MySQL笔记——表的修改查询相关的命令操作
系列文章目录
MySQL笔记——MySQL数据库介绍以及在Linux里面安装MySQL数据库,对MySQL数据库的简单操作,MySQL的外接应用程序使用说明
文章目录
系列文章目录
一 表的修改操作
1.1 修改表的名字
1.2 添加一列score
1.3 修改列名称
1.4 修改新增列的数据类型
二 表的查询语句
2.1 基础语法
2.2 添加一些数据进行编辑查询
2.3 新建一个score表
2.4 将学生的三门成绩进行相加
2.5 select 语法
2.6 MySQL WHERE 子句
语法
2.6.1 从学生表里面查询年龄大于等于20的
2.6.2 查询年龄大于等于20,并且年龄小于等于25的
2.6.3 查询年龄等于20,或者年龄等于26的
2.7 NULL的注意点
使用ifnull()函数将空值转换
2.8 查询姓名当中包含特殊字段的信息
2.8.1 查询姓名当中包含“m”的信息
2.8.2 查询姓名最后一位为“m”的信息
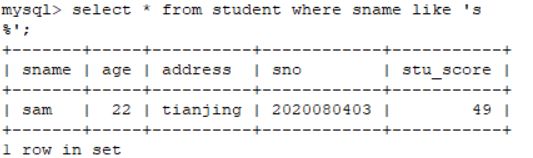
2.8.3 查询姓名第一位为“s”的信息
2.8.4 查询姓名当中第二个字段为“a”的信息
2.8.5 查询姓名当中第三个字段为“m”的信息
2.9 order by进行排序
2.9.1 按照年龄从小到大进行排序asc
2.9.2 按照年龄从大到小进行排序 desc
2.9.3 order by字段在最后面进行书写
2.10 聚合函数
2.10.1 统计student表当中姓名的总数
2.10.2 求学生表里面成绩的平均值
2.10.3 求学生表里面成绩的最大值与最小值
前言
本文主要讲解表的修改查询相关的命令操作
一 表的修改操作
1.1 修改表的名字
alter table stu rename student;1.2 添加一列score
alter table student add score varchar(30);查看修改完的表
desc student;1.3 修改列名称
假如对添加的列名称不满意,可以修改列名称
alter table student change score stu_score varchar(30);1.4 修改新增列的数据类型
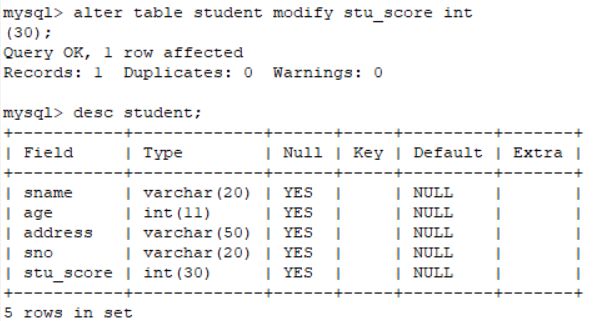
修改刚才列名称的数据类型为int型
alter table student modify stu_score int(30);可以看到数据类型变换成int型。
补充:物联网的数据存取需要多个表,每天创建一个新的数据存储表,就需要使用SQL语句来创建
二 表的查询语句
2.1 基础语法
select 字段1 , 字段2, 字段。。。。。
select * from 表名称2.2 添加一些数据进行编辑查询
insert into student values('james',18,'shanghai','2020080401',85);
insert into student values('tom',26,'beijin','2020080402',65);
insert into student values('sam',22,'tianjing','2020080403',49);
2.3 新建一个score表
create table score(sname varchar(40),chinese int(20),math int(20),english int(20));插入数据
insert into score values('james',49,90,88);
insert into score values('james',95,70,65);
insert into score values('tom',95,70,65);
