《算法系列》之双指针
简介
双指针并不是一种数据结构,也不是指C这种语言中的指针,而是一种经典的算法思想,可以用来求链表的中点、链表是否成环、移除数组中多余的元素、归并排序 等,核心思想是:设计不同速度、不同间距、或不同方向的两个指针对目标集合操作,解决我们的问题。
理论基础
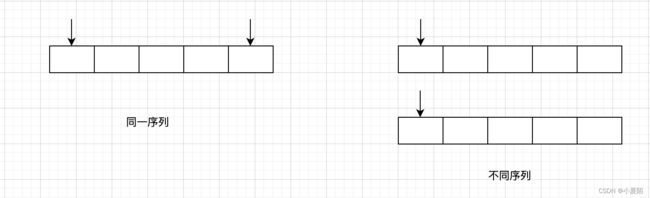
双指针是一种通过设置两个指针不断进行单向移动来解决问题的算法思想。一般包含两种形式:一、两个指针指向同一个序列。二、两个指针分别指向不同的序列。指向同一序列的比较常见,代表有快慢指针,首尾指针,固定间距指针等。指向不同序列的双指针代表有归并排序这种,需要合并时用双指针或者多指针。
解题心得
- 双指针并不是数据结构,也不是指C这种语言中的指针,而是一种解题思想。
- 很多时候双指针的题,会有多种解法,但双指针解法往往是最清晰易懂的解法。
- 双指针可用来提高效率,一般是将O(n^2)的时间复杂度,降为O(n)。
- 解题时要注意两指针索引的更新。
算法题目
11. 盛最多水的容器

题目解析:从两端开始选择左右两边的柱子,比当前低的柱子不用计算,因为面积一定更小。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int maxArea = 0;
// 左边柱子索引
int l = 0;
// 右边柱子索引
int r = height.length - 1;
while (l < r) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, Math.min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l));
int tmp = 0;
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
tmp = height[l++];
// 如果新柱子没有原来的柱子高,则一定没有原来面积大,不用计算与比较,直接索引加1
while (tmp > height[l]) {
l++;
}
} else {
tmp = height[r--];
// 如果新柱子没有原来的柱子高,则一定没有原来面积大,不用计算与比较,直接索引减1
while (tmp > height[r]) {
r--;
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}
}
15. 三数之和
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
// 升序排序
// -4 -1 -1 0 1 2
Arrays.sort(nums);
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 第一个数都大于0,其余的数相加,不可能为0,故直接返回
if (nums[i] > 0) {
return res;
}
// 两个数相等,直接前进一位,解决重复问题
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
// 两个指针分别从 i + 1 和 nums.length - 1 开始向彼此靠拢
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (right > left) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum > 0) {
right--;
} else if (sum < 0) {
left++;
} else {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]));
// 两个数相等,直接前进一位,解决重复问题
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
16. 最接近的三数之和
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) {
// 升序排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
// 初始化结果值
int res = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 两个指针分别从 i + 1 和 nums.length - 1 开始向彼此靠拢
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (right > left) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
// res 值取离target最近的sum值
if (Math.abs(res - target) > Math.abs(sum - target)) {
res = sum;
}
if (sum > target) {
right--;
} else if (sum < target){
left++;
} else if (sum == target){
return res;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
18. 四数之和

题目解析:采用排序加双指针的方法计算结果,在三数之和的基础上加一层循环。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public List> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 升序排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
int len = nums.length;
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 不足四个数,返回为空
if (nums == null || len < 4) {
return res;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len -3; i++) {
// 两个数相等,直接前进一位,解决重复问题
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {
continue;
}
// 剪枝
// 最小四个值都大于目标值,则此后无结果
if (nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] + nums[i + 3] > target) {
break;
}
// 最大四个值小于目标值,则本轮无结果,下一轮可能会有结果
if (nums[i] + nums[len - 1] + nums[len - 2] + nums[len - 3] < target) {
continue;
}
for (int j = i + 1; j < len -2; j++) {
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j - 1] == nums[j]) {
continue;
}
// 剪枝
if(nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[j + 1] + nums[j + 2] > target){
break;
}
if(nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[len - 2] + nums[len - 1] < target){
continue;
}
// 两个指针分别从 j + 1 和 len - 1 开始向彼此靠拢
int left = j + 1;
int right = len - 1;
while (right > left) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum > target) {
right--;
} else if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]));
while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点

