Mybatis学习注解开发,Spring整合Mybatis
Mybatis简介
1. 什么是Mybatis
1)mybatis 是一个优秀的基于java的持久层框架,它内部封装了jdbc,使开发者只需要关注sql语句本身,而不需要花费精力去处理加载驱动、创建连接、创建statement等繁杂的过程。
2)mybatis通过xml或注解的方式将要执行的各种 statement配置起来,并通过java对象和statement中sql的动态参数进行映射生成最终执行的sql语句。
3)最后mybatis框架执行sql并将结果映射为java对象并返回。采用ORM思想解决了实体和数据库映射的问题,对jdbc 进行了封装,屏蔽了jdbc api 底层访问细节,使我们不用与jdbc api 打交道,就可以完成对数据库的持久化操作。
2.Mybatis的快速入门
2.1Mybatis开发步骤
MyBatis官网地址:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
①添加MyBatis的坐标
②创建user数据表
③编写User实体类
④编写映射文件UserMapper.xml
⑤编写核心文件SqlMapConfig.xml
⑥编写测试类
2.2 环境搭建
1)导入MyBatis的坐标和其他相关坐标
添加MyBatis的依赖坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatisgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatisartifactId>
<version>3.4.5version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.6version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
编写UserMapper映射文件
DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="userMapper">
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.zeng.domain.User">
select * from User
select>
mapper>
编写MyBatis核心文件
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/zeng/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
编写测试代码
//加载核心配置文件
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//获得sqlSession工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
//获得sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行sql语句
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("userMapper.findAll");
//打印结果
System.out.println(userList);
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
3.MyBatis的映射文件概述
4. MyBatis的增删改查操作
4.1MyBatis的插入数据操作
1)编写UserMapper映射文件
<mapper namespace="userMapper">
<insert id="add" parameterType="com.zeng.domain.User">
insert into user values(#{id},#{username},#{password})
insert>
mapper>
2)编写插入实体User的代码
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
//会默认开启一个事务,但事务不会自动提交,需要手动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
int insert = sqlSession.insert("userMapper.add", user);
System.out.println(insert);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
3)插入操作注意问题
• 插入语句使用insert标签
• 在映射文件中使用parameterType属性指定要插入的数据类型
•Sql语句中使用**#{实体属性名}方式引用实体中的属性值
•插入操作使用的API是sqlSession.insert(“命名空间.id”,实体对象)**;
•插入操作涉及数据库数据变化,所以要使用sqlSession对象显示的提交事务,即sqlSession.commit()
4.2 MyBatis的修改数据操作
1)编写UserMapper映射文件
<mapper namespace="userMapper">
<update id="update" parameterType="com.zeng.domain.User">
update user set username=#{username},password=#{password} where id=#{id}
update>
mapper>
2)编写修改实体User的代码
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
int update = sqlSession.update("userMapper.update", user);
System.out.println(update);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
4.3 MyBatis的删除数据操作
1)编写UserMapper映射文件
<mapper namespace="userMapper">
<delete id="delete" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from user where id=#{id}
delete>
mapper>
2)编写删除数据的代码
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
int delete = sqlSession.delete("userMapper.delete",3);
System.out.println(delete);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
5. MyBatis核心配置文件概述
5.1 MyBatis核心配置文件层级关系

5.2 MyBatis常用配置解析
数据库环境的配置,支持多环境配置
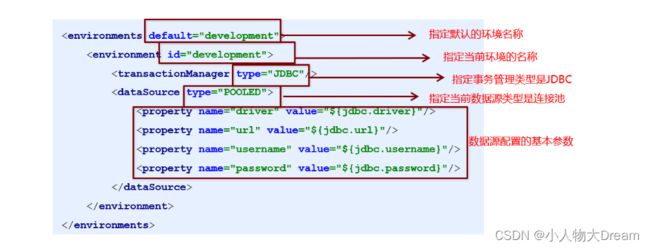 其中,事务管理器(transactionManager)类型有两种:
其中,事务管理器(transactionManager)类型有两种:
•JDBC:这个配置就是直接使用了JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。
•MANAGED:这个配置几乎没做什么。它从来不提交或回滚一个连接,而是让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 默认情况下它会关闭连接,然而一些容器并不希望这样,因此需要将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false 来阻止它默认的关闭行为。
其中,数据源(dataSource)类型有三种:
•UNPOOLED:这个数据源的实现只是每次被请求时打开和关闭连接。