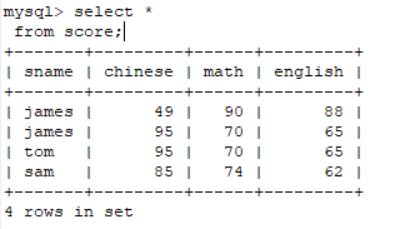
insert into score values('sam',85,74,62);查看所有的数据
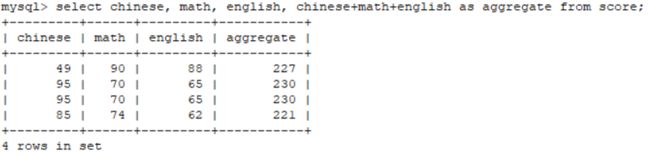
select * from score;2.4 将学生的三门成绩进行相加
select chinese, math, english, chinese+math+english as aggregate from score;衍生——将英文的列名起别名称为中文
select chinese as '语文',math as '数学',english as '英语', chinese+math+english as '总分' from score;score里面的名称是不改变的
2.5 select 语法
- 查询语句中你可以使用一个或者多个表,表之间使用逗号(,)分割,并使用WHERE语句来设定查询条件。
- SELECT 命令可以读取一条或者多条记录。
- 你可以使用星号(*)来代替其他字段,SELECT语句会返回表的所有字段数据
- 你可以使用 WHERE 语句来包含任何条件。
- 你可以使用 LIMIT 属性来设定返回的记录数。
- 你可以通过OFFSET指定SELECT语句开始查询的数据偏移量。默认情况下偏移量为0。
select * from 表名;
1. 语法:
select
字段列表
from
表名列表
where
条件列表
group by
分组字段
having
分组之后的条件
order by
排序
limit
分页限定
2.6 MySQL WHERE 子句
我们知道从 MySQL 表中使用 SQL SELECT 语句来读取数据。
如需有条件地从表中选取数据,可将 WHERE 子句添加到 SELECT 语句中。
语法
以下是 SQL SELECT 语句使用 WHERE 子句从数据表中读取数据的通用语法:
SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN FROM table_name1, table_name2... [WHERE condition1 [AND [OR]] condition2.....
- 查询语句中你可以使用一个或者多个表,表之间使用逗号, 分割,并使用WHERE语句来设定查询条件。
- 你可以在 WHERE 子句中指定任何条件。
- 你可以使用 AND 或者 OR 指定一个或多个条件。
- WHERE 子句也可以运用于 SQL 的 DELETE 或者 UPDATE 命令。
- WHERE 子句类似于程序语言中的 if 条件,根据 MySQL 表中的字段值来读取指定的数据。
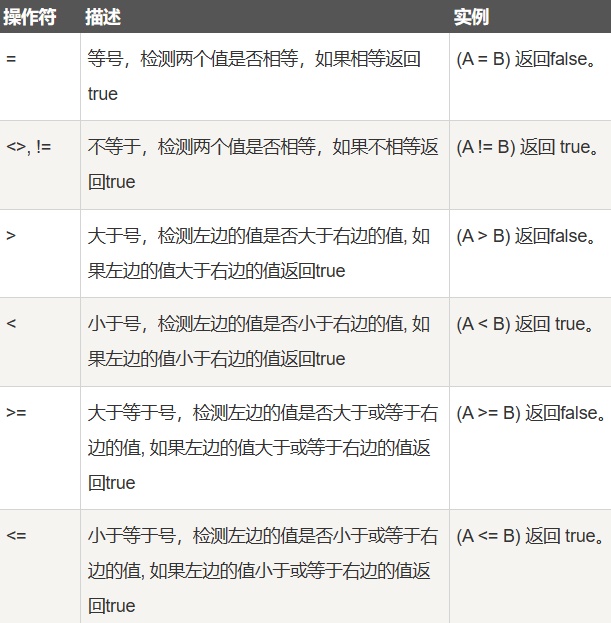
以下为操作符列表,可用于 WHERE 子句中。
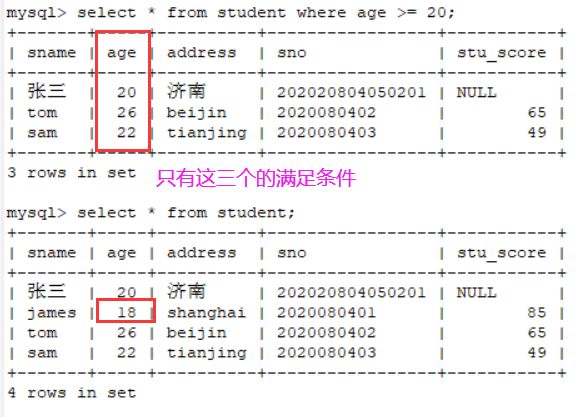
2.6.1 从学生表里面查询年龄大于等于20的
select * from student where age >= 20;2.6.2 查询年龄大于等于20,并且年龄小于等于25的
两个条件要同时满足才可以。
select * from student where age >= 20 and age <=25;另外一种
使用between and 查询
select * from student where age between 20 and 25;2.6.3 查询年龄等于20,或者年龄等于26的
两个条件只要满足一个即可。
select * from student where age = 20 or age=26;2.7 NULL的注意点
错误的实例为下面的第一个
数据库当中的null表示不知道。
