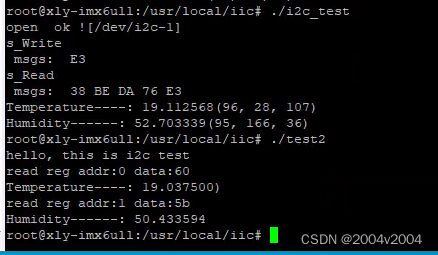
Linux ARM I2C 通讯读数据
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
// #define I2C_RETRIES 0x0701
// #define I2C_TIMEOUT 0x0702
// #define I2C_RDWR 0x0707
/*********定义struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data和struct i2c_msg,要和内核一致*******/
/***********主程序***********/
int main()
{
int fd, ret, i;
char s_Dev[] = "/dev/i2c-1";
unsigned char s_Write[4];
unsigned char s_Read[4];
unsigned char device_addr = 0x40; /* 设备地址 */
// struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data msg_rdwr;
struct i2c_msg i2cmsg[2];
fd = open(s_Dev, O_RDWR);
/* dev / i2c - 0是在注册i2c - dev.c后产生的,代表一个可操作的适配器。如果不使用i2c - dev.c *的方式,就没有,也不需要这个节点。 */
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open failed [%s]\n", s_Dev);
perror("open error");
return 0;
}
printf("open ok ![%s]\n", s_Dev);
// e2prom_data.nmsgs = 2;
// /*
// *因为操作时序中,最多是用到2个开始信号(字节读操作中),所以此将
// *e2prom_data.nmsgs配置为2
// */
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data msg_rdwr; // = {.msgs = i2cmsg, .nmsgs = 2};
msg_rdwr.msgs = i2cmsg;
msg_rdwr.nmsgs = 2;
// e2prom_data.msgs = (struct i2c_msg *)malloc(e2prom_data.nmsgs * sizeof(struct i2c_msg));
// if (!e2prom_data.msgs)
// {
// printf("malloc error ![%s]\n", s_Dev);
// perror("malloc error");
// exit(1);
// }
ioctl(fd, I2C_TIMEOUT, 1); /*超时时间*/
ioctl(fd, I2C_RETRIES, 2); /*重复次数*/
// msg_rdwr.msgs = i2cmsg;
// msg_rdwr.nmsgs = 2;
/***write data to e2prom**/
s_Write[0] = 0xe3;
s_Write[1] = 0;
// e2prom_data.nmsgs = 1;
// (e2prom_data.msgs[0]).len = strlen(s_Write); // 1个 e2prom 写入目标的地址和1个数据
// (e2prom_data.msgs[0]).addr = device_addr; // e2prom 设备地址
// (e2prom_data.msgs[0]).flags = 0; // write
// (e2prom_data.msgs[0]).buf = s_Write; //(unsigned char *)malloc(2);
// // (e2prom_data.msgs[0]).buf[0] = 0x10; // e2prom 写入目标的地址
// // (e2prom_data.msgs[0]).buf[1] = 0x58; // the data to write
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].addr = device_addr; // e2prom 设备地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].flags = 0; // write
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].buf = s_Write; // e2prom数据地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].len = strlen(s_Write); // e2prom 目标数据的地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].addr = device_addr; // e2prom 设备地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].flags = 1; // read
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].buf = s_Read; //(unsigned char *)malloc(1); //存放返回值的地址。
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].len = strlen(s_Read); //读出的数据
printf("s_Write \n msgs: ");
for (i = 0; i < strlen(s_Write); i++)
printf("%.2X ", s_Write[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("s_Read \n msgs: ");
for (i = 0; i < strlen(s_Read); i++)
printf("%.2X ", s_Read[i]);
printf("\n");
ret = ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, (unsigned long)&msg_rdwr);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("ioctl error1");
}
ret = 256 * s_Read[0] + s_Read[1];
float f_Temp = -46.85 + 175.7 * ret / 0x10000;
printf("Temperature----: %f(%d, %d, %d)\n", f_Temp, s_Read[0], s_Read[1], s_Read[2]);
sleep(1);
/******read data from e2prom*******/
s_Write[0] = 0xe5;
s_Write[1] = 0;
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].addr = device_addr; // e2prom 设备地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].flags = 0; // write
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].buf = s_Write; // e2prom数据地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[0].len = strlen(s_Write); // e2prom 目标数据的地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].addr = device_addr; // e2prom 设备地址