•POOLED:这种数据源的实现利用“池”的概念将 JDBC 连接对象组织起来。
•JNDI:这个数据源的实现是为了能在如 EJB 或应用服务器这类容器中使用,容器可以集中或在外部配置数据源,然后放置一个 JNDI 上下文的引用。
2)mapper标签
该标签的作用是加载映射的,加载方式有如下几种:
•使用相对于类路径的资源引用,例如:
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
•使用完全限定资源定位符(URL),例如:
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
•使用映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名,例如:
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/>
•将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器,例如:
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
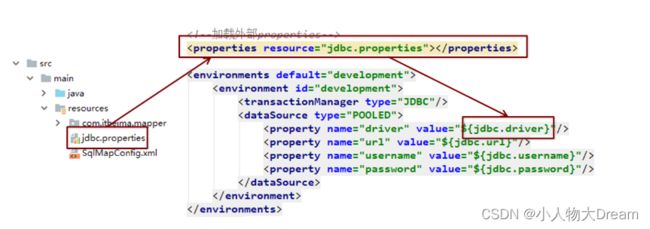
3)Properties标签
实际开发中,习惯将数据源的配置信息单独抽取成一个properties文件,该标签可以加载额外配置的properties文件
 4)typeAliases标签
4)typeAliases标签
类型别名是为Java 类型设置一个短的名字。原来的类型名称配置如下
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.zeng.entity.User">
select * from User
select>
配置别名后
核心配置文件里面配置别名
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.zeng.entity.User" alias="user">typeAlias>
typeAliases>
<select id="findAll" resultType="user">
select * from User
select>
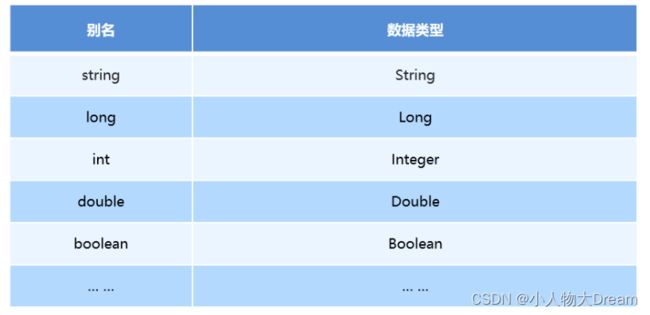
上面我们是自定义的别名,mybatis框架已经为我们设置好的一些常用的类型的别名
6.MyBatis相应API
6.1 SqlSession工厂构建器SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
常用API:SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream)
通过加载mybatis的核心文件的输入流的形式构建一个SqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "org/mybatis/builder/mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(inputStream);
其中, Resources 工具类,这个类在 org.apache.ibatis.io 包中。Resources 类帮助你从类路径下、文件系统或一个 web URL 中加载资源文件。
6.2SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory 有多个个方法创建SqlSession 实例。常用的有如下两个:
 6.3 SqlSession会话对象
6.3 SqlSession会话对象
SqlSession 实例在 MyBatis 中是非常强大的一个类。在这里你会看到所有执行语句、提交或回滚事务和获取映射器实例的方法。
执行语句的方法主要有:
<T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter)
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter)
int insert(String statement, Object parameter)
int update(String statement, Object parameter)
int delete(String statement, Object parameter)
操作事务的方法主要有:
void commit()
void rollback()
MyBatis的Dao层实现
1.1传统开发方式
1.1.1编写UserDao接口
public interface UserDao {
List<User> findAll() throws IOException;
}
1.1.2.编写UserDaoImpl实现
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
public List<User> findAll() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream =
Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("userMapper.findAll");
sqlSession.close();
return userList;
}
}
1.2 代理开发方式
1.2.1 代理开发方式介绍
采用 Mybatis 的代理开发方式实现 DAO 层的开发,这种方式是我们后面进入企业的主流。
Mapper 接口开发方法只需要程序员编写Mapper 接口(相当于Dao 接口),由Mybatis 框架根据接口定义创建接口的动态代理对象,代理对象的方法体同上边Dao接口实现类方法。
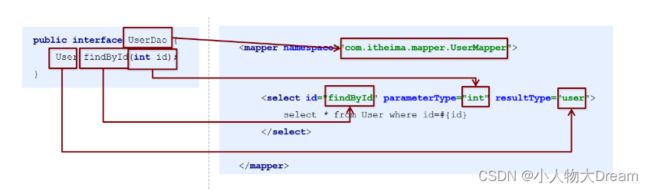
Mapper 接口开发需要遵循以下规范:
1) Mapper.xml文件中的namespace与mapper接口的全限定名相同
2) Mapper接口方法名和Mapper.xml中定义的每个statement的id相同
3) Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的parameterType的类型相同
4) Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同
1.2.3测试代理方式
@Test
public void testProxyDao() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//获得MyBatis框架生成的UserMapper接口的实现类
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = userMapper.findById(1);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
2.MyBatis映射文件深入
2.1.2动态 SQL 之<if>
我们根据实体类的不同取值,使用不同的 SQL语句来进行查询。比如在 id如果不为空时可以根据id查询,如果username 不同空时还要加入用户名作为条件。这种情况在我们的多条件组合查询中经常会碰到。
<select id="findByCondition" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from User
<where>
<if test="id!=0">
and id=#{id}
if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
if>
where>
select>
2.1.3 动态 SQL 之<foreach>
循环执行sql的拼接操作,例如:SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id IN (1,2,5)。