题目解析:用快慢双指针,第一个指针位置为x,第二个指针为 x + n。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode pre = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 如果 right.next 为空,则说明,n为链表长度,删除位置为头结点
if (pre.next != null) {
pre = pre.next;
} else {
return head.next;
}
}
// curr 前进到需要删除的节点
while (pre.next != null) {
curr = curr.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
// 删除节点
curr.next = curr.next.next;
return head;
}
}
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项

题目解析:用快慢指针,重复时,fast指针前进一位,low指针不变。。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null && nums.length == 0){
return 0;
}
int low = 0;
for(int fast =0 ; fast < nums.length; fast++ ){
if(nums[low] != nums[fast]){
low += 1;
nums[low] = nums[fast];
}
}
return low + 1;
}
}
27. 移除元素
题目解析:使用快慢指针,出现目标值val,fast进一位,low不动即可。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
if(nums == null && nums.length == 0){
return 0;
}
// low fast
int l = 0;
for(int f = 0; f31. 下一个排列

题目解析:从右往左找到第一个不再递增的位置,然后在右边找到刚好大于当前位的数字即可。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int i = nums.length - 2;
// 找到第一个不再递增的位置
while (i >= 0 && nums[i + 1] <= nums[i]) {
i--;
}
// 如果找到最左边,倒置输出
if (i < 0) {
reverse(nums, 0);
return;
}
// 找到刚好大于nums[i]的位置
int j = nums.length - 1;
while (j >= 0 && nums[j] <= nums[i]) {
j--;
}
// 交换
swap(nums, i, j);
reverse(nums, i + 1);
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
}
private void reverse(int[] nums, int start) {
int i = start, j = nums.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
swap(nums, i, j);
i++;
j--;
}
}
}
61. 旋转链表

题目解析:先测出链表的长度,然后用K值取余,再用长度 - K值,将剩余链表和头节点拼接。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode res = null;
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode tail = head;
// 特殊情况,直接返回
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 测出链表的长度
int len = 1;
while (tail.next != null) {
len++;
tail = tail.next;
}
// 如果k长度为len的整数倍,直接返回head
if (k % len == 0) {
return head;
}
// len - 对K值取余 - 1,为断开处
int index = len - k % len - 1;
// 找到断开处
while (index != 0) {
curr = curr.next;
index--;
}
// 断开
res = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
// 拼接
tail.next = head;
return res;
}
}
75. 颜色分类
题目解析:左右双指针,如果等于1则不管,等于0,则向头部交换,等于2则向尾部交换。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int index = 0;
int l = -1;
int r = nums.length;
while(index < r){
// 当前数等于1则不变
if(nums[index]==1){
index++;
// 当前数等于0,则和头部交换
}else if(nums[index] == 0){
swap(nums,index++,++l);
// 当前数等于2,则和尾部交换
}else if(nums[index] == 2){
swap(nums,index,--r);
}
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr,int a,int b){
int temp = arr[a];
arr[a] = arr[b];
arr[b]=temp;
}
}
80. 删除有序数组中的重复项 II

题目解析:只能原地修改数组,最多使用O(1)额外空间,故:用新的数组覆盖旧数组即可。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0 || nums.length == 1 || nums.length == 2) {
return nums.length;
}
int res = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[res] && nums[i] == nums[res - 1]) {
} else {
res++;
nums[res] = nums[i];
}
}
return res + 1;
}
}
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II

