IO进程线程day1(2023.7.25)
一、Xmind整理:
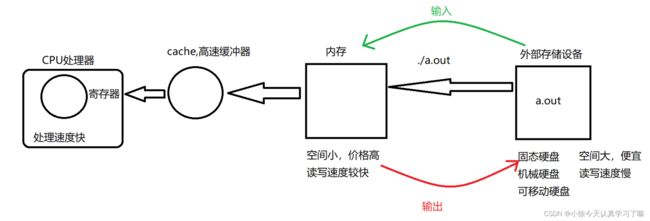
什么是IO:
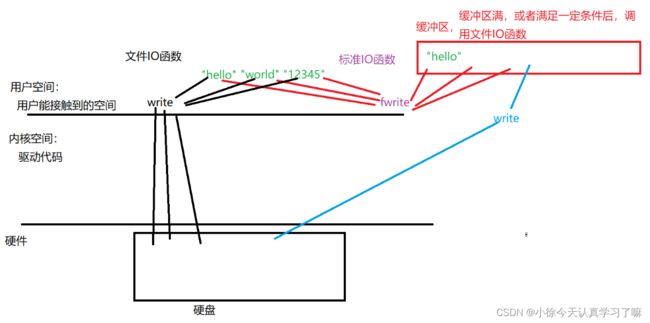
文件IO函数与标准IO函数:
二、课上练习:
练习1:标准IO函数的简单示例
scanf:
if(OS == Linux)
{
去调用Linux的文件IO
read();
}
else if(OS == windows)
{
去调用windows的文件IO
fread();
}练习2:FILE结构体
struct _IO_FILE {
char* _IO_buf_base; 缓冲区的起始地址
char* _IO_buf_end; 缓冲区的结尾地址
int _fileno; 文件描述符,在文件IO的时候再讲解。
}
缓冲区大小:尾地址-首地址。练习3:fopen
功能:打开一个文件
原型:
#include
FILE *fopen(const char *pathname, const char *mode); 参数:
char *pathname:指定要打开的文件路径以及名字;
char *mode:以什么方式打开文件;
r 以读的方式打开文件; 流在文件开头位置---> 若要读取文件,则从开头开始读取
若文件不存在,打开失败。
r+ 以读写的方式打开文件; 流在文件开头位置---> 若要读写取文件,则从开头开始操作
若文件不存在,打开失败.
w 以写的方式打开文件,---> 若要写取文件,则从开头开始操作
若文件不存在,则会创建文件,并打开;
若文件存在,则清空文件,并打开;
w+ 以读写的方式打开文件,---> 若要读写取文件,则从开头开始操作
若文件不存在,则会创建文件,并打开;
若文件存在,则清空文件,并打开;
a 以写的方式打开文件,---> 若要写取文件,则从结尾开始操作
若文件不存在,则会创建文件,并打开;
若文件存在,则文件的流在文件结尾,不清空;
a+ 以读写方式打开文件,
若文件不存在,则会创建文件,并打开;
若文件存在,则流的初始位置:
1. 若开始是读文件,则流在文件开头
2. 若开始是写文件,则流在文件结尾。返回值:
成功,返回FILE *类型指针;
失败,返回NULL,同时更新errno;
errno:本质上是一个整型数,不同的错误会更新不同的errno; 定义在errno.h这个头文件中
所有情况:/usr/include/asm-generic errno.h errno-base.h
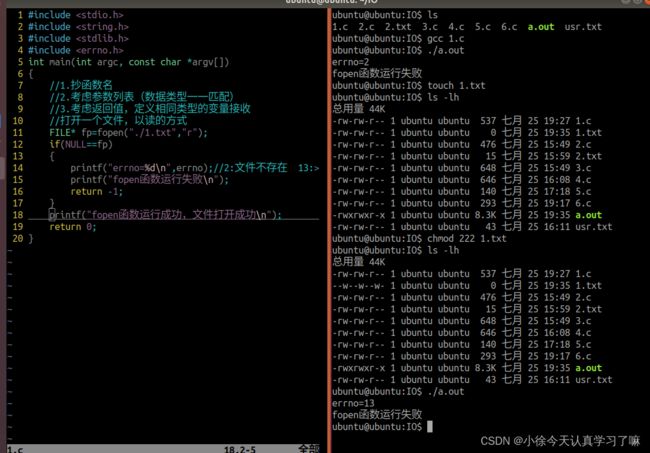
打开一个文件,以读的方式
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//1.抄函数名
//2.考虑参数列表(数据类型一一匹配)
//3.考虑返回值,定义相同类型的变量接收
//打开一个文件,以读的方式
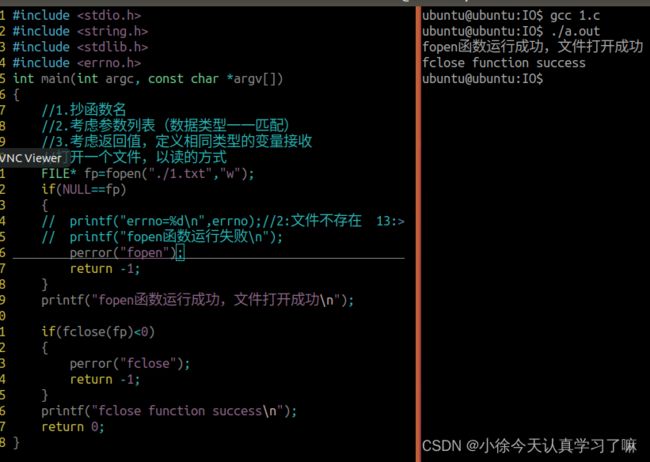
FILE* fp=fopen("./1.txt","w");
if(NULL==fp)
{
// printf("errno=%d\n",errno);//2:文件不存在 13:文件权限不足
// printf("fopen函数运行失败\n");
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
printf("fopen函数运行成功,文件打开成功\n");
if(fclose(fp)<0)
{
perror("fclose");
return -1;
}
printf("fclose function success\n");