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].flags = 1; // read
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].buf = s_Read; //(unsigned char *)malloc(1); //存放返回值的地址。
msg_rdwr.msgs[1].len = strlen(s_Read); //读出的数据
ret = ioctl(fd, I2C_RDWR, (unsigned long)&msg_rdwr);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("ioctl error2");
}
// printf("buff[0]=%x\n", (e2prom_data.msgs[1]).buf[0]);
ret = 256 * s_Read[0] + s_Read[1];
f_Temp = 6.0 + 125.0 * ret / 0x10000;
printf("Humidity------: %f(%d, %d, %d)\n", f_Temp, s_Read[0], s_Read[1], s_Read[2]);
/***打印读出的值,没错的话,就应该是前面写的0x58了***/
close(fd);
return 0;
} #include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define CHIP "/dev/i2c-1"
#define I2C_DEVICE_ADDR 0x40 // eeprom addr
static int iic_write(int i2c_fd, int device_addr, unsigned int reg_address, unsigned int reg_val)
{
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data work_queue;
int ret = 0;
work_queue.nmsgs = 1;
work_queue.msgs = (struct i2c_msg *)malloc(work_queue.nmsgs * sizeof(struct i2c_msg));
if (!work_queue.msgs)
{
printf("msgs memery alloc error\n");
close(i2c_fd);
return -1;
}
if ((work_queue.msgs[0].buf = (unsigned char *)malloc(2 * sizeof(unsigned char))) == NULL)
{
printf("buf memery alloc error...\n");
close(i2c_fd);
return -1;
}
(work_queue.msgs[0]).len = 2;
(work_queue.msgs[0]).flags = !I2C_M_RD;
(work_queue.msgs[0]).addr = device_addr;
(work_queue.msgs[0]).buf[0] = reg_address;
(work_queue.msgs[0]).buf[1] = reg_val;
work_queue.nmsgs = 1;
ret = ioctl(i2c_fd, I2C_RDWR, (unsigned long)&work_queue);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf("Error during I2C_RDWR ioctl with error code: %d\n", ret);
return -1;
}
free(work_queue.msgs[0].buf);
free(work_queue.msgs);
return 0;
}
static int iic_read(int i2c_fd, int device_addr, unsigned int reg_address)
{
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data work_queue;
unsigned char val;
int ret;
work_queue.nmsgs = 2;
work_queue.msgs = (struct i2c_msg *)malloc(work_queue.nmsgs * sizeof(struct i2c_msg));
if (!work_queue.msgs)
{
printf("Memery alloc error\n");
close(i2c_fd);
return -1;
}
val = (unsigned char)reg_address;
(work_queue.msgs[0]).len = 1;
(work_queue.msgs[0]).flags = 0;// write
(work_queue.msgs[0]).addr = device_addr;// 设备地址
(work_queue.msgs[0]).buf = &val;
(work_queue.msgs[1]).len = 1;
(work_queue.msgs[1]).flags = 1;// read
(work_queue.msgs[1]).addr = device_addr;// 设备地址
(work_queue.msgs[1]).buf = &val;
ret = ioctl(i2c_fd, I2C_RDWR, (unsigned long)&work_queue);
if (ret < 0)
{
printf("Error during I2C_RDWR ioctl with error code: %d\n", ret);
return -1;
}
free(work_queue.msgs);
return val;
}
int main()
{
printf("hello, this is i2c test\n");
int ret = 0;
int ik;
int fd = open(CHIP, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s failed\n", CHIP);
goto exit;
}
if (ioctl(fd, I2C_SLAVE, I2C_DEVICE_ADDR) < 0)
{ // device addr
printf("ioictl: set slave address failed\n");
goto close;
}
// ret = iic_write(fd, I2C_DEVICE_ADDR, 0, 0xaa);
// if (ret)
// printf("write failed\n");
// usleep(1000 * 1000 * 0.1);
// ret = iic_write(fd, I2C_DEVICE_ADDR, 1, 0xbb);
// if (ret)
// printf("write failed\n");
usleep(1000 * 1000 * 0.1);
ret = iic_read(fd, I2C_DEVICE_ADDR, 0xe3);
printf("read reg addr:0 data:%x\n", ret);
ret = 256 * ret;
float f_Temp = -46.85 + 175.7 * ret / 0x10000;
printf("Temperature----: %f)\n", f_Temp);
ret = iic_read(fd, I2C_DEVICE_ADDR, 0xe5);
printf("read reg addr:1 data:%x\n", ret);
ret = 256 * ret;
f_Temp = 6.0 + 125.0 * ret / 0x10000;
printf("Humidity------: %f\n", f_Temp);
close:
close(fd);
exit:
return 0;
} 上述是两个文件,分别执行的结果如上,记录下经历, 是读,写没有测试环境,没有测试。