题目解析:一个指针前进,一个指针记录不重复的节点即可。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
// 虚拟头节点
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
ListNode temp = dummyHead;
while (head != null) {
if (head.next != null && head.val == head.next.val) {
int i = head.val;
// 如当前节点值重复,则把等于当前值的节点,全部跳过,即跳过了所有重复的节点
while (head != null && head.val == i) {
head = head.next;
}
} else {
// 记录
temp.next = new ListNode(head.val);
temp = temp.next;
head = head.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
86. 分隔链表
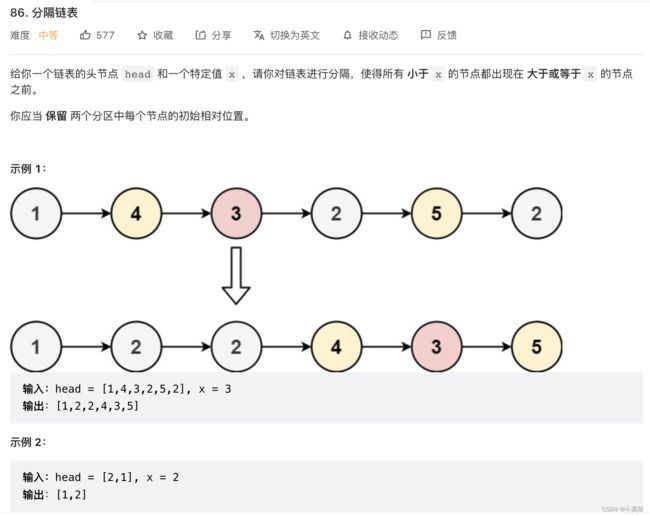
题目解析:声明两个链表,一个记录小于x的值,一个记录大于等于x的值,最后拼接即可。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode dummyHead1 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode dummyHead2 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode node1 = dummyHead1;
ListNode node2 = dummyHead2;
while (head != null) {
// 记录小于x的值
if (head.val < x) {
node1.next = head;
head = head.next;
node1 = node1.next;
node1.next = null;
// 记录大于等于x的值
} else {
node2.next = head;
head = head.next;
node2 = node2.next;
node2.next = null;
}
}
node1.next = dummyHead2.next;
return dummyHead1.next;
}
}
88. 合并两个有序数组

题目解析:从后往前,进行归并。选择最大的数放在nums1最后一位。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int i = m-- + n--;
// 如果nums2不为空则继续
while (n >= 0) {
nums1[--i] = m >= 0 && nums1[m] >= nums2[n] ? nums1[m--] : nums2[n--];
}
}
}
125. 验证回文串