return 0;
}
练习4:perror
功能:根据errno,打印对应的错误信息
原型:
#include
void perror(const char *s);
参数:
char *s:用于提示的字符串;练习5:fclose
功能:关闭指定的文件; 释放资源,例如缓冲区空间。若不关闭,则可能会造成内存泄漏
原型:
#include
int fclose(FILE *stream); 参数:
FILE *stream:指定要关闭的文件对应的流指针;返回值:
成功,返回0;
失败,返回EOF,同时更新errno; # define EOF (-1) 打开文件,以写的方式
if(fclose(fp)<0)
{
perror("fclose");
return -1;
}
printf("fclose function success\n");
return 0;练习6:fprintf
功能:将数据格式化输出到指定文件中
原型:
#include
int printf(const char *format, ...);
printf("hello world %d %c %f \r\n\t", 1, 'a', 10.1);
int fprintf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...); 参数:
FILE *stream:流指针,指定要输出到哪个文件中,就填对应文件的流指针;
char *format:格式化字符串:字符,占位符,转义字符;
...:不定参数,不定数据个数,不定数据类型。返回值:
成功,返回被打印的字符个数;
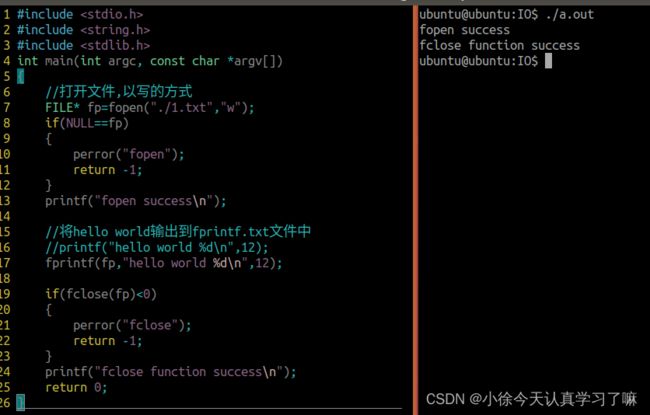
失败,返回负数,打开文件,以写的方式
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//打开文件,以写的方式
FILE* fp=fopen("./1.txt","w");
if(NULL==fp)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
printf("fopen success\n");
//将hello world输出到fprintf.txt文件中
//printf("hello world %d\n",12);
fprintf(fp,"hello world %d\n",12);
if(fclose(fp)<0)
{
perror("fclose");
return -1;
}
printf("fclose function success\n");
return 0;
}
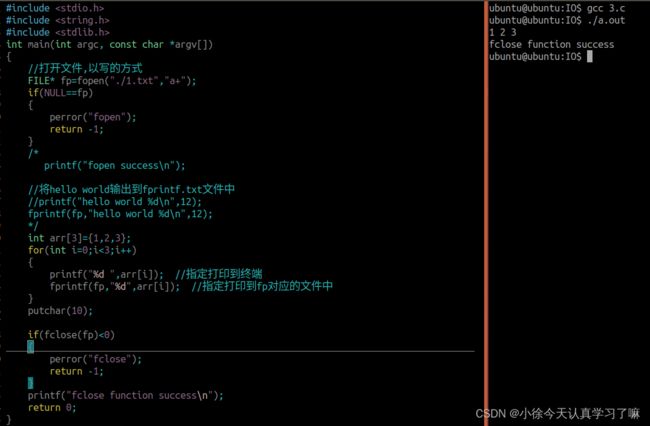
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//打开文件,以写的方式
FILE* fp=fopen("./1.txt","a+");
if(NULL==fp)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
/*
printf("fopen success\n");
//将hello world输出到fprintf.txt文件中
//printf("hello world %d\n",12);
fprintf(fp,"hello world %d\n",12);
*/
int arr[3]={1,2,3};
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]); //指定打印到终端
fprintf(fp,"%d",arr[i]); //指定打印到fp对应的文件中