<select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="user">
select * from User
<where>
<foreach collection="array" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
foreach>
where>
select>
foreach标签的属性含义如下:
标签用于遍历集合,它的属性:
•collection:代表要遍历的集合元素,注意编写时不要写#{}
•open:代表语句的开始部分
•close:代表结束部分
•item:代表遍历集合的每个元素,生成的变量名
•sperator:代表分隔符
2.2 SQL片段抽取
Sql 中可将重复的 sql 提取出来,使用时用 include 引用即可,最终达到 sql 重用的目的
sql>
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="user">
<include refid="selectUser">include> where id=#{id}
select>
<select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="user">
<include refid="selectUser">include>
<where>
<foreach collection="array" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
foreach>
where>
select>
3. MyBatis核心配置文件深入
3.1typeHandlers标签
无论是 MyBatis 在预处理语句(PreparedStatement)中设置一个参数时,还是从结果集中取出一个值时, 都会用类型处理器将获取的值以合适的方式转换成 Java 类型。下表描述了一些默认的类型处理器(截取部分)。
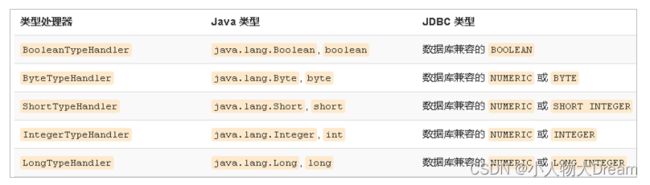
你可以重写类型处理器或创建你自己的类型处理器来处理不支持的或非标准的类型。具体做法为:实现 org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler 接口, 或继承一个很便利的类 org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler, 然后可以选择性地将它映射到一个JDBC类型。例如需求:一个Java中的Date数据类型,我想将之存到数据库的时候存成一个1970年至今的毫秒数,取出来时转换成java的Date,即java的Date与数据库的varchar毫秒值之间转换。
开发步骤:
①定义转换类继承类BaseTypeHandler
②覆盖4个未实现的方法,其中setNonNullParameter为java程序设置数据到数据库的回调方法,getNullableResult为查询时 mysql的字符串类型转换成 java的Type类型的方法
③在MyBatis核心配置文件中进行注册
测试转换是否正确
public class MyDateTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Date> {
//将java类型,转换成数据库需要的类型
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i, Date date, JdbcType type) {
//i 表示放入的位置 ,将时间转成时间戳类型
long time = date.getTime();
preparedStatement.setLong(i,time);
}
//将数据库中类型,转换成java类型
//String 参数,要转换的字段名称
//ResultSet 查询出的结果集
public Date getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s) throws SQLException {
return new Date(resultSet.getLong(s));
}
public Date getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
return new Date(resultSet.getLong(i));
}
public Date getNullableResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
long aLong = callableStatement.getLong(i);
Date date = new Date(aLong);
return aLong;
}
}
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="com.zeng.typeHandlers.MyDateTypeHandler">typeHandler>
typeHandlers>
3.2 plugins标签
MyBatis可以使用第三方的插件来对功能进行扩展,分页助手PageHelper是将分页的复杂操作进行封装,使用简单的方式即可获得分页的相关数据
开发步骤:
①导入通用PageHelper的坐标
②在mybatis核心配置文件中配置PageHelper插件
③测试分页数据获取
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId>
<artifactId>pagehelperartifactId>
<version>3.7.5version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.jsqlparsergroupId>
<artifactId>jsqlparserartifactId>
<version>0.9.1version>
dependency>
核心配置文件加入
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql"/>
plugin>
代码实现
@Test
public void testPageHelper(){
//设置分页参数
PageHelper.startPage(1,2);
List<User> userList = mapper.findAll();
//显示两条数据
for(User user : userList){
System.out.println(user);
}
//其他分页的数据
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<User>(userList);
System.out.println("总条数:"+pageInfo.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页数:"+pageInfo.getPages());
System.out.println("当前页:"+pageInfo.getPageNum());
System.out.println("每页显示长度:"+pageInfo.getPageSize());
System.out.println("是否第一页:"+pageInfo.isIsFirstPage());
System.out.println("是否最后一页:"+pageInfo.isIsLastPage());
}
1.Mybatis多表查询
1.1 一对一查询
用户表和订单表的关系为,一个用户有多个订单,一个订单只从属于一个用户
1.1.3 创建Order和User实体
public class Order {
private int id;
private Date ordertime;
private double total;
//代表当前订单从属于哪一个客户
private User user;
}
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