题目解析:先去除字符和数字以外的字符,再用双指针比较。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l < r) {
while (l < r && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(l))) {
l++;
}
while (l < r && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(r))) {
r--;
}
if (l < r) {
if (Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(l)) != Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(r)))
return false;
}
r--;
l++;
}
return true;
}
}
141. 环形链表
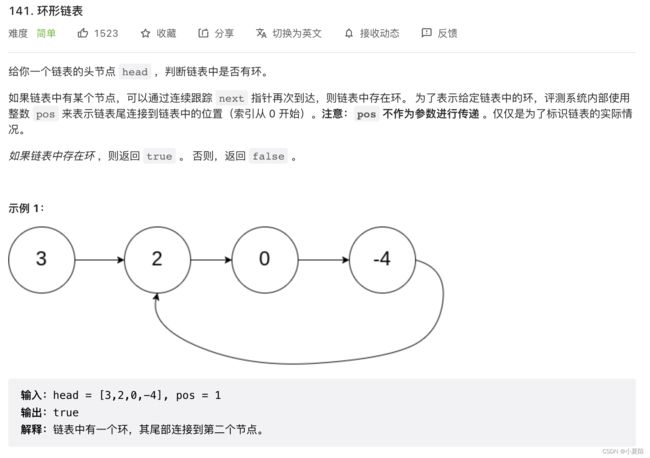
题目解析:经典快慢指针,指针能相遇,则说明有环。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
/**
* 快慢指针
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
// 快指针,一次前进两步
fast = fast.next.next;
// 慢指针,一次移动一步
slow = slow.next;
// 快慢指针能相遇,则说明有环
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
// 正常到链尾,则无环
return false;
}
}
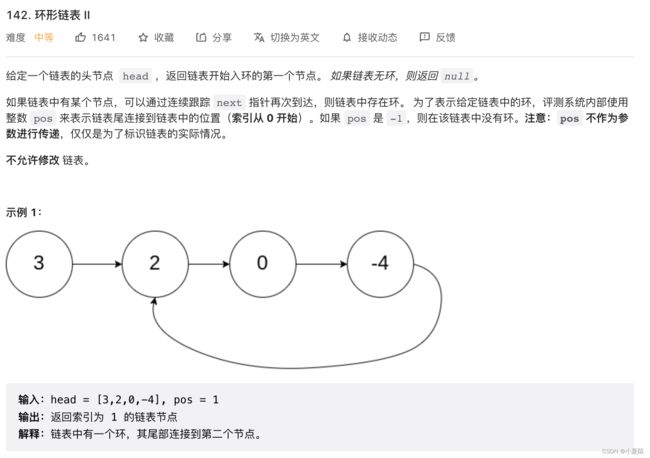
142. 环形链表 II
快慢指针,快慢指针能相遇,则说明有环。第一次相遇时:
7<-6<- 5
| ^
| |
0->1->2->3->4
[-----]
a
设置快慢两个指针,fast, slow fast一次前进两步,slow一次前进一步,
设a为第一个节点到入环节点的距离。 a = [0->2]
设b为入环口到相遇点的距离。b = [2->6]
设c为相遇点到入环口的距离。c = [6->2]
当fast,和slow相遇的时候,fast经过的节点是slow的两倍,设slow经过的节点数为S
则有:S=a+b ,2S=a+b+c+b,化解得:2(a+b) = a+b+c+b --> 2a+2b = a+b+c+b --> 2a = a+c --> a =c
则分别从头节点、相遇点出发至下一个相遇点,即为入环口点
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
boolean hasCycle = false;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
// 快指针,一次前进两步
fast = fast.next.next;
// 慢指针,一次移动一步
slow = slow.next;
// 快慢指针能相遇,则说明有环
if (fast == slow) {
hasCycle = true;
break;
}
}
// 若有环,找到入口点
// 从head和相遇点同时出发,再次相遇时,即为入口点
if (hasCycle) {
ListNode temp = head;
while (slow != temp) {
slow = slow.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
143. 重排链表

题目解析:先用双指针找到链表中点,再反转后半段链表,最后合并两段链表即可。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return;
}
// 用双指针找到链表中点
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 反转后半段链表,并与后半段分开
ListNode left = head;
// 反转
ListNode right = helper(slow.next);
slow.next = null;
// 合并两段链表
while (left != null && right != null) {
ListNode t1 = left.next;
ListNode t2 = right.next;
left.next = right;
left = t1;
right.next = t1;
right = t2;
}
}
// 直接用插入虚拟节点后的方式反转链表,再返回头节点
public ListNode helper(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
151. 翻转字符串里的单词

题目解析:首先去除所有空格,再反转整个字符串,再单独反转每个单词。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
// 1.去除首尾以及中间多余空格
StringBuilder sb = removeSpace(s);
// 2.反转整个字符串
reverseString(sb, 0, sb.length() - 1);
// 3.反转各个单词
reverseEachWord(sb);
return sb.toString();
}
private StringBuilder removeSpace(String s) {
int start = 0;
int end = s.length() - 1;
while (s.charAt(start) == ' ') start++;
while (s.charAt(end) == ' ') end--;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (start <= end) {
char c = s.charAt(start);
if (c != ' ' || sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1) != ' ') {
sb.append(c);
}
start++;
}
return sb;
}
/**
* 反转字符串指定区间[start, end]的字符
*/
public void reverseString(StringBuilder sb, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
char temp = sb.charAt(start);
sb.setCharAt(start, sb.charAt(end));
sb.setCharAt(end, temp);
start++;
end--;
}
}
private void reverseEachWord(StringBuilder sb) {
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
int n = sb.length();
while (start < n) {
while (end < n && sb.charAt(end) != ' ') {
end++;
}
reverseString(sb, start, end - 1);
start = end + 1;
end = start + 1;
}
}
}
160. 相交链表