}
putchar(10);
if(fclose(fp)<0)
{
perror("fclose");
return -1;
}
printf("fclose function success\n");
return 0;
}
练习7:fscanf
功能:从指定文件中格式化读取数据; scanf fscanf的%s %d默认不识别空格,\n, \t
%c形式获取单个字符会识别空格,换行。
原型:
#include
int scanf(const char *format, ...);
int fscanf(FILE *stream, const char *format, ...); 参数:
FILE *stream:流指针,从哪个文件中读取,填对应的流指针;
char *format:格式化字符串:字符,占位符,转义字符;
...:不定参数,不定数据个数,不定数据类型。返回值:
成功,返回成功读取的数据个数;
=EOF,文件读取完毕
=EOF,函数运行失败,同时更新errno;注意:
1.%s %d不识别空格 \n \t,若想要获取到上述字符,需要使用%c形式
2.读写操作后,文件偏移量会自动偏移,所以若想要从头读取数据,就需要想办法将偏移量修改到开头位置
a.将文件关闭重新开
b.fseek ftell
3.printf ,scanf怎么使用 ,fprintf fscanf就怎么使用。
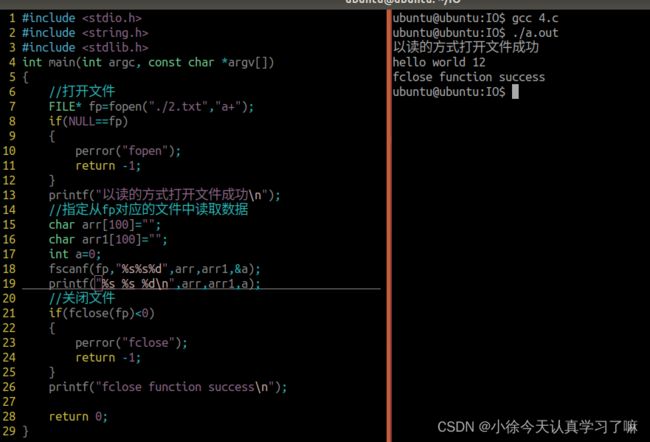
打开文件,以写的方式
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//打开文件
FILE* fp=fopen("./2.txt","a+");
if(NULL==fp)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
printf("以读的方式打开文件成功\n");
//指定从fp对应的文件中读取数据
char arr[100]="";
char arr1[100]="";
int a=0;
fscanf(fp,"%s%s%d",arr,arr1,&a);
printf("%s %s %d\n",arr,arr1,a);
//关闭文件
if(fclose(fp)<0)
{
perror("fclose");
return -1;
}
printf("fclose function success\n");
return 0;
}
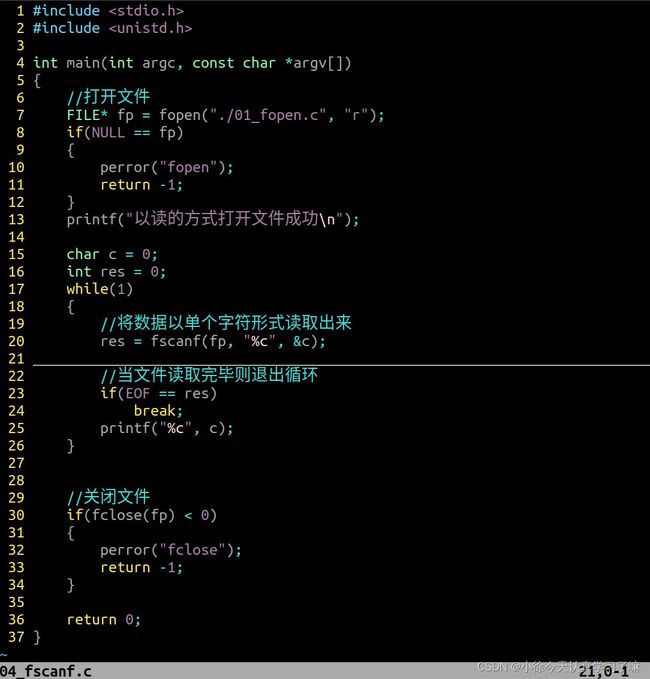
用fprintf与fscanf函数实现:文件拷贝,例如将1.txt的内容拷贝到2.txt中:
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//以读的方式打开源文件
FILE* fp_r = fopen("./01_fopen.c", "a+");
if(NULL == fp_r)
{
printf("__%d__\n", __LINE__);
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
//以写的方式打开目标文件
FILE* fp_w = fopen("copy.c", "w+");
if(NULL == fp_w)
{
printf("__%d__\n", __LINE__);
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
char c = 0;
while(fscanf(fp_r, "%c", &c) != EOF)
{
//写文件
