TreeSet集合的使用
①.插入是按字典序排序的
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet ts=new TreeSet();
ts.add("agg");
ts.add("abcd");
ts.add("ffas");
Iterator it=ts.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}输出 : 按照字典序排序的方式进行排序
abcd
agg
ffas②.如果插入的是自定义对象 需要让类实现 Comparable 接口并且必须要重写compareTo
class Person implements Comparable{
String name;
int age;
Person(String name,int age)
{
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Person p=(Person)o;
//先对姓名字典序比较 如果相同 比较年龄
if(this.name.compareTo(p.name)!=0) {
return this.name.compareTo(p.name);
}
else
{
if(this.age>p.age) return 1;
else if(this.age输出
abcd:12
agg:12
agg:21
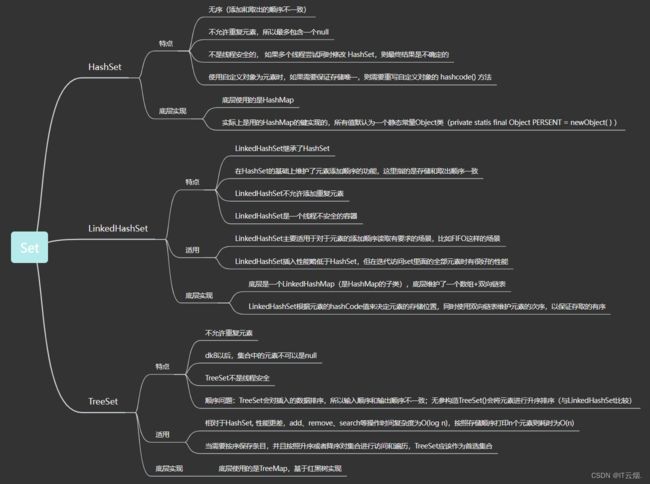
ffas:8三、HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet的使用场景
- HashSet:HashSet的性能基本上比LinkedHashSet和TreeSet要好,特别是添加和查询,这也是用的最多的两个操作
- LinkedHashSet:LinkedHashSet的查询稍慢一些,但是他可以维持元素的添加顺序。所以只有要求当插入顺序和取出顺序一致的时候 才使用LinkedHashSet。
- TreeSet:只有在需要对元素进行排序时使用