题目解析:当pA和pB分别前进到队尾未相遇时,pA指前B队头,pB指前A队头。继续前进,此时若地址能相等,则为交点。因为若两条链表相交,此时两指针前行的距离刚好一致。若行驶最后两指针都为null则不相交。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}
}
167. 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int i = 0, j = numbers.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
if (numbers[i] + numbers[m] > target) {
j = m - 1;
} else if (numbers[m] + numbers[j] < target) {
i = m + 1;
} else if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] > target) {
j--;
} else if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] < target) {
i++;
} else {
return new int[]{i + 1, j + 1};
}
}
return new int[]{0, 0};
}
}
189. 轮转数组

题目解析:翻转整个数组,翻转反转k个区间,再反转剩余区间。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
k %= nums.length;
reverse(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
reverse(nums, 0, k - 1);
reverse(nums, k, nums.length - 1);
}
public void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
int temp = nums[start];
nums[start] = nums[end];
nums[end] = temp;
start += 1;
end -= 1;
}
}
}
234. 回文链表

题目解析:先从中分成两条链,然后反转后半段,然后依次比较,只要一个值不相等,则返回false。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 为空直接返回
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
// 找到中点
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 反转后半段
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
// 判断是否是回文
while(head != slow){
if(head.val != slow.val){
return false;
}
if(head.next == slow){
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}
283. 移动零
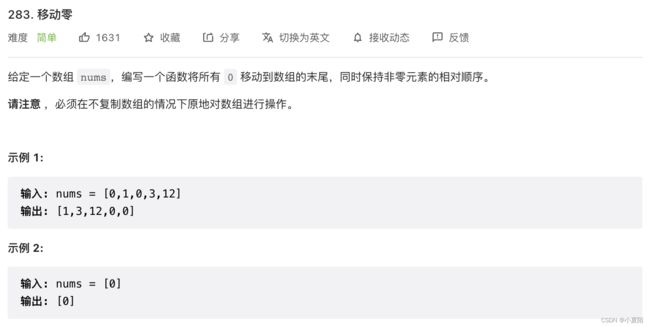
题目解析:low指针指向非零数的个数,fast循环整个数组,每次把fast位置上的数字交换过来即可。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int low = 0;
for (int fast = 0; fast < nums.length; fast++) {
if (nums[fast] != 0) {
if (low < fast) {
nums[low] = nums[fast];
nums[fast] = 0;
}
low++;
}
}
}
}
287. 寻找重复数
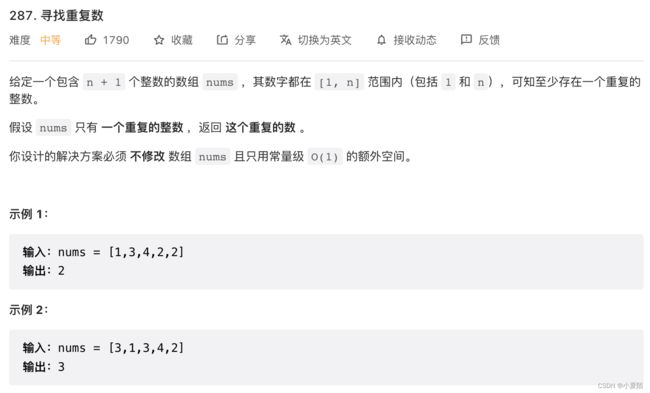
题目解析:可抽象为成环链表找入口问题,nums[slow] 表示取指针对应的元素,注意 nums 数组中的数字都是在 1 到 n 之间的(在数组中进行游走不会越界),入口处即为重复元素。
代码如下:
/**
* 双指针
*/
class Solution {
public int findDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int fast = 0, slow = 0;
while(true) {
// fast 前进两步,slow前进一步
fast = nums[nums[fast]];
slow = nums[slow];
// 相遇时,fast从入口出发,再次与slow相遇时,即为环入口,也为重复数
if(slow == fast) {
fast = 0;
while(nums[slow] != nums[fast]) {
fast = nums[fast];
slow = nums[slow];
}
return nums[slow];
}
}
}
}
回到首页
刷 leetcode 500+ 题的一些感受
下一篇
《算法系列》之栈