正确的写法是将=换成is
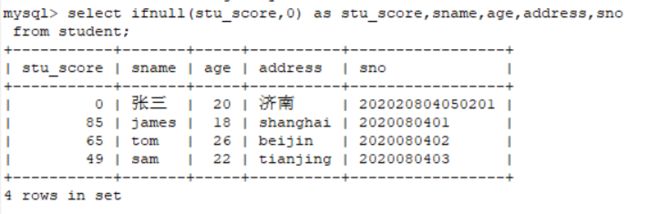
select * from student where stu_score is NULL;使用ifnull()函数将空值转换
select ifnull(stu_score,0) as stu_score,sname,age,address,sno from student;可以看到张三的null空值被替换成0了。
注意转换后的数据类型要与原来的字段数据类型保持一致。
2.8 查询姓名当中包含特殊字段的信息
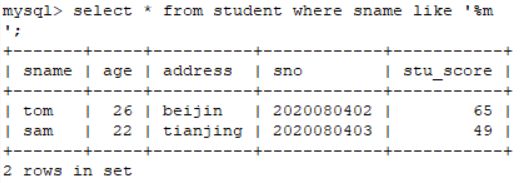
2.8.1 查询姓名当中包含“m”的信息
select * from student where sname like '%m%';使用%%将需要查询的字段选择出来。
2.8.2 查询姓名最后一位为“m”的信息
select * from student where sname like '%m';2.8.3 查询姓名第一位为“s”的信息
select * from student where sname like 's%';2.8.4 查询姓名当中第二个字段为“a”的信息
select * from student where sname like '_a%';2.8.5 查询姓名当中第三个字段为“m”的信息
select * from student where sname like '__m%';" % "为一个占位符【占0个或者多个位】,“ _ ”也是一个占位符【只表示占一个位】
修改数据和删除数据要加上条件,不跟条件会导致误删除。
2.9 order by进行排序
2.9.1 按照年龄从小到大进行排序asc
select * from student order by age asc;2.9.2 按照年龄从大到小进行排序 desc
select * from student order by age desc;order by 可以跟着多个字段,只有第一个字段相同的时候才从后面的字段上面进行对应的排序
案例如下:
select * from score order by chinese desc ,math asc ;2.9.3 order by字段在最后面进行书写
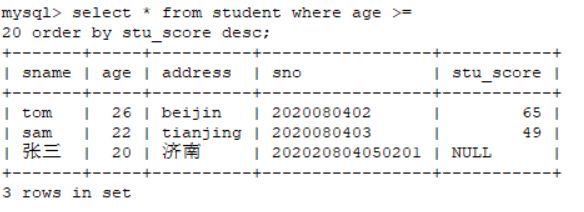
案例如下:对student表当中年龄大于等于20岁的并且对其成绩进行从大到小进行排序。
select * from student where age >= 20 order by stu_score desc;2.10 聚合函数
常见的几个函数
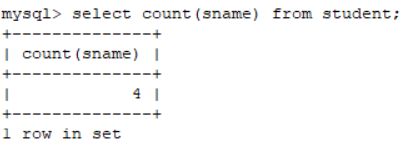
2.10.1 统计student表当中姓名的总数
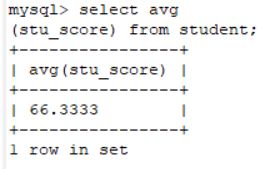
select count(sname) from student;2.10.2 求学生表里面成绩的平均值
select avg(stu_score) from student;2.10.3 求学生表里面成绩的最大值与最小值
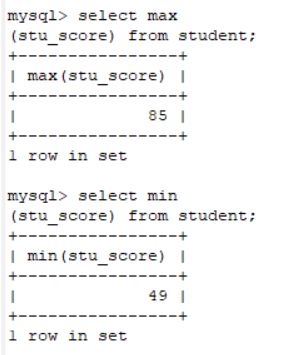
select max(stu_score) from student;
select min(stu_score) from student;注意:聚合函数对空值不能进行计算,对于空值要进行处理
案例如下:此处有函数的嵌套。
select count(ifnull(stu_score,0)) from student;总结
以上就是今天的内容~
欢迎大家点赞,收藏⭐,转发,
如有问题、建议,请您在评论区留言哦。
最后:转载请注明出处!!!