javaFX按钮控件、事件检测、读取输入
一、创建按键控件
按钮是一个矩形控件,它显示为一个按钮,在其表面写有一个标题。通常情况下,当用户点击Button控件时(用鼠标或在触摸屏上触摸它),会发生一个动作。
要创建一个Button控件,你将使用Button类,它位于JavaFX.scene.control包中。
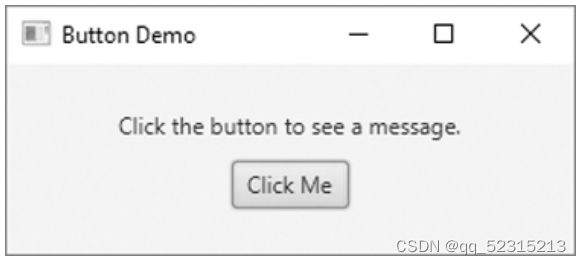
Button myButton = new Button("Click Me");下面的代码将显示一个按钮和一行文字,文字属于label控件:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
/**
A Button Demo
*/
public class ButtonDemo extends Application
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Launch the application.
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage)
{
// Create a Label control.
Label myLabel = new Label("Click the button to see a message.");
// Create a Button control.
Button myButton = new Button("Click Me");
// Put the Label and Button in a VBox with 10 pixels of spacing.
VBox vbox = new VBox(10, myLabel, myButton);
// Create a Scene with the VBox as its root node.
Scene scene = new Scene(vbox, 300, 100);
// Set the scene's alignment to center.
vbox.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
// Add the Scene to the Stage.
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
// Set the stage title.
primaryStage.setTitle("Button Demo");
// Show the window.
primaryStage.show();
}
}二、处理事件
(1)处理事件的格式
事件是在程序运行时发生的动作。例如,每当用户点击一个 按钮控件,就会有一个事件发生。当一个事件发生时,负责该事件的控件创建 一个事件对象,其中包含关于该事件的信息。创建该事件对象的GUI控件被称为 被称为事件源event source。
事件对象是Event类(来自javafx.event包)的实例,或其子类之一。当一个Button控件被点击时,一个ActionEvent类(Event类的一个子类)的对象被创建,它也在javafx.event包中。
当一个event实例被创建时,我们应该连接到相应的event handler去处理这个事件,这个过程被称为event firing。
我们的任务就是完成event handler。
当你写一个事件处理类时,它必须实现EventHandler接口,接口位于javafx.event包中。接口中有一个名为handler的void方法,这个方法接收一个event类的参数。
如果我们想写一个类去处理“点击按钮”这个事件,回顾之前的内容,当按钮被点击,会产生一个ActionEvent type的事件,那我们就可以按下面的格式去完成这个handler:
class ButtonClickHandler implements EventHandler
{
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent event)
{
// Write event handling code here.
}
} (2)注册event handler
当你完成event handler之后,你需要将这个event handler和某个控件连接,这个过程被称为注册registering event handler。Button controls有一个名为setOnAction的方法,这个方法被用于注册event handler。我们需要调用setOnAction,传入一个event handler的对象作为参数,这个button控件就和event handler连接了:
myButton.setOnAction(new ButtonClickHandler());我们常常将handler类写为私有内部类。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
/**
An Event Demo
*/
public class EventDemo extends Application
{
// Field for the Label control
private Label myLabel;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Launch the application.
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage)
{
// Create a Label control.
myLabel = new Label("Click the button to see a message.");
// Create a Button control.
Button myButton = new Button("Click Me");
// Register the event handler.
myButton.setOnAction(new ButtonClickHandler());
// Put the Label and Button in a VBox with 10 pixels of spacing.
VBox vbox = new VBox(10, myLabel, myButton);
// Create a Scene with the VBox as its root node.
Scene scene = new Scene(vbox, 300, 100);
// Set the scene's alignment to center.
vbox.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
// Add the Scene to the Stage.