}
1.1.4 创建OrderMapper接口
public interface OrderMapper {
List<Order> findAll();
}
1.1.5 配置OrderMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.zeng.mapper.OrderMapper">
<resultMap id="orderMap" type="order">
<id column="oid" property="id">id>
<result property="ordertime" column="ordertime">result>
<result property="total" column="total">result>
<result column="uid" property="user.id">result>
<result column="username" property="user.username">result>
<result column="password" property="user.password">result>
<result column="birthday" property="user.birthday">result>
resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="orderMap">
select *,o.id oid from orders o,user u where o.uid=u.id
select>
mapper>
其中还可以配置如下:
<resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.zeng.domain.Order">
<result property="id" column="id">result>
<result property="ordertime" column="ordertime">result>
<result property="total" column="total">result>
<association property="user" javaType="com.zeng.domain.User">
<result column="uid" property="id">result>
<result column="username" property="username">result>
<result column="password" property="password">result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday">result>
association>
resultMap>
1.2 一对多查询
用户表和订单表的关系为,一个用户有多个订单,一个订单只从属于一个用户
1.2.3 修改User实体
public class Order {
private int id;
private Date ordertime;
private double total;
//代表当前订单从属于哪一个客户
private User user;
}
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
//代表当前用户具备哪些订单
private List<Order> orderList;
}
1.2.4 创建UserMapper接口
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> findAll();
}
1.2.5 配置UserMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.zeng.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.zeng.domain.User">
<result column="id" property="id">result>
<result column="username" property="username">result>
<result column="password" property="password">result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday">result>
<collection property="orderList" ofType="com.zeng.domain.Order">
<result column="oid" property="id">result>
<result column="ordertime" property="ordertime">result>
<result column="total" property="total">result>
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select *,o.id oid from user u left join orders o on u.id=o.uid
select>
mapper>
1.3 多对多查询
用户表和角色表的关系为,一个用户有多个角色,一个角色被多个用户使用
对应的sql语句:select u.,r.,r.id rid from user u left join user_role ur on u.id=ur.user_id
inner join role r on ur.role_id=r.id;
1.3.3 创建Role实体,修改User实体
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Date birthday;
//代表当前用户具备哪些订单
private List<Order> orderList;
//代表当前用户具备哪些角色
private List<Role> roleList;
}
//关系表
public class Role {
private int id;
private String rolename;
}
1.3.4 添加UserMapper接口方法
List<User> findAllUserAndRole();
1.3.5 配置UserMapper.xml
<resultMap id="userRoleMap" type="com.zeng.domain.User">
<result column="id" property="id">result>
<result column="username" property="username">result>
<result column="password" property="password">result>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday">result>
<collection property="roleList" ofType="com.zeng.domain.Role">
<result column="rid" property="id">result>
<result column="rolename" property="rolename">result>
collection>
resultMap>
<select id="findAllUserAndRole" resultMap="userRoleMap">
select u.*,r.*,r.id rid from user u left join user_role ur on u.id=ur.user_id
inner join role r on ur.role_id=r.id
select>
MyBatis多表配置方式:
一对一配置:使用做配置
一对多配置:使用+做配置
多对多配置:使用+做配置
2.Mybatis的注解开发
这几年来注解开发越来越流行,Mybatis也可以使用注解开发方式,这样我们就可以减少编写Mapper