fprintf(fp_w, "%c", c);
}
printf("拷贝成功\n");
//此时文件偏移量在文件的结尾,如果想要从copy.c文件中读取数据
//则需要将文件描述符重新偏移打破文件开头位置
//所以需要关闭文件重新打开,将偏移量重新改回到开头位置
//关闭文件
fclose(fp_w);
fclose(fp_r);
//从fp_w中读取数据,然后打印到终端
fp_w = fopen("copy.c", "r");
while(fscanf(fp_w, "%c", &c) != EOF)
{
printf("%c", c);
}
fclose(fp_w);
return 0;
} 练习8:fputc
功能:将单个字符打印到指定的文件中
原型:
#include
int fputc(int c, FILE *stream);
int putchar(int c); putchar('a'); putchar(97); putchar(10); putchar('\n'); 参数:
int c:指定要输出的字符对应的字符形式或者整型形式,填'a', 也可以填97;
FILE *stream:流指针,想要打印到哪个文件中就填哪个文件对应的流指针;返回值:
成功,返回成功输出字符对应的整型形式;
失败,返回EOF;注意:
Linux操作系统,默认以\n结尾,若用编辑器保存检测到没有以\n结尾,则会自动补充'\n'
unix操作系统,默认以\r\n结尾,
windows操作系统,默认以\r结尾。
练习9:fgetc
功能:从指定文件中读取单个字符
原型:
#include
int fgetc(FILE *stream); 参数:
FILE *stream:指定要从哪个文件中读取返回值:
成功,返回成功读取到的字符对应的整型形式;
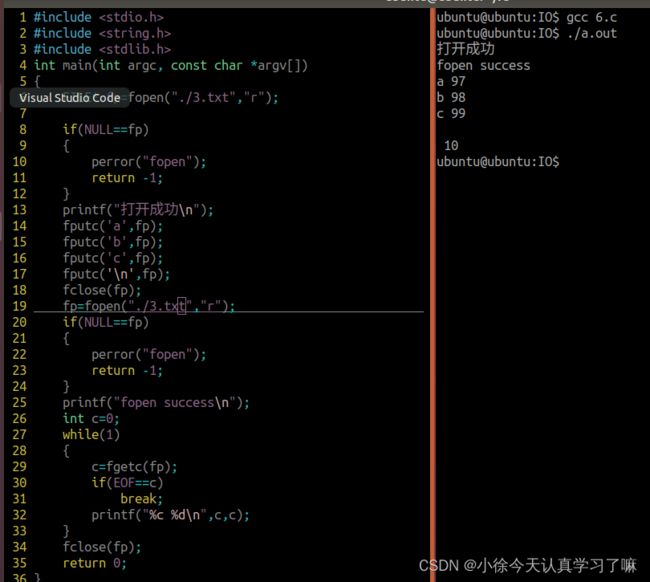
当文件读取完毕或者函数运行失败,返回EOF;#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE* fp=fopen("./3.txt","r");
if(NULL==fp)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
printf("打开成功\n");
fputc('a',fp);
fputc('b',fp);
fputc('c',fp);
fputc('\n',fp);
fclose(fp);
fp=fopen("./3.txt","r");
if(NULL==fp)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
printf("fopen success\n");
int c=0;
while(1)
{
c=fgetc(fp);
if(EOF==c)
break;
printf("%c %d\n",c,c);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
三、课后作业:
1.实现登录功能。自定义一个usr.txt,手动输入账户密码,格式如下:账户 密码
例如: zhangsan 12345
lisi abcde
wangwu abc123
需求如下:从终端获取账户密码,与文件中的账户密码比较
若终端输入的账户不存在,则输出账户不存在
若终端输入的账户存在,但是密码不正确,则输出密码错误
若账户密码均正确,则输出登录成功
附加题:
实现注册功能,注册的账户密码存储在上一题的文件中。需求:不能重复注册。
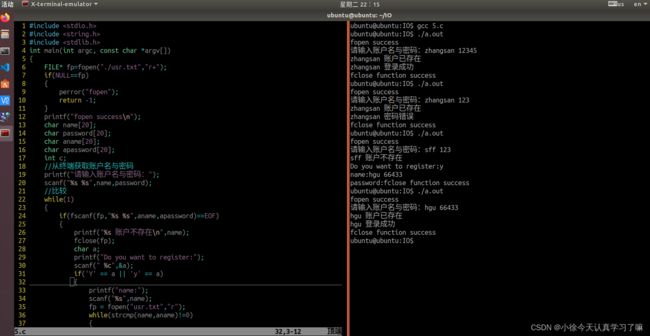