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
// Set the stage title.
primaryStage.setTitle("Button Demo");
// Show the window.
primaryStage.show();
}
/**
Event handler class for myButton
*/
class ButtonClickHandler implements EventHandler
{
public void handle(ActionEvent event)
{
myLabel.setText("Thanks for clicking the button!");
}
}
} 我们没有在start方法中声明mylabel变量,因为内部类需要使用它。最后的语句改变了mylabel控件显示的内容。
三、读取输入
TextField控件常用于接收用户的输入。一个TextField控件显示为一个矩形区域。当应用程序运行时,用户可以将文本输入TextField控件。在程序中,你可以检索到用户输入的文本,并对其进行操作。TextField控件需要使用TextField类,位于javafx.scene.control包。创建实例如下;
TextField myTextField = new TextField();我们可以在输入框中显示原始内容:
TextField myTextField = new TextField("Example data");为了得到用户的输入,可以调用getText方法:
String input;
input = myTextField.getText();下面我们用之前所学的知识创建一个英里公里转换器。
在这个转换器中,我们需要用到两种布局容器:HBox nested inside of a VBox。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
/**
Kilometer Converter application
*/
public class KiloConverter extends Application
{
// Fields
private TextField kiloTextField;
private Label resultLabel;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Launch the application.
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage)
{
// Create a Label to display a prompt.
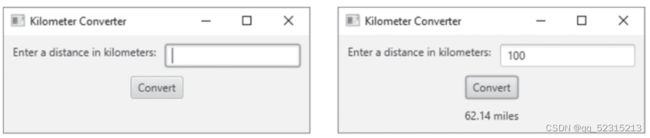
Label promptLabel = new Label("Enter a distance in kilometers:");
// Create a TextField for input.
kiloTextField = new TextField();
// Create a Button to perform the conversion.
Button calcButton = new Button("Convert");
// Register the event handler.
calcButton.setOnAction(new CalcButtonHandler());
// Create an empty Label to display the result.
resultLabel = new Label();
// Put the promptLabel and the kiloTextField in an HBox.
HBox hbox = new HBox(10, promptLabel, kiloTextField);
// Put the HBox, calcButton, and resultLabel in a VBox.
VBox vbox = new VBox(10, hbox, calcButton, resultLabel);
// Set the VBox's alignment to center.
vbox.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
// Set the VBox's padding to 10 pixels.
vbox.setPadding(new Insets(10));
// Create a Scene.
Scene scene = new Scene(vbox);
// Add the Scene to the Stage.
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
// Set the stage title.
primaryStage.setTitle("Kilometer Converter");
// Show the window.
primaryStage.show();
}
/**
Event handler class for calcButton
*/
class CalcButtonHandler implements EventHandler
{
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent event)
{
// Get the kilometers.
double kilometers = Double.parseDouble(kiloTextField.getText());
// Convert the kilometers to miles.
double miles = kilometers * 0.6214;
// Display the results.
resultLabel.setText(String.format("%,.2f miles", miles));
}
}
} 注意在第一张图里,并不是没有结果框,只是结果label的内容为空,没有显示。当handler执行后,调用了setText方法,label不为空了,就显示出来了。
四、利用匿名内部类和lambda表达式写handler
我们以刚刚的转换器为例。
匿名内部类:
// Create an event handler.
calcButton.setOnAction(new EventHandler()
{
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent event)
{
// Get the kilometers.
Double kilometers =
Double.parseDouble(kiloTextField.getText());
// Convert the kilometers to miles.
Double miles = kilometers * 0.6214;
// Display the results.
resultLabel.setText(String.format("%,.2f miles", miles));
}
}); lambda表达式:
calcButton.setOnAction(event −>
{
// Get the kilometers.
double kilometers = Double.parseDouble(kiloTextField.getText());
// Convert the kilometers to miles.
double miles = kilometers * 0.6214;
// Display the results.
resultLabel.setText(String.format("%,.2f miles", miles));
});