映射文件了。
@Insert:实现新增
@Update:实现更新
@Delete:实现删除
@Select:实现查询
@Result:实现结果集封装
@Results:可以与@Result 一起使用,封装多个结果集
@One:实现一对一结果集封装
@Many:实现一对多结果集封装
2.2 MyBatis的增删改查
@Insert("insert into user values(#{id},#{username},#{password},#{birthday})")
publi void save(User user);
@Update("update user set username #{username},password=#{password},where id=#{id}")
public void update(User user);
@Delete("delete from user where id=#{id}")
public void delete(int id);
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
public User findById(int id);
@Select("select * from user")
public List<User> findAll();
修改MyBatis的核心配置文件,我们使用了注解替代的映射文件,所以我们只需要加载使用了注解的Mapper接口即可
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.zeng.mapper.UserMapper">mapper>
mappers>
或者指定扫描包含映射关系的接口所在的包也可以
<mappers>
<package name="com.zeng.mapper">package>
mappers>
2.3 MyBatis的注解实现复杂映射开发
2.4 一对一查询
public interface OrderMapper {
//第一种方式
@Select("select *.o.id oid from orders o ,user u where o.uid=u.id")
@Results({
@Result(property = "oid",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "ordertime",column = "ordertime"),
@Result(property = "total",column = "total"),
@Result(property = "uid",column = "user.id"),
@Result(property = "username",column = "user.username"),
@Result(property = "password",column = "user.password")
})
public List<Order> findAll();
//第二种方式
@Select("select * from orders")
@Results({
@Result(id=true,property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "ordertime",column = "ordertime"),
@Result(property = "total",column = "total"),
@Result(property = "user",//要封装的属性名称
column = "uid", //根据那个字段去查询user表数据
javaType = User.class, //要封装的实体类型
//select属性 代表查询那个接口的方法获取的数据
one = @One(select = "com.zeng.mapper.UserMapper.findById"))
})
List<Order> findAll();
}
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
User findById(int id);
}
2.5 一对多查询
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user")
@Results({
@Result(id = true,property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "username",column = "username"),
@Result(property = "password",column = "password"),
@Result(property = "birthday",column = "birthday"),
@Result(property = "orderList",column = "id",
javaType = List.class,
many = @Many(select = "com.zeng.mapper.OrderMapper.findByUid"))
})
List<User> findAllUserAndOrder();
}
public interface OrderMapper {
@Select("select * from orders where uid=#{uid}")
List<Order> findByUid(int uid);
}
2.6 多对多查询
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user")
@Results({
@Result(id = true,property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "username",column = "username"),
@Result(property = "password",column = "password"),
@Result(property = "birthday",column = "birthday"),
@Result(property = "roleList",column = "id",
javaType = List.class,
many = @Many(select = "com.zeng.mapper.RoleMapper.findByUid"))
})
List<User> findAllUserAndRole();}
public interface RoleMapper {
@Select("select * from role r,user_role ur where r.id=ur.role_id and ur.user_id=#{uid}")
List<Role> findByUid(int uid);
}
Spring框架整合MyBatis
1.整合思路
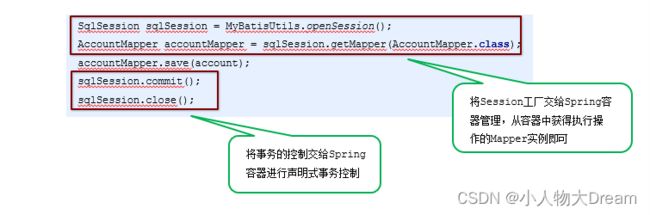
2.将SqlSessionFactory配置到Spring容器中
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:sqlMapConfig.xml"/>
bean>
3.扫描Mapper,让Spring容器产生Mapper实现类
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.zeng.mapper"/>
bean>
4.配置声明式事务控制
<bean id="transacionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transacionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPointcut" expression="execution(* com.zeng.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut"/>
aop:config>