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE* fp=fopen("./usr.txt","r+");
if(NULL==fp)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
printf("fopen success\n");
char name[20];
char password[20];
char aname[20];
char apassword[20];
int c;
//从终端获取账户名与密码
printf("请输入账户名与密码:");
scanf("%s %s",name,password);
//比较
while(1)
{
if(fscanf(fp,"%s %s",aname,apassword)==EOF)
{
printf("%s 账户不存在\n",name);
fclose(fp);
char a;
printf("Do you want to register:");
scanf(" %c",&a);
if('Y' == a || 'y' == a)
{
printf("name:");
scanf("%s",name);
fp = fopen("usr.txt","r");
while(strcmp(name,aname)!=0)
{
c = fscanf(fp,"%s",aname);
if(EOF == c)
break;
}
if(strcmp(name,aname)==0)
{
printf("账户已存在!\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("password:");
scanf("%s",password);
fclose(fp);
fp = fopen("usr.txt","a");
fprintf(fp,"%s %s\n",name,password);
}
}
if(EOF == c)
break;
}
if(strcmp(name,aname)==0)
{
printf("%s 账户已存在\n", name);
if(strcmp(password,apassword)==0)
{
printf("%s 登录成功\n",name);
}
else
{
printf("%s 密码错误\n",name);
}
break;
}
}
if(fclose(fp)<0)
{
perror("fclose");
return -1;
}
printf("fclose function success\n");
return 0;
}
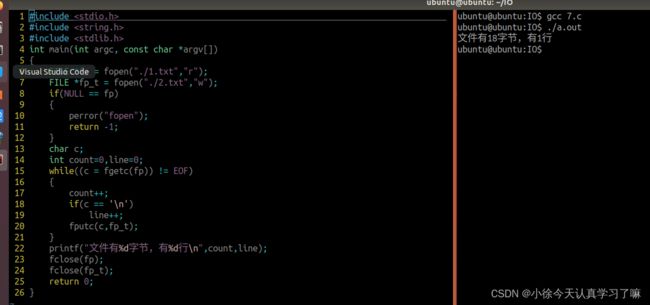
2.文件拷贝,例如将1.txt的内容拷贝到2.txt中
要求用fgetc计算一个文件有多少个字节
用fgetc计算一个文件有几行? 计算\n个数
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp = fopen("./1.txt","r");
FILE *fp_t = fopen("./2.txt","w");
if(NULL == fp)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
char c;
int count=0,line=0;
while((c = fgetc(fp)) != EOF)
{
count++;
if(c == '\n')
line++;
fputc(c,fp_t);
}
printf("文件有%d字节,有%d行\n",count,line);
fclose(fp);
fclose(fp_t);
return 0;
}